HINT1
-
Official Full Name
histidine triad nucleotide binding protein 1 -
Overview
Histidine triad nucleotide-binding protein 1 is a protein that in humans is encoded by the HINT1 gene. -
Synonyms
HINT1;histidine triad nucleotide binding protein 1;HINT, histidine triad nucleotide binding protein , PRKCNH1;histidine triad nucleotide-binding protein 1;PKCI 1;protein kinase C inhibitor 1;adenosine 5-monophosphoramidase;protein kinase C-interac
Recombinant Proteins
- Human
- Rabbit
- Zebrafish
- Rhesus macaque
- Rat
- Chicken
- Mouse
- E.coli
- HEK293
- Mammalian Cells
- Human
- Wheat Germ
- In Vitro Cell Free System
- GST
- His
- Myc
- DDK
- Non
- Avi
- Fc
- Flag
Background
What is HINT1 Protein?
HINT1, short for histidine triad nucleotide-binding protein 1, is a small but important enzyme in humans. It helps to break down certain nucleotide molecules and acts as a scaffold protein that influences gene transcription. Known as a tumor suppressor, HINT1 can block pathways like Wnt/β-catenin in colon cancer and adjust MITF activity in mast cells. It plays a part in the LysRS-Ap4A-MITF signaling pathway by releasing from MITF when activated, which affects gene expression. HINT1’s diverse roles make it crucial for cellular functions and a focus in cancer research.What is the Function of HINT1 Protein?
HINT1, or histidine triad nucleotide-binding protein 1, is pretty versatile in its roles. It helps break down nucleotide molecules, which are essential for DNA and RNA. But there's more to it—HINT1 acts as a tumor suppressor. It helps keep things in check by blocking cell growth pathways, like the Wnt/β-catenin pathway, often linked to colon cancer. It also regulates how genes are turned on or off by interacting with transcription factors such as MITF, particularly in mast cells. All these actions make HINT1 crucial for cell signaling and maintaining healthy cell functions, making it an important subject in cancer and cell regulation research.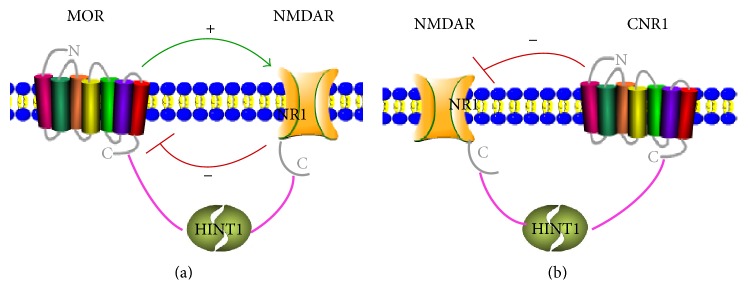
Fig1. The pattern of HINT1 interacting with GPCRs. (Peng Liu, 2017)
HINT1 Related Signaling Pathway
When diving into the world of HINT1 related signaling pathways, it’s like stepping into a complex orchestra of biological processes where HINT1 plays a crucial role. This protein is involved in various cell signaling pathways and acts as a kind of molecular switch in cellular communication. Interested in how this ties into mental health? Well, researchers are keen on exploring HINT1 because it’s linked with mood regulation and cognitive function, and its dysregulation is often associated with psychiatric disorders like depression and anxiety. What's more, HINT1 interacts with NMDA receptors, which are key players in memory and learning. By understanding these interactions, scientists aim to develop targeted therapies that could potentially rectify these imbalances, which are popular topics in neuroscience research today.HINT1 Related Diseases
Exploring the connection between HINT1 and various diseases is like uncovering hidden threads in a complex web of human health. This little protein might not be on everyone's radar, but it plays a big role in some serious conditions. For instance, changes in HINT1 activity are linked to mood disorders like depression and anxiety, with some studies suggesting it could influence how we respond to stress. Beyond mental health, HINT1 is also wrapped up in neurodegenerative diseases such as Alzheimer's, which makes it a hot topic in ongoing research. It's all about how it interacts with other molecules that control the brain’s communication network. Researchers are looking into ways to tweak these interactions, hoping to develop new treatments that get right to the source of these issues. HINT1 might just turn out to be a key player in tackling these big health challenges, making it a popular focus in the field.Bioapplications of HINT1
HINT1 is not just a protein in the backdrop; it’s becoming a star in the research community for its potential uses. One exciting area is its role in developing treatments for mood disorders. By targeting HINT1 interactions, scientists are working on new meds that could offer better outcomes for depression and anxiety. But that’s not all—this protein’s involvement in the molecular pathways gives it a hand in cancer research too. Its ability to affect cell signaling makes it a candidate for innovative cancer therapies that aim to interrupt the growth and spread of tumors. With these promising avenues, HINT1 is emerging as a key element in next-gen treatment strategies, making waves in both neuroscience and oncology research fields, and generating buzz among scientists eager to explore its full potential.Case Study
Case Study 1: Amor-Barris S. et al. Orphanet J Rare Dis. 2021
Autosomal recessive axonal neuropathy, tied to HINT1 loss, often occurs in parts of Europe and Turkey due to a specific variant. In a study of 748 Norwegian neuropathy patients, two had both a new (c.284G > A) and known variant (c.110G > C) in HINT1. Their symptoms were mainly motor neuropathy with muscle stiffness, cramps, and unusual pain. Tests suggest the new variant impairs HINT1, offering clues for future treatments.-
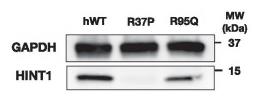 Fig1. Western blot analysis of protein extract from HNT1-deleted yeast strain expressing either the wild-type HINT1 or the disease-causing variants.
Fig1. Western blot analysis of protein extract from HNT1-deleted yeast strain expressing either the wild-type HINT1 or the disease-causing variants. -
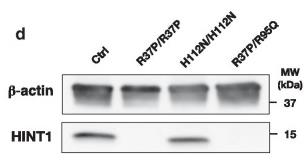 Fig2. Western blot analysis of total protein extracts from HINT1 patients or control (Ctrl) lymphoblasts.
Fig2. Western blot analysis of total protein extracts from HINT1 patients or control (Ctrl) lymphoblasts.
Case Study 2: Yu J. et al. Nat Commun. 2019
Signal transduction helps cells react to their environment. In mast cells, Ap4A binds to HINT1, disrupting its connection with MITF, leading to gene activation. But how HINT1 is affected by Ap4A isn't fully known. Through crystal structures and lab tests, Researchers found that Ap4A makes HINT1 polymerize in cells. This polymerization happens where HINT1 usually interacts with MITF, hinting at a competitive mechanism that frees MITF to activate transcription. This process is specifically linked to the length of Ap4A's phosphodiester bond, showcasing a unique signaling pathway.-
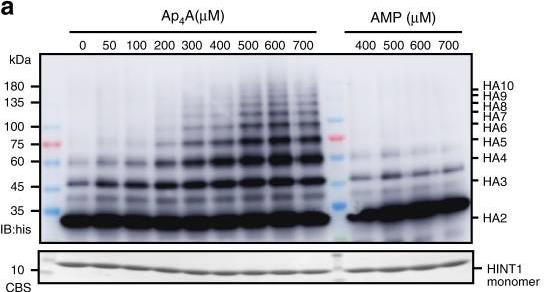 Fig3. Electrophoretic mobility shift assay (EMSA) was performed with 25 μM HINT1H114A incubated with 0–700 μM Ap4A or 400–700 μM AMP.
Fig3. Electrophoretic mobility shift assay (EMSA) was performed with 25 μM HINT1H114A incubated with 0–700 μM Ap4A or 400–700 μM AMP. -
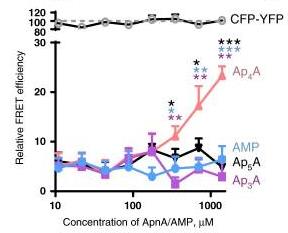 Fig4. FRET assay showing that only Ap4A, but not Ap5A/Ap3A/AMP, could induce the interaction between HINT1V97D-CFP and HINT1V97D-YFP.
Fig4. FRET assay showing that only Ap4A, but not Ap5A/Ap3A/AMP, could induce the interaction between HINT1V97D-CFP and HINT1V97D-YFP.
Quality Guarantee
High Purity
-
.jpg) Fig1. SDS-PAGE (HINT1-4750H)
Fig1. SDS-PAGE (HINT1-4750H)
Involved Pathway
HINT1 involved in several pathways and played different roles in them. We selected most pathways HINT1 participated on our site, such as , which may be useful for your reference. Also, other proteins which involved in the same pathway with HINT1 were listed below. Creative BioMart supplied nearly all the proteins listed, you can search them on our site.
| Pathway Name | Pathway Related Protein |
|---|
-
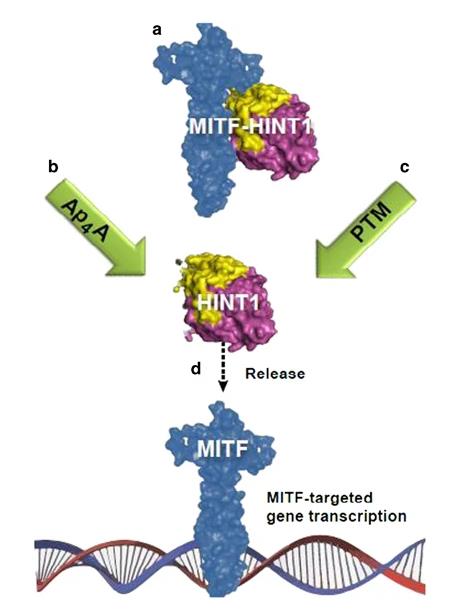 Fig1. Proposed LysRS-HINT1-MITF regulation in metastatic melanoma. (A Motzik, 2017)
Fig1. Proposed LysRS-HINT1-MITF regulation in metastatic melanoma. (A Motzik, 2017) -
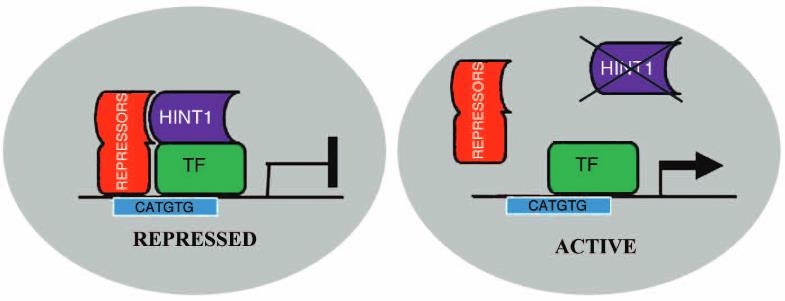 Fig2. proposed model of HINt1-mediated transcriptional repression in human melanoma cells. (Giannicola Genovese, 2012)
Fig2. proposed model of HINt1-mediated transcriptional repression in human melanoma cells. (Giannicola Genovese, 2012)
Protein Function
HINT1 has several biochemical functions, for example, hydrolase activity,nucleotide binding,protein kinase C binding. Some of the functions are cooperated with other proteins, some of the functions could acted by HINT1 itself. We selected most functions HINT1 had, and list some proteins which have the same functions with HINT1. You can find most of the proteins on our site.
| Function | Related Protein |
|---|---|
| protein kinase C binding | PRKCSH,C1QBP,HAND2,AVPR1A,SDPR,MARCKS,HDAC5,CASQ2,PARD3,SDPRA |
| hydrolase activity | ACOT5,CAPN3B,POR,EAR4,IRGC,PPM1DB,EIF4A1A,PCSK5B,CTS7,CTDNEP1 |
| nucleotide binding | HNRNPL,SFRS3A,TUBA8L2,Abca2,EIF4BB,ATP1A1A.1,CSNK1DB,EIF4BA,PRKCHB,ARL8BA |
Interacting Protein
HINT1 has direct interactions with proteins and molecules. Those interactions were detected by several methods such as yeast two hybrid, co-IP, pull-down and so on. We selected proteins and molecules interacted with HINT1 here. Most of them are supplied by our site. Hope this information will be useful for your research of HINT1.
HLA-B;VHL;CDC16;TRIM29;manX;arsB;ywbC;ppsC;alsS
Resources
Related Services
Related Products
References
- Symes, AJ; Eilertsen, M; et al. Quantitative Analysis of BTF3, HINT1, NDRG1 and ODC1 Protein Over-Expression in Human Prostate Cancer Tissue. PLOS ONE 8:-(2013).
- Genovese, G; Ghosh, P; et al. The tumor suppressor HINT1 regulates MITF and beta-catenin transcriptional activity in melanoma cells. CELL CYCLE 11:2206-2215(2012).
- Liu, Q; Puche, AC; et al. Distribution and expression of protein kinase c interactive protein (PKCI/HINT1) in mouse central nervous system (CNS). NEUROCHEMICAL RESEARCH 33:1263-1276(2008).


