IAPP
-
Official Full Name
Islet amyloid polypeptide -
Overview
Amylin, or Islet Amyloid Polypeptide (IAPP), is a 37-residue peptide hormone. It is cosecreted with insulin from the pancreatic β-cells in the ratio of approximately 100:1. Amylin plays a role in glycemic regulation by slowing gastric emptying and promoting satiety, thereby preventing post-prandial spikes in blood glucose levels. IAPP is processed from an 89-residue coding sequence. Proislet Amyloid Polypeptide (proIAPP,Proamylin, Amyloid Polypeptide Precursor, Proislet Protein) is produced in the pancreatic beta cells (β-cells) as a 67 amino acid, 7404 Dalton pro-peptide and undergoes post-translational modifications including protease cleavage to produce amylin. -
Synonyms
DAP;IAP;Islet amyloid polypeptide (diabetes-associated peptide;amylin);amylin;diabetes-associated peptide;insulinoma amyloid peptide;IAPP
Recombinant Proteins
- Human
- Rat
- Chicken
- Mouse
- Synthetic
- E.coli
- HEK293
- Mammalian Cells
- Yeast
- Non
- GST
- DDK
- Myc
- His
- Avi
- Fc
- Flag
Background
What is IAPP protein?
IAPP (islet amyloid polypeptide) gene is a protein coding gene which situated on the short arm of chromosome 12 at locus 12p12. IAPP is also known as Amylin or diabetes related Peptide (DAP). IAPP plays a role in regulating blood sugar and is able to inhibit glucose utilization and glycogen deposition in insulin-stimulated muscles without affecting glucose metabolism in fat cells. Mature proteins of IAPP are largely unstructured in the absence of ligands and have a strong tendency to form fibrous aggregates. Homodimerization may be the first step in amyloid formation. At the molecular level, IAPP exerts its biological function through signaling pathways including G protein-coupled calcitonin receptor (Calcr) and related receptor activity modes. IAPP protein is consisted of 89 amino acids and its molecular mass is approximately 9.8 kDa.
What is the function of IAPP protein?
IAPP was able to selectively inhibit glucose utilization and glycogen deposition in insulin-stimulated muscle without affecting glucose metabolism in fat cells. IAPP is a major component of islet amyloid deposition in type 2 diabetes mellitus (T2D). These amyloid deposits are found in more than 90% of T2D patients and can cause damage to islet beta cells. IAPP can inhibit insulin secretion by blocking the cholinergic mechanism. IAPP also has a certain inhibitory effect on glucagon secretion, but does not affect the normal function of glucagon. IAPP also has some other physiological functions, such as dilating blood vessels and lowering blood calcium; Activate renin-angiotensin system; Inhibit gastric acid secretion and keep gastric mucosa intact; Inhibition of atrial natriuretic peptide secretion; Helps amino acids cross the blood-brain barrier, raises body temperature, etc.
IAPP Related Signaling Pathway
IAPP aggregates, especially oligomers, are capable of inducing apoptosis of islet beta cells, a process involved in reactive oxygen species production, mitochondrial dysfunction, chromatin concentration, and apoptosis mechanisms. Cellular stress responses triggered by misfolded Iapps, including ER stress and ER related degradation pathways, may lead to beta cell dysfunction. IAPP aggregates can induce an inflammatory response with increased expression of pro-inflammatory cytokines such as IL-1β, which may lead to islet beta cell death and dysfunction. IAPP aggregates interact with lipid components of the cell membrane, leading to the opening of non-selective ion channels of the cell membrane, increasing the permeability of the cell membrane, and damaging the islet beta cells. IAPP aggregates activate pathways such as c-Jun amino-terminal kinin (JNK) signaling, leading to apoptosis.
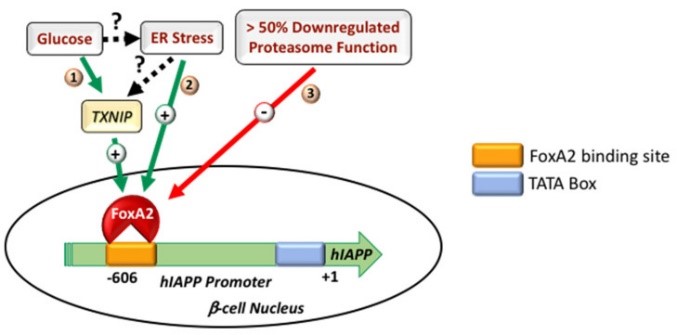
Fig1. Regulatory mechanisms driving IAPP transcription in normal and stressed pancreatic β-cells. (Diti Chatterjee Bhowmick, 2022)
IAPP Related Diseases
IAPP deposits in the islets of people with type 2 diabetes in the form of amyloid, a pathological feature of type 2 diabetes. In addition, there are many diabetic diseases: diabetic retinopathy, diabetic nephropathy, diabetic peripheral neuropathy. IAPP and amyloid beta (Aβ) have similar biological characteristics and cytotoxic mechanisms, both of which can aggregate in pathological states to form amyloid plaques. IAPP has been found in the brain tissue of Alzheimer's patients and may be involved in cognitive dysfunction and the occurrence and development of the disease. In addition to Alzheimer's disease, Iapps may also be involved in the pathogenesis of Parkinson's disease and other neurodegenerative diseases. IAPP can regulate bone mineral density, and its abnormal expression may be related to the occurrence of osteoporosis.
Bioapplications of IAPP
Iapp-based research has led to the development of corresponding drugs, such as Symlin (Pramlinpeptide acetate), an IAPP-based analogue drug used to aid the treatment of patients with type 1 diabetes. In the process of developing new drugs, recombinant Iapps can be used as a target for drug screening to test the effect of potential inhibitors on IAPP aggregation. In the field of health management and disease prevention, retooling iApps may be used to develop new surveillance tools and prevention strategies.
Case Study
Case Study 1: Joseph J Castillo, 2022
The islet vasculature, including its constituent islet endothelial cells, is a key contributor to the microenvironment necessary for normal beta cell health and function. In type 2 diabetes, islet amyloid polypeptide (IAPP) aggregates, forming amyloid deposits that accumulate between beta cells and islet capillaries. This process is known to be toxic to beta cells but its impact on the islet vasculature has not previously been studied. Here, the researchers report the first characterisation of the effects of IAPP aggregation on islet endothelial cells/capillaries using cell-based and animal models. Primary and immortalised islet endothelial cells were treated with amyloidogenic human IAPP (hIAPP) alone or in the presence of the amyloid blocker Congo Red or the Toll-like receptor (TLR) 2/4 antagonist OxPAPc. Islet capillary abundance, morphology and pericyte coverage were determined in pancreases from transgenic mice with beta cell expression of hIAPP using conventional and confocal microscopy. The results showed that aggregated hIAPP decreased endothelial cell viability in immortalised and primary islet endothelial cells. Islets from high-fat-diet-fed amyloid-laden hIAPP transgenic mice also exhibited significantly increased expression of most markers of endothelial inflammation along with decreased capillary density compared with non-transgenic littermates fed the same diet.
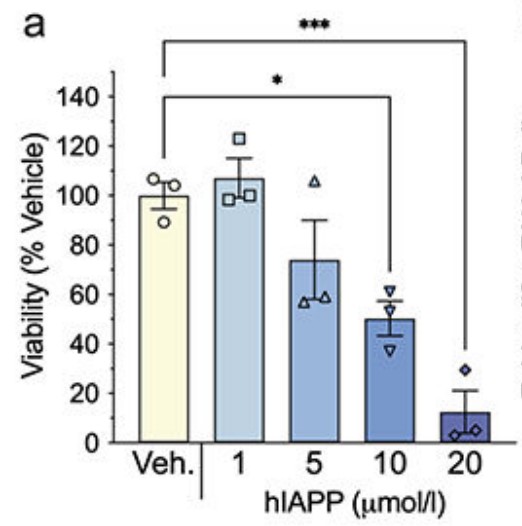
Fig1. Dose–response curve for hIAPP treatment of MS1 cells.
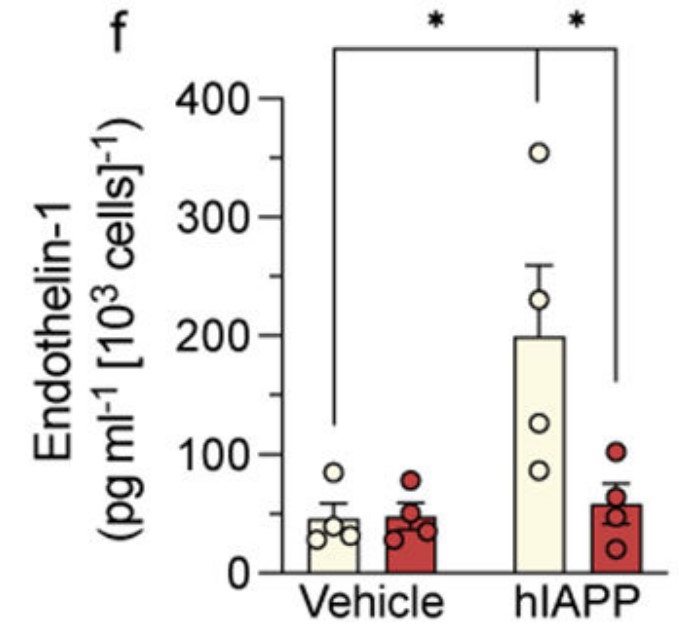
Fig2. Relative gene expression of endothelin-1 protein secreted from MS-1 cells.
Case Study 2: Charles F DeLisle, 2020
Pro-islet amyloid polypeptide (proIAPP) is the prohormone precursor molecule to IAPP, also known as amylin. IAPP is a calcitonin family peptide hormone that is cosecreted with insulin, and largely responsible for hunger satiation and metabolic homeostasis. Amyloid plaques containing mixtures of mature IAPP and misprocessed proIAPP deposit on, and destroy pancreatic β-cell membranes, and they are recognized as a clinical hallmark of type 2 diabetes mellitus. In order to better understand the interaction with cellular membranes, the researchers solved the solution NMR structure of proIAPP bound to dodecylphosphocholine micelles at pH 4.5. They show that proIAPP is a dynamic molecule with four α-helices. The first two helices are contained within the mature IAPP sequence, while the second two helices are part of the C-terminal prohormone segment (Cpro). They mapped the membrane topology of the amphipathic helices by paramagnetic relaxation enhancement, and we used CD and diffusion-ordered spectroscopy to identify environmental factors that impact proIAPP membrane affinity.
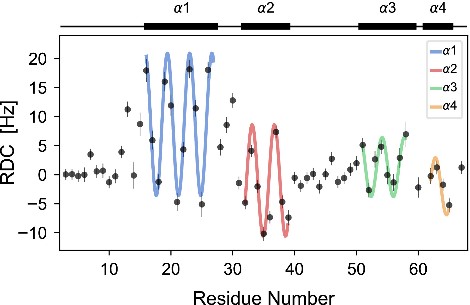
Fig3. Observed 1H-15N RDCs for proIAPP plotted by residue number.
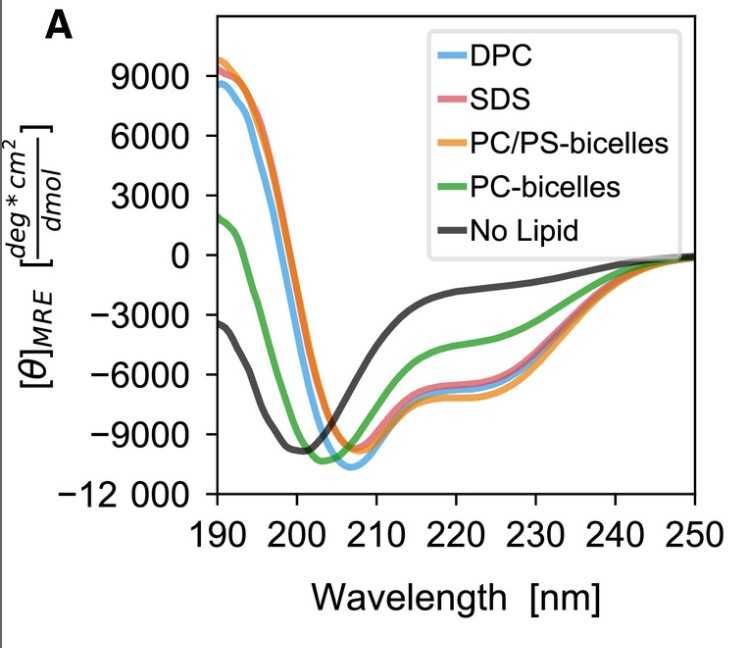
Fig4. Mean residue ellipticity curves of proIAPP in the absence of lipid (black) and in the presence DPC micelles (blue), SDS micelles (red).
Quality Guarantee
High Purity
.jpg)
Fig1. SDS-PAGE (IAPP-1250H)
.
.jpg)
Fig2. SDS-PAGE (IAPP-153H)
Involved Pathway
IAPP involved in several pathways and played different roles in them. We selected most pathways IAPP participated on our site, such as Maturity onset diabetes of the young, which may be useful for your reference. Also, other proteins which involved in the same pathway with IAPP were listed below. Creative BioMart supplied nearly all the proteins listed, you can search them on our site.
| Pathway Name | Pathway Related Protein |
|---|---|
| Maturity onset diabetes of the young | HNF1B,PDX1,INS2,NKX6-1,NKX6,SLC2A2,BHLHA15,FOXA2,MNX1,INS1 |
Protein Function
IAPP has several biochemical functions, for example, hormone activity,identical protein binding,receptor binding. Some of the functions are cooperated with other proteins, some of the functions could acted by IAPP itself. We selected most functions IAPP had, and list some proteins which have the same functions with IAPP. You can find most of the proteins on our site.
| Function | Related Protein |
|---|---|
| identical protein binding | TRIM39,SERPINA1A,UBE2G2,NQO1,GRIN3A,PARK7,PLK4,EPOR,RBM10,MICALL1 |
| hormone activity | PRL7A2,PTH1A,EDN2,PRL,ADIPOQ,PRL2,EDN1,SCT,TTR,PRL2A1 |
| receptor binding | TNFSF10,LHB,DAO,HTT,RAB8B,BLK,ANKRD13C,RIPK2,STRAP,PRDX5 |
Interacting Protein
IAPP has direct interactions with proteins and molecules. Those interactions were detected by several methods such as yeast two hybrid, co-IP, pull-down and so on. We selected proteins and molecules interacted with IAPP here. Most of them are supplied by our site. Hope this information will be useful for your research of IAPP.
Resources
Related Services
Related Products
References
- Bram, Y; Frydman-Marom, A; et al. Apoptosis induced by islet amyloid polypeptide soluble oligomers is neutralized by diabetes-associated specific antibodies. SCIENTIFIC REPORTS 4:-(2014).
- Fawver, JN; Ghiwot, Y; et al. Islet Amyloid Polypeptide (IAPP): A Second Amyloid in Alzheimer's Disease. CURRENT ALZHEIMER RESEARCH 11:928-940(2014).



