COX5A
-
Official Full Name
cytochrome c oxidase subunit Va -
Overview
Cyclooxygenase (COX) is an important enzyme in the conversion of arachidonic acid to Prostaglandin H2, the precursor of the series-2 prostanoids. At least 3 splice variants have been found (COX-1, COX-2 and COX-3). COX-1 is constitutively expressed in mos -
Synonyms
COX5A;cytochrome c oxidase subunit Va;cytochrome c oxidase subunit 5A, mitochondrial;cytochrome c oxidase polypeptide Va;mitochondrial cytochrome c oxidase subunit Va;cytochrome c oxidase polypeptide, mitochondrial;VA;COX;COX-VA
Recombinant Proteins
- Rat
- Human
- Mouse
- Rhesus macaque
- Mammalian Cells
- Wheat Germ
- E.coli
- HEK293
- In Vitro Cell Free System
- His
- GST
- Non
- Avi
- Fc
- DDK
- Myc
- SUMO
Background
What is COX5A Protein?
COX5A protein is a crucial part of the mitochondrial respiratory chain, specifically within the cytochrome c oxidase (COX) complex. It works with other subunits to transfer electrons to oxygen, producing water, essential for cellular energy metabolism. Beyond energy production, COX5A is vital for maintaining mitochondrial function and cell health. Its expression levels change under various conditions and are linked to diseases like mitochondrial disorders and oxidative stress-related issues. COX5A might serve as a biomarker for systemic lupus erythematosus (SLE), as it's linked to how active the disease is and the extent of organ damage. Research on newborn rats with brain injuries due to oxygen deprivation showed that lower COX5A levels were connected to mitochondrial energy issues, influencing the progression of neurological diseases. This highlights COX5A’s critical role in cellular respiration and energy metabolism, and its potential impact on disease progression and treatment.What is the Function of COX5A Protein?
COX5A plays a key role in energy metabolism within cells, as part of the cytochrome c oxidase in mitochondria. It helps in converting oxygen to water, driving ATP production through oxidative phosphorylation. Besides generating energy, COX5A is vital for keeping mitochondria and cells healthy. Research links COX5A levels to various health issues, including heart disease and cancer. Boosting COX5A can lessen heart damage from doxorubicin, prevent heart cell death, and improve mitochondrial function, making it a potential target for heart treatments. Abnormal COX5A expression is also connected to mitochondrial problems, which can lead to metabolic diseases and heart issues.COX5A Related Signaling Pathway
COX5A is key in keeping mitochondria working well and is linked to memory issues and brain aging. Studies show that COX5A affects brain aging and memory loss by regulating the BDNF/ERK1/2 signaling pathway. Boosting COX5A can improve spatial memory and hippocampal synaptic plasticity, restore dendrites in the CA1 area, and activate the BDNF/ERK1/2 pathway. In contrast, mice with high COX5A and low BDNF levels showed poor recovery in spatial memory and dendritic density in the CA1 region. Lab studies also support that COX5A influences neuron growth via BDNF. These findings suggest that COX5A might impact cognitive function through the BDNF/ERK1/2 pathway and could be a target for anti-aging treatments.COX5A Related Diseases
COX5A is involved in several diseases, and research is shedding light on its roles. In systemic lupus erythematosus (SLE), COX5A might be a useful marker for predicting how active the disease is and potential organ damage. It is more expressed in T cells of SLE patients compared to healthy people and is linked to disease severity, organ issues, and steroid treatments. Additionally, COX5A impacts memory loss and brain aging by influencing cognitive function via the BDNF/ERK1/2 pathway. In heart conditions, COX5A reduces doxorubicin's harmful effects on the heart, protecting against oxidative stress, mitochondrial problems, and cell death. Studies show that increasing COX5A levels can enhance heart function and protect heart cells from damage and death in doxorubicin-treated heart models. These insights suggest COX5A's potential as a treatment target and biomarker in various health issues.Bioapplications of COX5A
COX5A protein is valuable in both biomedical research and industrial applications. In research, COX5A is often analyzed using techniques like Western Blot, immunohistochemistry, immunofluorescence, and ELISA, aiding in studying mitochondrial function and diseases in human, mouse, and rat samples. It's also seen as a potential biomarker for disease activity and organ damage in SLE, with studies exploring its expression through RNA sequencing data. Industrially, understanding COX5A helps in developing treatments for mitochondrial dysfunction and oxidative stress-related diseases. For instance, in blood vessel health, COX5A aids vascular smooth muscle cells by enhancing mitochondrial function and reducing damage. It also plays a protective role against doxorubicin-induced heart toxicity by countering oxidative stress and mitochondrial issues. These developments underline COX5A's significant potential in research and therapy, particularly for mitochondrial-related conditions.Case Study
Case Study 1: Zhang P. et al. Int J Mol Sci. 2023
Doxorubicin (DOX), a cancer drug, can lead to mitochondrial problems and heart failure. COX5A plays a vital role in mitochondrial energy regulation. We looked into how COX5A affects DOX-induced heart issues and its mechanisms. In experiments with mice and heart cells, we found that DOX reduced COX5A levels, affecting heart and mitochondrial function. COX5A was much lower in patients with severe heart disease. Enhancing COX5A expression improved heart performance, glucose uptake, and mitochondrial function by overexpressing it, also reducing oxidative stress and cell death in both living organisms and in lab studies. DOX decreased Akt phosphorylation, a problem fixed by increasing COX5A. PI3K inhibitors blocked COX5A's protective effects against DOX in heart cells, showing that COX5A relies on PI3K/Akt signaling to shield against DOX-induced heart damage.-
 Fig1. Western blot analysis of the protein level of COX5A, SOD2, Bax/Bcl-2, cleaved caspase-3/caspase-3, and p-Akt(S473)/t-Akt.
Fig1. Western blot analysis of the protein level of COX5A, SOD2, Bax/Bcl-2, cleaved caspase-3/caspase-3, and p-Akt(S473)/t-Akt. -
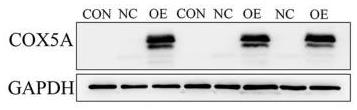 Fig2. Expression of COX5A in H9c2 cells after transfection of lentivirus-COX5A and lentivirus-NC by Western blot.
Fig2. Expression of COX5A in H9c2 cells after transfection of lentivirus-COX5A and lentivirus-NC by Western blot.
Case Study 2: Takallou S. et al. FASEB J. 2024
Reactive oxygen species (ROS) are major cell stress factors that can damage vital biomolecules. High ROS levels are linked to conditions like neurodegeneration, diabetes, atherosclerosis, and cancer. If ROS levels aren't managed, it can cause cell death, so it's crucial to understand how cells detoxify these compounds. H2O2, a common ROS, comes mainly from mitochondrial electron transport. Several genes help with detoxification, including yeast YAP1, which boosts antioxidant genes. This study uncovers new roles for COX5A and NPR3 in stress from H2O2, showing that deleting them makes cells more vulnerable. Further research suggests COX5A and NPR3 control YAP1 expression through a unique translation method, shedding light on gene regulation and yeast's defense against oxidative stress.-
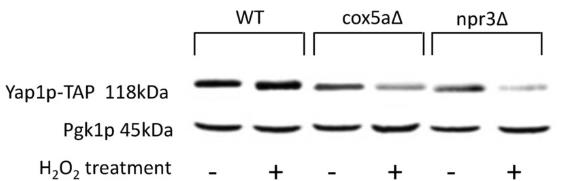 Fig3. The level of YAP1-TAP protein in deletion of COX5A and NPR3 is decreased more dramatically when cells are treated with H2O2 compared to control condition.
Fig3. The level of YAP1-TAP protein in deletion of COX5A and NPR3 is decreased more dramatically when cells are treated with H2O2 compared to control condition. -
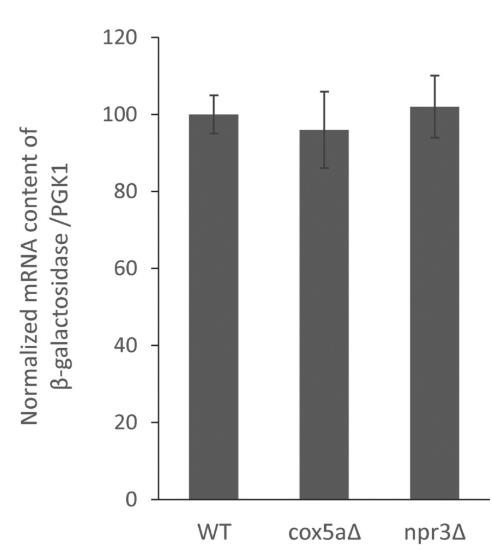 Fig4. Deletion of COX5A and NPR3 has no effect on the transcription level of β-galactosidase expression.
Fig4. Deletion of COX5A and NPR3 has no effect on the transcription level of β-galactosidase expression.
Quality Guarantee
High Purity
-
.jpg) Fig1. SDS-PAGE (COX5A-1750H)
Fig1. SDS-PAGE (COX5A-1750H) -
.jpg) Fig2. SDS-PAGE (COX5A-5140H)
Fig2. SDS-PAGE (COX5A-5140H)
Involved Pathway
COX5A involved in several pathways and played different roles in them. We selected most pathways COX5A participated on our site, such as Oxidative phosphorylation,Metabolic pathways,Cardiac muscle contraction, which may be useful for your reference. Also, other proteins which involved in the same pathway with COX5A were listed below. Creative BioMart supplied nearly all the proteins listed, you can search them on our site.
| Pathway Name | Pathway Related Protein |
|---|---|
| Parkinsons disease | SNCA,MT-ND1,PARK7,NDUFA3,PRKACA,APAF1,GNAI1,SLC18A1,GPR37,NDUFB10 |
| Huntingtons disease | NDUFB2,ATP5G3,VDAC1,NDUFS4,POLR2L,CASP8,BAX,NDUFV3,SOD2,ATP5J |
| Non-alcoholic fatty liver disease (NAFLD) | IL-8,MAP3K5,NDUFB9,NDUFC1,EIF2AK3,LEP,INS2,COX6B2,PIK3CA,NDUFA4L2 |
| Metabolic pathways | POLE2,ST3GAL1,AK7,ALOX15B,PLCG1,GALT,NME2B.2,NT5C1B,LPIN2,CYP2P7 |
| Oxidative phosphorylation | ATP6V1BA,ATP6AP1,ATP5IB,NDUFA6,ATPV0E2,NDUFA4L2,ATP6V1F,UQCR10,ATP5IA,NDUFV3 |
| Alzheimers disease | BID,ITPR1,GAPDH,APP,UQCR11,NDUFB9,ATP5O,PPP3CC,NDUFB11,COX8C |
| Cardiac muscle contraction | COX5B2,UQCRC1,TPM4A,UQCRFS1,TNNI3,CACNG2A,CACNB4A,ATP1B2B,ATP1A3B,UQCRC2B |
-
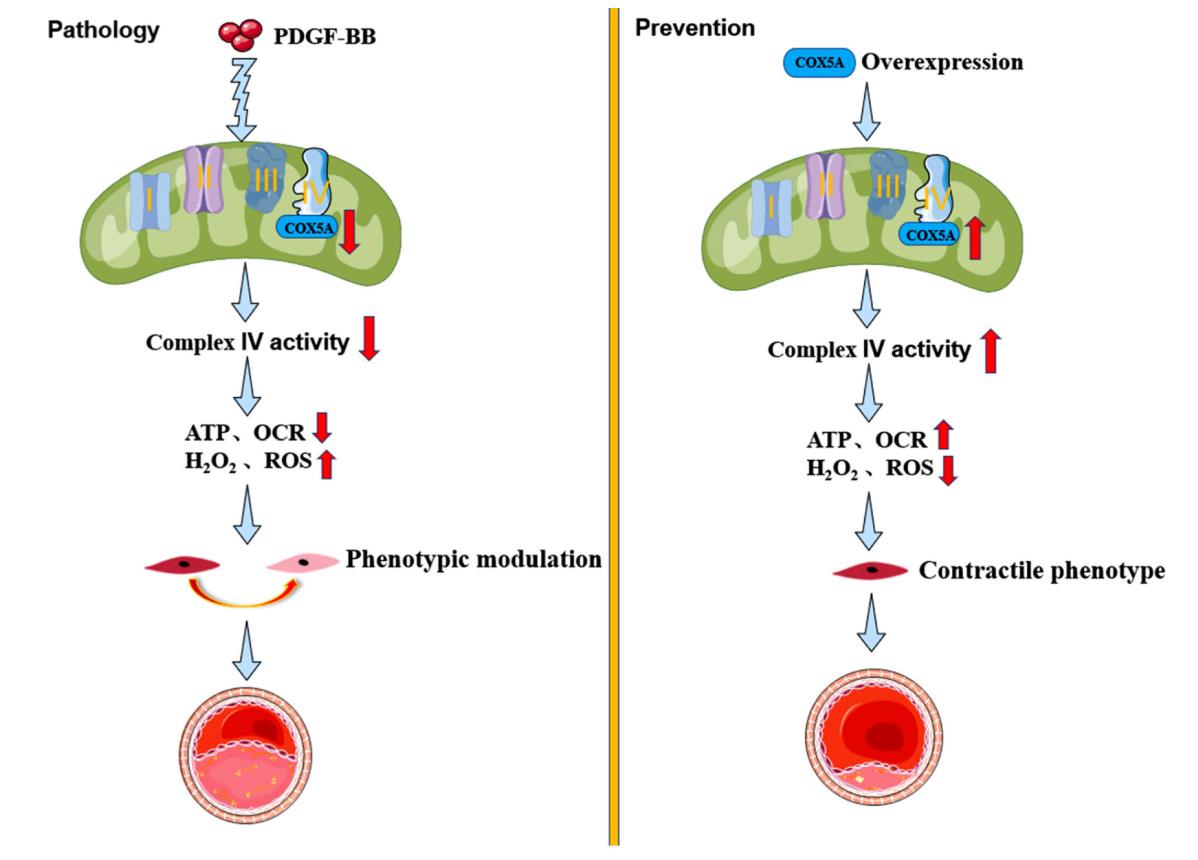 Fig1. The protective roles of mitochondrial COXsA against mitochondrial disorder and oxidative stress in VSMC phenotypic modulation and neointima formation. (Haijing Guan, 2023)
Fig1. The protective roles of mitochondrial COXsA against mitochondrial disorder and oxidative stress in VSMC phenotypic modulation and neointima formation. (Haijing Guan, 2023) -
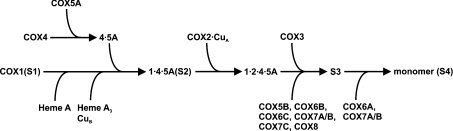 Fig2. Proposed model of the assembly pathway of human COX. (Lukas Stiburek, 2005)
Fig2. Proposed model of the assembly pathway of human COX. (Lukas Stiburek, 2005)
Protein Function
COX5A has several biochemical functions, for example, cytochrome-c oxidase activity,electron carrier activity,metal ion binding. Some of the functions are cooperated with other proteins, some of the functions could acted by COX5A itself. We selected most functions COX5A had, and list some proteins which have the same functions with COX5A. You can find most of the proteins on our site.
| Function | Related Protein |
|---|---|
| metal ion binding | RXRAA,ZBTB46,TNNI3,ALKBH6,CSH2,KDM6BB,NPEPPS,VEPH1,ZNF45L,CAR13 |
| electron carrier activity | AOX1,HSD17B6,MAOB,AOC2,GLRX2,ACAD8,DERL3,GPX2,ACADSB,ACOX3 |
| cytochrome-c oxidase activity | COX5B2,COX7C,COX6C,COX6B1,COX7A3,COX7A2,COX5AA,COA6,COX11,COX6A2 |
| protein binding | HSPA4,ARHGAP1,ZNF514,PIK3CG,TIMM23,HIST1H2BF,FAM46B,TOM1,LZTS1,PALM |
Interacting Protein
COX5A has direct interactions with proteins and molecules. Those interactions were detected by several methods such as yeast two hybrid, co-IP, pull-down and so on. We selected proteins and molecules interacted with COX5A here. Most of them are supplied by our site. Hope this information will be useful for your research of COX5A.
KRT31;KRT40;EXOSC8;40038273;MT-CO2;VHL;PINX1;TMBIM4;PDE4DIP;COPS6;Cenpe;SYNCRIP;env
Resources
Related Services
Related Products
References
- Helling, S; Vogt, S; et al. Phosphorylation and kinetics of mammalian cytochrome c oxidase. MOLECULAR & CELLULAR PROTEOMICS 7:1714-1724(2008).
- Ren, JC; Rebrin, I; et al. Cytochrome c oxidase loses catalytic activity and structural integrity during the aging process in Drosophila melanogaster. BIOCHEMICAL AND BIOPHYSICAL RESEARCH COMMUNICATIONS 401:64-68(2010).


