F13A1
-
Official Full Name
coagulation factor XIII, A1 polypeptide -
Overview
Factor XIIIa is a blood proenzyme that has been identified in platelets, megakaryocyte, and fibroblast-like mesenchymal or histiocytic cells present in the placenta, uterus, and prostate; it is also present in monocytes and macrophages and dermal dendriti -
Synonyms
F13A1;coagulation factor XIII, A1 polypeptide;F13A;coagulation factor XIII A chain;TGase;factor XIIIa;fibrinoligase;FSF, A subunit;coagulation factor XIIIa;transglutaminase A chain;transglutaminase. plasma;fibrin stabilizing factor, A subunit
Recombinant Proteins
- Human
- Mouse
- Rat
- Chicken
- E.coli
- HEK293
- Wheat Germ
- Mammalian Cells
- Human Plasma
- In Vitro Cell Free System
- Yeast
- His
- DDK
- Myc
- T7
- GST
- Non
- Flag
- Avi
- Fc
Background
What is F13A1 protein?
F13A1 gene (coagulation factor XIII A chain) is a protein coding gene which situated on the short arm of chromosome 6 at locus 6p25. This gene encodes the coagulation factor XIII A subunit. Coagulation factor XIII is the last zymogen to become activated in the blood coagulation cascade. Upon cleavage of the activation peptide by thrombin and in the presence of calcium ion, the plasma factor XIII dissociates its B subunits and yields the same active enzyme, factor XIIIa, as platelet factor XIII. This enzyme acts as a transglutaminase to catalyze the formation of gamma-glutamyl-epsilon-lysine crosslinking between fibrin molecules, thus stabilizing the fibrin clot. It also crosslinks alpha-2-plasmin inhibitor, or fibronectin, to the alpha chains of fibrin. The F13A1 protein is consisted of 732 amino acids and F13A1 molecular weight is approximately 83.3 kDa.
What is the function of F13A1 protein?
The F13A1 protein, also known as the coagulation factor XIII A chain, plays a crucial role in the blood coagulation process by catalyzing the cross-linking of fibrin chains to stabilize blood clots and prevent further blood loss. It is selectively expressed in tissues such as fibroblasts and immune cells in the placenta, and its secretion into the blood suggests additional physiological roles beyond coagulation, including wound healing, immune function, pregnancy maintenance, bone formation, and angiogenesis. Interestingly, the activation peptide of F13A1 (AP-F13A1) has been found to be reduced in the serum of colorectal cancer patients, indicating its potential as a biomarker for disease detection and progression.
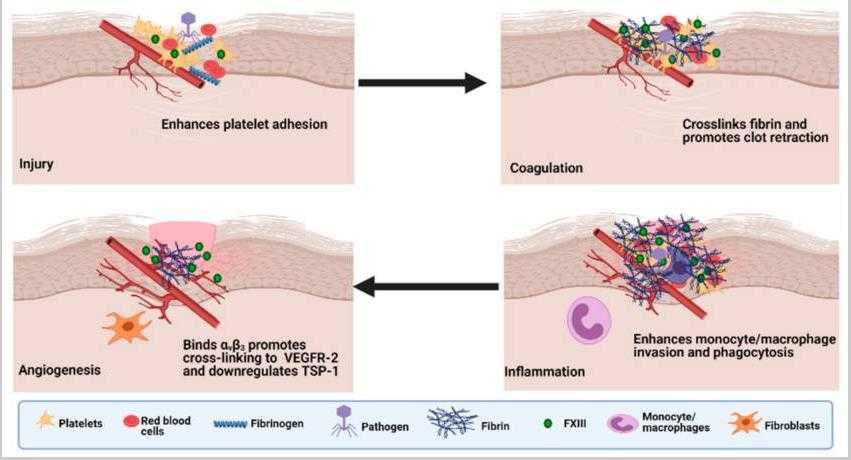
Fig1. The roles of Factor XIII in wound healing. (Fahad S. M. Alshehri, 2021)
F13A1 related signaling pathway
The F13A1-related signaling pathway plays a pivotal role in cellular processes, particularly in the context of immune regulation and inflammation. F13A1, also known as coagulation factor XIII A chain-like 1, is involved in the regulation of blood coagulation and wound healing. This protein functions by facilitating the cross-linking of fibrin molecules, which is crucial for the formation of a stable clot to prevent excessive bleeding during injury. Moreover, F13A1 has been implicated in various signaling pathways that influence cell adhesion, migration, and proliferation, thereby contributing to tissue remodeling and repair processes. Dysregulation of F13A1 can lead to impaired hemostasis, increased susceptibility to infections due to compromised immune responses, and possibly other pathological conditions associated with chronic inflammation or autoimmune diseases. Therefore, understanding the F13A1-related signaling pathway is essential for developing targeted therapies aimed at modulating these biological activities in disease management.
F13A1 related diseases
F13A1-related diseases encompass a range of pathological conditions primarily associated with dysregulated coagulation and inflammatory responses. This protein, also known as coagulation factor XIII A chain-like 1, is crucial for blood clotting and wound healing. Aberrations in F13A1 can lead to hemorrhagic disorders due to impaired formation of stable blood clots, increasing the risk of excessive bleeding. Additionally, altered F13A1 activity has been implicated in chronic inflammatory diseases and autoimmune conditions, where it may contribute to abnormal immune response regulation and tissue damage. Furthermore, mutations or deficiencies in F13A1 could potentially result in delayed wound healing and heightened susceptibility to infections. Therefore, a comprehensive understanding of F13A1's role in these diseases is vital for the development of targeted therapeutic interventions aimed at correcting hemostasis imbalances and modulating immune responses effectively.
Bioapplications of F13A1
The F13A1 protein, a subunit of coagulation factor XIII, plays a critical role in blood clotting by catalyzing the cross-linking of fibrin, which stabilizes clots and prevents bleeding. Beyond its traditional function in hemostasis, F13A1 has been identified as a potential biomarker for colorectal cancer (CRC). Research has shown that the activation peptide of F13A1 (AP-F13A1) is reduced in the serum of CRC patients, suggesting its utility in cancer screening. This discovery opens new avenues for the application of F13A1 in clinical diagnostics, complementing its established role in coagulation and offering a potential new tool in the fight against CRC.
Case Study
Case Study 1: Julien Peltier, 2018
Studying colorectal cancer (CRC), a leading cause of cancer deaths, we explored AP-F13A1 as a possible biomarker. Researcherds analyzed FXIII protein levels in 40 serum samples via ELISA and AP-F13A1 levels in an additional 113 samples using LC-PRM assays. This analysis revealed decreased AP-F13A1 levels in CRC patients, with high sensitivity and specificity. This indicates that AP-F13A1 could be a promising biomarker for CRC screening.
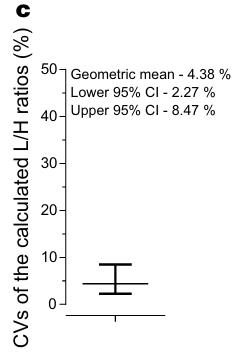
Fig1. Coefficients of variations (CVs) of the light/heavy ratios distribution for the two peptides.
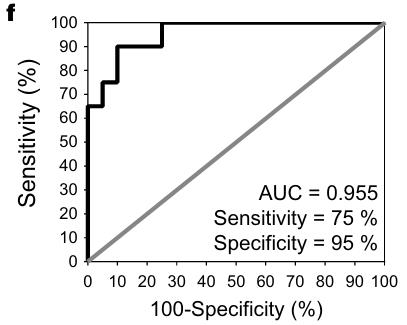
Fig2. Receiver Operating Characteristic curves (ROC) for AP-F13A1 from first sample bank.
Case Study 2: Laura Somodi, 2023
Macrophages, which express coagulation factor XIII A subunit (FXIII-A) and are prevalent in atherosclerotic plaques, can stabilize these plaques through protein cross-linking. During their transformation into foam cells—characterized by the accumulation of oxidized LDL (oxLDL)—these macrophages retain FXIII-A, as shown by Oil Red O and immunofluorescent staining. This transformation increases intracellular FXIII-A levels, a phenomenon unique to macrophage-derived foam cells, not observed in vascular smooth muscle cells. FXIII-A's presence and activity in the plaque, indicated by antibody labeling of iso-peptide bonds, suggest that these macrophages contribute to plaque's lipid core and structural development.
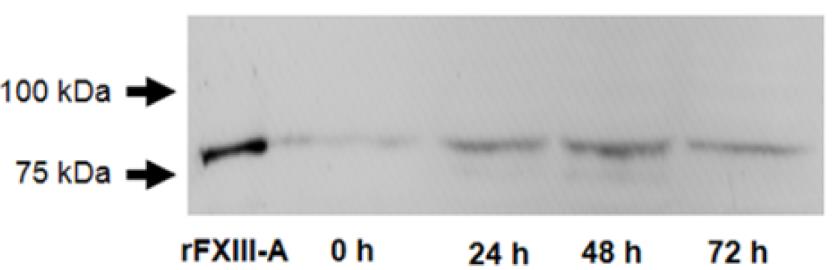
Fig3. A representative Western blot demonstrates an elevated FXIII-A level in macrophages.
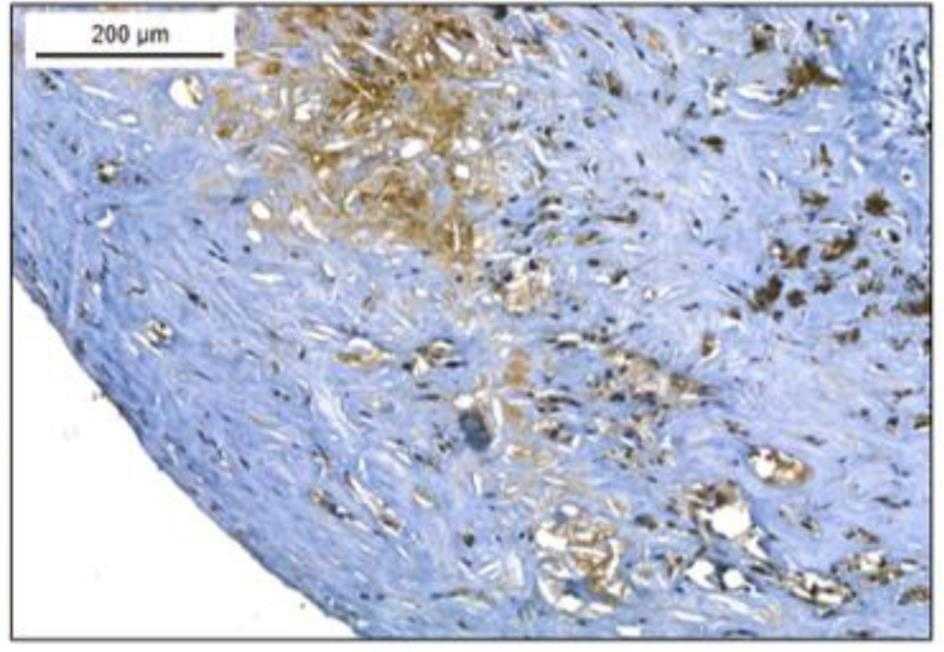
Fig4. FXIII-A-positive cells are detected in the plaque by immune-peroxidase staining.
Quality Guarantee
High Purity
.jpg)
Fig1. SDS-PAGE (F13A1-3609H)
.
.jpg)
Fig2. SDS-PAGE (F13A1-1330H)
Involved Pathway
F13A1 involved in several pathways and played different roles in them. We selected most pathways F13A1 participated on our site, such as Complement and coagulation cascades, which may be useful for your reference. Also, other proteins which involved in the same pathway with F13A1 were listed below. Creative BioMart supplied nearly all the proteins listed, you can search them on our site.
| Pathway Name | Pathway Related Protein |
|---|---|
| Complement and coagulation cascades | CFI,MASP2,F13B,C4BPB,C1QA,SERPINE1,CPB2,SERPINA1,C8G,FGA |
Protein Function
F13A1 has several biochemical functions, for example, metal ion binding,protein-glutamine gamma-glutamyltransferase activity. Some of the functions are cooperated with other proteins, some of the functions could acted by F13A1 itself. We selected most functions F13A1 had, and list some proteins which have the same functions with F13A1. You can find most of the proteins on our site.
| Function | Related Protein |
|---|---|
| metal ion binding | ZNF83,PARP12A,RAD50,GALNS,ZBTB12,GCM2,NSF,ZFP503,ZNF609A,KLF11 |
| protein-glutamine gamma-glutamyltransferase activity | TGM3,TGM2B,TGM2A,EPB42,F13A1A.1,TGM2,TGM5,EPB4.2,TGM4,TGM1 |
Interacting Protein
F13A1 has direct interactions with proteins and molecules. Those interactions were detected by several methods such as yeast two hybrid, co-IP, pull-down and so on. We selected proteins and molecules interacted with F13A1 here. Most of them are supplied by our site. Hope this information will be useful for your research of F13A1.
dqmmlpwpaval;HSPB1;NUDT21;TK1;ANXA7;CDKN1A;PTK2;UFD1L;SH3GL2;PLEK
Resources
Related Services
Related Products
References


