HDLBP
-
Official Full Name
high density lipoprotein binding protein -
Overview
The protein encoded by this gene binds high density lipoprotein (HDL) and may function to regulate excess cholesterol levels in cells. The encoded protein also binds RNA and can induce heterochromatin formation. Three transcript variants encoding two different isoforms have been found for this gene. [provided by RefSeq, Aug 2011] -
Synonyms
HDLBP;high density lipoprotein binding protein;HBP;VGL;PRO2900;vigilin;HDL-binding protein;high density lipoprotein-binding protein
Recombinant Proteins
- Human
- Chicken
- Mouse
- E.coli
- Human Plasma
- Mammalian Cells
- HEK293
- GST
- Non
- His
- T7
- Avi
- Fc
- DDK
- Myc
- Flag
| Cat.# | Product name | Source (Host) | Species | Tag | Protein Length | Price |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| HDLBP-13719H | Recombinant Human HDLBP, GST-tagged | E.coli | Human | GST | 909-1268a.a. | |
| HDLBP-4931H | Recombinant Human High Density Lipoprotein Binding Protein | Human Plasma | Human | Non |
|
|
| HDLBP-6653C | Recombinant Chicken HDLBP | Mammalian Cells | Chicken | His |
|
|
| HDLBP-7856H | Recombinant Human HDLBP protein, His & T7-tagged | E.coli | Human | His&T7 | Pro158~Ala371 |
|
| HDLBP-1058H | Recombinant Human HDLBP Protein, His (Fc)-Avi-tagged | HEK293 | Human | Avi&Fc&His |
|
|
| HDLBP-1058H-B | Recombinant Human HDLBP Protein Pre-coupled Magnetic Beads | HEK293 | Human |
|
||
| HDLBP-1098H | Recombinant Human HDLBP Protein, MYC/DDK-tagged | HEK293 | Human | DDK&Myc |
|
|
| HDLBP-1917HFL | Recombinant Full Length Human HDLBP Protein, C-Flag-tagged | Mammalian Cells | Human | Flag | Full L. |
|
| Hdlbp-477M | Recombinant Mouse Hdlbp Protein, MYC/DDK-tagged | HEK293 | Mouse | DDK&Myc |
|
|
| HDLBP-86H | Native Human Lipoproteins | Human Plasma | Human | Non |
|
Background
What is HDLBP protein?
HDLBP gene (high density lipoprotein binding protein) is a protein coding gene which situated on the long arm of chromosome 2 at locus 2q37. HDLBP, or high-density lipoprotein binding protein, is an RNA-binding protein with multiple roles in various diseases and cancers. It is involved in processes such as translation, chromosome segregation, cholesterol transport, and carcinogenesis, and has been associated with lipid metabolism and viral infections. The HDLBP protein is consisted of 1268 amino acids and HDLBP molecular weight is approximately 141.4 kDa.
What is the function of HDLBP protein?
HDLBP is a significant RNA-binding protein with multiple roles in various diseases and cancers. It is involved in processes such as translation, chromosome segregation, cholesterol transport, and carcinogenesis. HDLBP's association with lipid metabolism and its role in viral infections make it a protein of interest in biomedical research. It has been linked to the promotion of hepatocellular carcinoma metastasis through BRAF-dependent epithelial-mesenchymal transition and is associated with atherosclerosis. Furthermore, HDLBP's expression is connected to the severity of several diseases and it may serve as a biomarker or therapeutic target in cancer treatment.
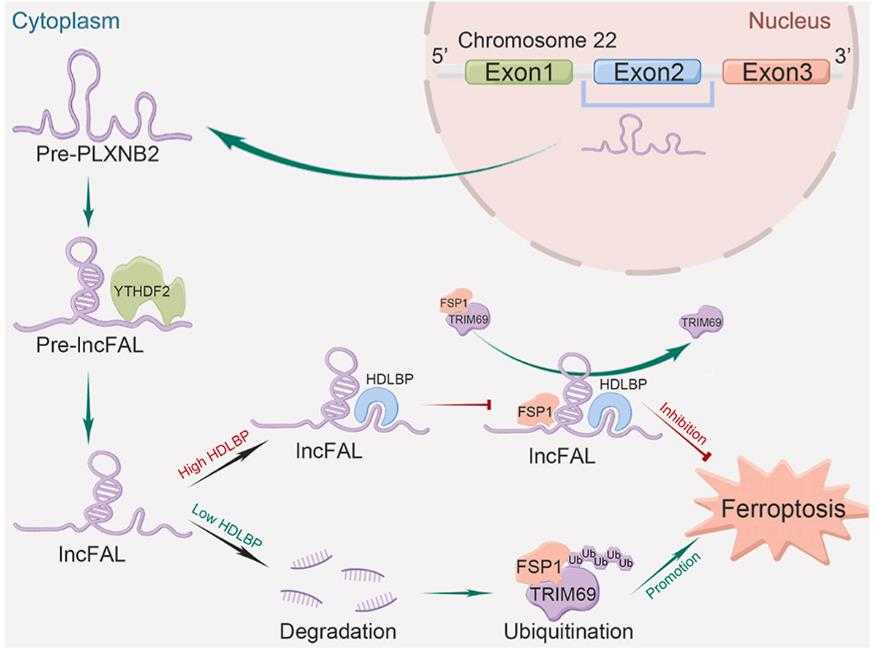
Fig1. Schematic showing the regulation of ferroptosis vulnerability in HCC by HDLBP, which stabilizes PLXNB2-derived lncFAL. (Jingsheng Yuan, 2022)
HDLBP related signaling pathway
The HDLBP-related signaling pathway is primarily involved in high-density lipoprotein (HDL) metabolism and cholesterol efflux from peripheral tissues to the liver. HDL binding protein (HDLBP), also known as lectin domain containing 1 (LDL1), facilitates the interaction between HDL and cell surface receptors, enhancing the removal of cholesterol from macrophages and other cells. This process is crucial for reverse cholesterol transport, which helps prevent atherosclerosis by reducing cholesterol accumulation in blood vessels. Dysregulation of this pathway can lead to impaired cholesterol efflux and increased risk of cardiovascular diseases. Understanding the mechanisms underlying HDLBP-mediated signaling is essential for developing therapeutic strategies to promote HDL function and cardiovascular health.
HDLBP related diseases
The HDLBP-related diseases primarily involve conditions associated with dysregulated high-density lipoprotein (HDL) metabolism and cholesterol efflux. Overexpression of HDL binding protein (HDLBP), also known as lectin domain containing 1 (LDL1), has been implicated in certain types of cancer, where it may contribute to tumor progression by modulating cell adhesion and invasion. Additionally, mutations or deficiencies in HDLBP can impair the interaction between HDL and cell surface receptors, leading to reduced cholesterol efflux from peripheral tissues to the liver. This impairment can result in increased risk of atherosclerosis and cardiovascular diseases due to the accumulation of cholesterol in blood vessels. Therefore, understanding the role of HDLBP in these diseases is crucial for developing targeted therapies and preventive measures to improve patient outcomes.
Bioapplications of HDLBP
The bioapplications of HDLBP focus on its role in modulating high-density lipoprotein (HDL) metabolism and cholesterol efflux, which are critical for cardiovascular health. By enhancing the interaction between HDL and cell surface receptors, HDLBP facilitates the removal of excess cholesterol from peripheral tissues to the liver, thereby promoting reverse cholesterol transport and reducing the risk of atherosclerosis. Additionally, targeting HDLBP has potential therapeutic implications in treating cancers where it is overexpressed, as modulating its activity can affect tumor progression. Understanding the mechanisms through which HDLBP operates is essential for developing novel therapeutic strategies aimed at improving HDL function and preventing cardiovascular diseases.
Case Study
Case Study 1: Shahid Banday, 2021
Vigilin, a conserved RNA-binding protein with roles in heterochromatin formation, chromosome segregation, and mRNA stability, is implicated in autism and cancer. Here vigilin depletion sensitizes cells to cisplatin or ionizing radiation by disrupting DNA repair mechanisms, including delaying dephosphorylation of γ-H2AX, affecting focus formation of DNA repair proteins, and impairing RAD51 and BRCA1 recruitment to double-strand break sites. Additionally, vigilin interacts with DDR proteins and is involved in replication stress response, with histone acetylation mediating its recruitment to DNA breaks. This reveals a new role for vigilin in DNA damage repair, with potential implications for autism and cancer-related disorders.
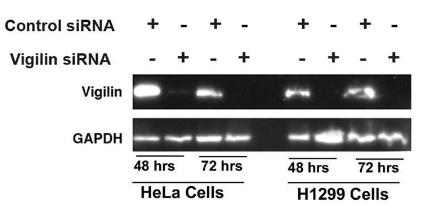
Fig1. Western blot showing the knockdown of vigilin in HeLa and H1299 cell lines using vigilin-specific and control siRNAs.
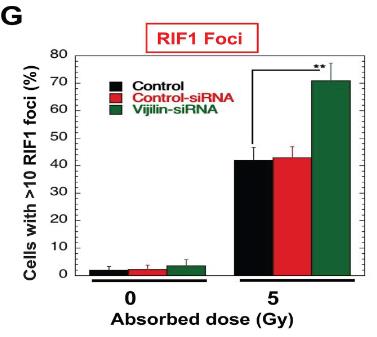
Fig2. HeLa cells were irradiated with 5 Gy, and RIF1 foci were quantified for RIF1 foci in control and vigilin-depleted HeLa cells with and without IR treatment.
Case Study 2: Orit Berhani, 2017
NK cells, a key component of the innate immune system, use receptors like NKG2D to detect and eliminate stressed or transformed cells. NKG2D binds to stress-induced ligands like MICA, MICB, and UL16-binding proteins, but the regulation of these ligands is not fully understood. This study revealed that vigilin, a multifunctional RNA-binding protein, negatively regulates MICB expression through its 5' untranslated region (UTR). Depletion of vigilin increased NK cell activation, uncovering a new mechanism of MICB regulation that impacts NK cell-mediated immunity.
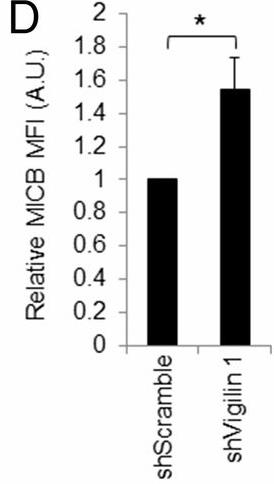
Fig3. Quantification of MICB expression on RKO transduced cells.
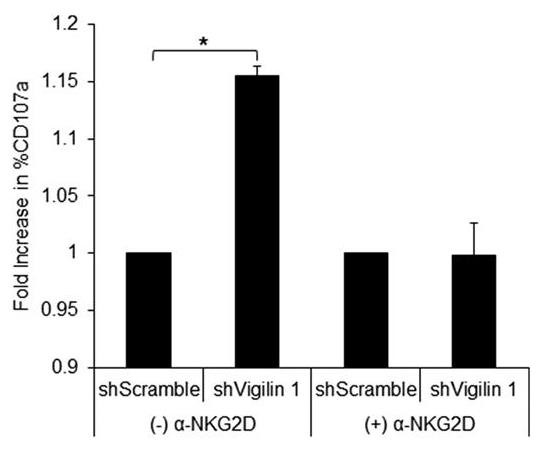
Fig4. Downregulation of vigilin in target cells increases NK cell activation against target cells.
Quality Guarantee
High Purity
.jpg)
Fig1. SDS-PAGE (HDLBP-7856H)
.
.jpg)
Fig2. SDS-PAGE (HDLBP-1917HFL)
Involved Pathway
HDLBP involved in several pathways and played different roles in them. We selected most pathways HDLBP participated on our site, such as , which may be useful for your reference. Also, other proteins which involved in the same pathway with HDLBP were listed below. Creative BioMart supplied nearly all the proteins listed, you can search them on our site.
| Pathway Name | Pathway Related Protein |
|---|
Protein Function
HDLBP has several biochemical functions, for example, lipid binding,poly(A) RNA binding,protein binding. Some of the functions are cooperated with other proteins, some of the functions could acted by HDLBP itself. We selected most functions HDLBP had, and list some proteins which have the same functions with HDLBP. You can find most of the proteins on our site.
| Function | Related Protein |
|---|---|
| lipid binding | FAM123C,S1PR2,APOL2,ALOX8,PSAP,SH3GL3,CYTH4,Ar,CRABP1B,OSBPL11 |
| protein binding | LSAMP,FAM195B,RAI1,OAZ2,LDLRAD1,AP1M2,PDCD10,EMD,CCDC47,CDK16 |
| poly(A) RNA binding | JUN,SRSF2,NARG1,MRPL42,SERBP1,HSP90AA1,U2SURP,CPEB2,NOM1,ZYX |
Interacting Protein
HDLBP has direct interactions with proteins and molecules. Those interactions were detected by several methods such as yeast two hybrid, co-IP, pull-down and so on. We selected proteins and molecules interacted with HDLBP here. Most of them are supplied by our site. Hope this information will be useful for your research of HDLBP.
CTCF;CSNK2A1;MAGEA6;ARF6;AKTIP;ERBB2;HSPB1;SOS1;SMAD4;FAM46A;q7cig0_yerpe;lptE;argF;q8d1m8_yerpe;ssrna_ug
Resources
Related Services
Related Products
References
- Shetty, KA; Kosloski, MP; et al. Soy Phosphatidylinositol Containing Nanoparticle Prolongs Hemostatic Activity of B-Domain Deleted Factor VIII in Hemophilia A Mice. JOURNAL OF PHARMACEUTICAL SCIENCES 104:388-395(2015).
- Haller, E; Lindner, W; et al. Gold nanoparticle-antibody conjugates for specific extraction and subsequent analysis by liquid chromatography-tandem mass spectrometry of malondialdehyde-modified low density lipoprotein as biomarker for cardiovascular risk. ANALYTICA CHIMICA ACTA 857:53-63(2015).


