FAAH
-
Official Full Name
fatty acid amide hydrolase -
Overview
This gene encodes a protein that is responsible for the hydrolysis of a number of primary and secondary fatty acid amides, including the neuromodulatory compounds anandamide and oleamide. -
Synonyms
FAAH;fatty acid amide hydrolase;fatty-acid amide hydrolase 1;FAAH 1;Anandamide amidohydrolase 1;Anandamide amidohydrolase;FA2H;FAAH-1;FAAH1_HUMAN;Fatty acid 2-hydroxylase;Fatty acid alpha-hydroxylase;MGC102823;MGC138146;Oleamide hydrolase 1;Oleamide hydrolase;OTTHUMP00000009480
Recombinant Proteins
- Human
- Rat
- Zebrafish
- Mouse
- Arabidopsis thaliana
- Mus musculus
- E.coli
- Insect Cells
- HEK293
- Mammalian Cells
- Wheat Germ
- GST
- His
- DDK
- Myc
- Avi
- Fc
- Flag
- Non
Background
What is FAAH protein?
FAAH (fatty acid amide hydrolase) gene is a protein coding gene which situated on the short arm of chromosome 1 at locus 1p33. FAAH is a membrane binding enzyme that is widespread in mammals and is primarily responsible for breaking down a class of endogenous signaling lipids called fatty acid amides, which include the well-known endocannabinoid anandamide (AEA) as well as other bioactive amides. FAAH is a homologous dimer enzyme belonging to the serine hydrolase family. It is a membrane protein that locates mainly on organelles such as the endoplasmic reticulum, mitochondria and peroxisome within cells. The activity of FAAH is regulated by a variety of factors, including the availability of the substrate, the expression level of the enzyme itself, and the action of multiple cofactors and inhibitors. The FAAH protein is consisted of 579 amino acids and its molecular mass is approximately 63.1 kDa.
What is the function of FAAH protein?
FAAH regulates the activity of the endocannabinoid system by breaking down endocannabinoids such as anandamide (AEA) and 2-arachidonic acid ethanolamine (2-AG). These molecules play an important role in regulating pain, mood, appetite, memory and immune response, among other things. The activity of FAAH directly affects the concentration of these signaling molecules, which in turn affects their biological effects. FAAH helps maintain physiological balance in living organisms by controlling the levels of bioactive amides. The expression and activity of FAAH in the nervous system affect neurotransmission and neuroprotection. By regulating levels of endocannabinoids, it may have an impact on the onset and development of neurodegenerative diseases such as Alzheimer's and Parkinson's disease, as well as mood disorders such as depression.
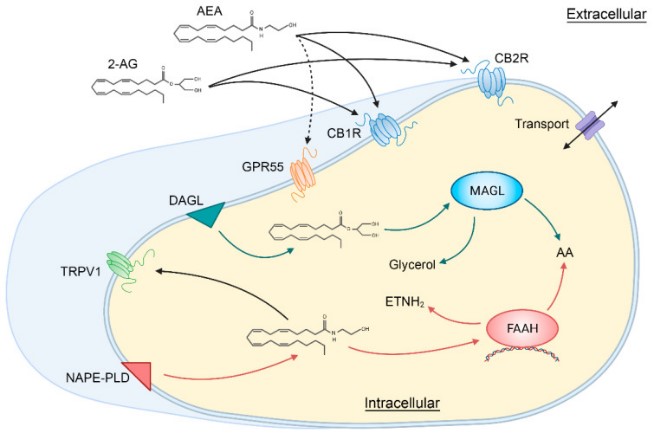
Fig1. Schematic illustration showing the main components of the classical endocannabinoid system. (Joseph Bouskila, 2021)
FAAH Related Signaling Pathway
By regulating levels of AEA, FAAH affects signaling mediated through CB1 and CB2 receptors, which are associated with physiological processes such as pain perception, appetite control, mood regulation, memory, and immune response. FAAH is involved in the regulation of pain signals by hydrolyzing AEA. AEA exerts an analgesic effect by activating the CB1 receptor, and the activity of FAAH causes AEA levels to decline, thereby reducing its analgesic effect. FAAH is also involved in metabolic processes, including energy balance and fat metabolism. The inhibition of FAAH may affect appetite and energy expenditure and is associated with the therapeutic potential of obesity and metabolic diseases.
FAAH Related Diseases
Deficiency or inhibition of FAAH can lead to overactivity of the cannabinoid system, which has been linked to anxiety, depression, and other mental disorders. The cannabinoid system plays a key role in appetite and energy balance. Abnormalities in FAAH may affect these processes, leading to obesity. Abnormalities in FAAH may affect appetite and food intake, leading to overeating or loss of appetite. In addition to the diseases described above, abnormalities in FAAH may be associated with a variety of other diseases, including but not limited to neurodegenerative diseases, inflammatory diseases, and tumors.
Bioapplications of FAAH
FAAH inhibitors have shown potential in the treatment of pain by increasing levels of endocannabinoids such as AEA. These endocannabinoids are associated with pain regulation, so FAAH inhibitors may help relieve chronic pain and inflammation-related pain. FAAH inhibitors have also shown promise in the treatment of mood disorders such as depression and anxiety. Although no FAAH inhibitors are currently on the market, several drugs are in clinical and preclinical bioactivity testing. This indicates that FAAH inhibitor research is continuing to progress and is expected to be used in the future to treat a variety of diseases.
Case Study
Case Study 1: Isabel Tundidor, 2023
Clinical management of breast cancer (BC) metastasis remains an unmet need as it accounts for 90% of BC-associated mortality. Although the luminal subtype, which represents >70% of BC cases, is generally associated with a favorable outcome, it is susceptible to metastatic relapse as late as 15 years after treatment discontinuation. Seeking therapeutic approaches as well as screening tools to properly identify those patients with a higher risk of recurrence is therefore essential. Here, this study reports that the lipid-degrading enzyme fatty acid amide hydrolase (FAAH) is a predictor of long-term survival in patients with luminal BC, and that it blocks tumor progression and lung metastasis in cell and mouse models of BC. Together, these findings highlight the potential of FAAH as a biomarker with prognostic value in luminal BC and as a therapeutic target in metastatic disease.
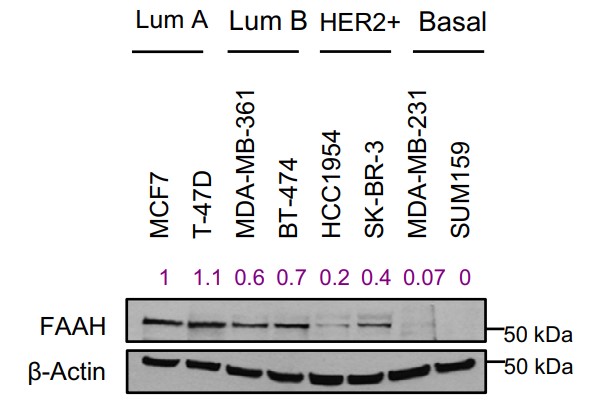
Fig1. Representative WB analysis of FAAH in a panel of human BC cell lines representative of the main intrinsic subtypes.
 in T-47D FAAH KO cells.jpg)
Fig2. Volcano plot showing some of the top DEGs (downregulated in red, upregulated in green) in T-47D FAAH KO cells compared to parental/rescued cells.
Case Study 2: Katrin Winkler, 2016
Inhibition of endocannabinoid degradation has been suggested as tool for activation of endogenous tumor defense. One of these strategies lies in blockade of fatty acid amide hydrolase (FAAH). This study addressed the impact of two FAAH inhibitors (arachidonoyl serotonin [AA-5HT], URB597) on A549 lung cancer cell metastasis and invasion. LC-MS analyses revealed increased levels of FAAH substrates (AEA, 2-AG, OEA, PEA) in cells incubated with either FAAH inhibitor. In athymic nude mice FAAH inhibitors were shown to elicit a dose-dependent antimetastatic action. In vitro, a concentration-dependent anti-invasive action of either FAAH inhibitor was demonstrated, accompanied with upregulation of tissue inhibitor of matrix metalloproteinases-1 (TIMP-1). Using siRNA approaches, a causal link between the TIMP-1-upregulating and anti-invasive action of FAAH inhibitors was confirmed. Moreover, knockdown of FAAH by siRNA was shown to confer decreased cancer cell invasiveness and increased TIMP-1 expression. Inhibitor experiments point toward a role of CB2 and transient receptor potential vanilloid 1 in conferring anti-invasive effects of FAAH inhibitors and FAAH siRNA.
.jpg)
Fig3. Concentration-dependency of FAAH inhibitors' anti-invasive action (black bars) and its impact on cell viability (open bars) and migration through uncoated Boyden chambers (grey bars).
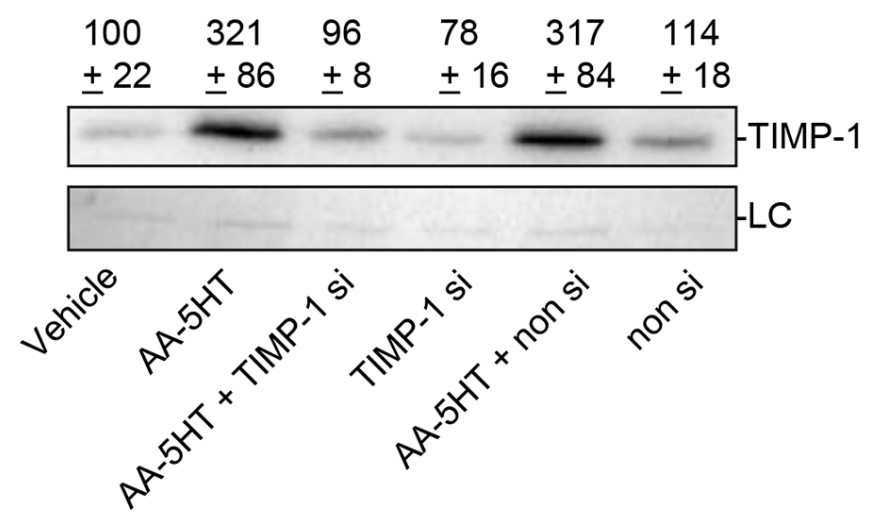
Fig4. Concentration-dependent effect of FAAH inhibitors on TIMP-1 protein levels.
Quality Guarantee
Involved Pathway
FAAH involved in several pathways and played different roles in them. We selected most pathways FAAH participated on our site, such as Retrograde endocannabinoid signaling, which may be useful for your reference. Also, other proteins which involved in the same pathway with FAAH were listed below. Creative BioMart supplied nearly all the proteins listed, you can search them on our site.
| Pathway Name | Pathway Related Protein |
|---|---|
| Retrograde endocannabinoid signaling | GNG3,GNG2,GNAI2,GNG8,GNG12,GNAI1,GABRR3,NAPEPLD,GNAQ,GABRG1 |
Protein Function
FAAH has several biochemical functions, for example, acylglycerol lipase activity,carbon-nitrogen ligase activity, with glutamine as amido-N-donor,fatty acid amide hydrolase activity. Some of the functions are cooperated with other proteins, some of the functions could acted by FAAH itself. We selected most functions FAAH had, and list some proteins which have the same functions with FAAH. You can find most of the proteins on our site.
| Function | Related Protein |
|---|---|
| carbon-nitrogen ligase activity, with glutamine as amido-N-donor | PET112L,GATB,FAAH2A,FAAH2,FAAH2B |
| protein binding | WNT2,CDC27,PKP2,NOS1AP,HOXC4,SCRN2,MOCS3,GPBP1,SLC30A8,FRA10AC1 |
| acylglycerol lipase activity | PNLIPRP2,ABHD6,MGLL,ABHD12 |
Interacting Protein
FAAH has direct interactions with proteins and molecules. Those interactions were detected by several methods such as yeast two hybrid, co-IP, pull-down and so on. We selected proteins and molecules interacted with FAAH here. Most of them are supplied by our site. Hope this information will be useful for your research of FAAH.
NOTCH2NL;dinB;MME
Resources
Related Services
Related Products
References
- Suarez, J; Romero-Zerbo, SY; et al. Endocannabinoid System in the Adult Rat Circumventricular Areas: An Immunohistochemical Study. JOURNAL OF COMPARATIVE NEUROLOGY 518:3065-3085(2010).
- Straiker, A; Hu, SSJ; et al. Monoacylglycerol Lipase Limits the Duration of Endocannabinoid-Mediated Depolarization-Induced Suppression of Excitation in Autaptic Hippocampal Neurons. MOLECULAR PHARMACOLOGY 76:1220-1227(2009).

.jpg)
.jpg)

