CLEC2D
-
Official Full Name
C-type lectin domain family 2, member D -
Overview
This gene encodes a member of the natural killer cell receptor C-type lectin family. The encoded protein inhibits osteoclast formation and contains a transmembrane domain near the N-terminus as well as the C-type lectin-like extracellular domain. Several alternatively spliced transcript variants have been identified for this gene. [provided by RefSeq, Oct 2010] -
Synonyms
CLEC2D;C-type lectin domain family 2, member D;CLAX;LLT1;OCIL;C-type lectin domain family 2 member D;LLT-1;C-type lectin related f;lectin-like transcript 1;lectin-like NK cell receptor;osteoclast inhibitory lectin;C-type lectin superfamily 2, member D
Recombinant Proteins
- Rat
- Human
- Mouse
- Mammalian Cells
- Wheat Germ
- HEK293
- E.coli
- Human Cells
- In Vitro Cell Free System
- His
- GST
- Fc
- Non
- Avi
- DDK
- Myc
- mFc
- Flag
Background
What is CLEC2D Protein?
CLEC2D, short for C-Type Lectin Domain Family 2 Member D, is part of the natural killer cell receptor family known as C-type lectins. This protein plays a crucial role in the immune system, especially in stopping bone-resorbing cells, or osteoclasts, from forming. It has a transmembrane domain near the N-terminus and a C-type lectin-like domain outside the cell, which helps it regulate B lymphocyte proteins during viral infections. After an infection, CLEC2D gets expressed more in lymphocytes, which can dampen natural killer cells’ attack capabilities and their interferon-gamma release. Interestingly, CLEC2D also carries histone-bound DNA complexes into the endoplasmic reticulum, activating TLR9-mediated inflammatory responses in macrophages and microglial cells. Its functions include controlling the differentiation of osteoclasts and protecting against cell death. Overall, CLEC2D is vital for immune regulation, bone health, and possibly sensing cell death.What is the Function of CLEC2D Protein?
CLEC2D, also known as C-Type Lectin Domain Family 2 Member D, is a receptor in the natural killer cell’s C-type lectin family. This protein is quite the multitasker—it helps inhibit the formation of osteoclasts, protects cells from being lysed by natural killer cells, and even keeps bone resorption in check. Plus, it modulates the release of interferon-gamma and binds to large, sulfated glycosaminoglycans. In terms of cellular mechanics, CLEC2D plays a role in sensing cell death and can carry histone-bound DNA complexes into the endoplasmic reticulum, kicking off TLR9-mediated inflammatory responses in macrophages and microglia. Interestingly, it can form both homodimers and heterodimers with TLR2, which negatively modulates the antifungal immune response driven by IRF5. All these functions show that CLEC2D is key in immune regulation, bone metabolism, and sensing cell death, having implications for defenses against pathogens like Candida albicans.CLEC2D Related Signaling Pathway
CLEC2D protein is deeply involved in immune regulation and inflammatory responses. It’s known to recognize histone sequences released from necrotic cells, setting off inflammation and tissue damage. In immune cells, CLEC2D forms both hetero- and homodimers with TLR2, dampening IRF5-mediated IL-12 production, which in turn affects antifungal immunity. There’s also some cross-talk with TLRs, where CLEC2D interacts with the Syk pathway to enhance TLR signaling, even though CLEC2D doesn’t directly activate Syk itself. Additionally, CLEC2D might boost TLR9 responses by ferrying immune-stimulating ligand complexes. In macrophages, it’s situated on the plasma membrane and ER. While the binding of histones to CLEC2D doesn’t kickstart kinases or cytokine production right away, it does lead to an ER-based TLR9 response through a CLEC2D-dependent mechanism. Through its interactions with TLRs and histone-DNA complexes, CLEC2D plays a crucial role in modulating immune responses, inflammation, and sensing cell death.CLEC2D Related Diseases
The CLEC2D protein is linked to a variety of diseases, playing a significant role in cancer and immune responses. For instance, its elevated expression in clear cell renal cell carcinoma (ccRCC) is associated with tumor size and patient prognosis, affecting how tumors interact with the immune system. Removing CLEC2D can halt the growth of kidney cancer cells and diminish tumor growth and immune infiltration. Beyond kidney cancer, CLEC2D acts as a prognostic marker in cervical cancer, head and neck squamous cell carcinoma, and ccRCC, potentially predicting cancer progression and patient survival rates. In neuroblastoma, pathways involving CLEC2D and CD161 might alter T cell capabilities to attack the tumor. Additionally, CLEC2D may detect histones released from necrotic cells, prompting inflammation and tissue damage, impacting how cell death is sensed by the immune system. Therefore, CLEC2D stands out as a crucial target for studying and treating diseases related to tumor progression, immune response, and inflammation.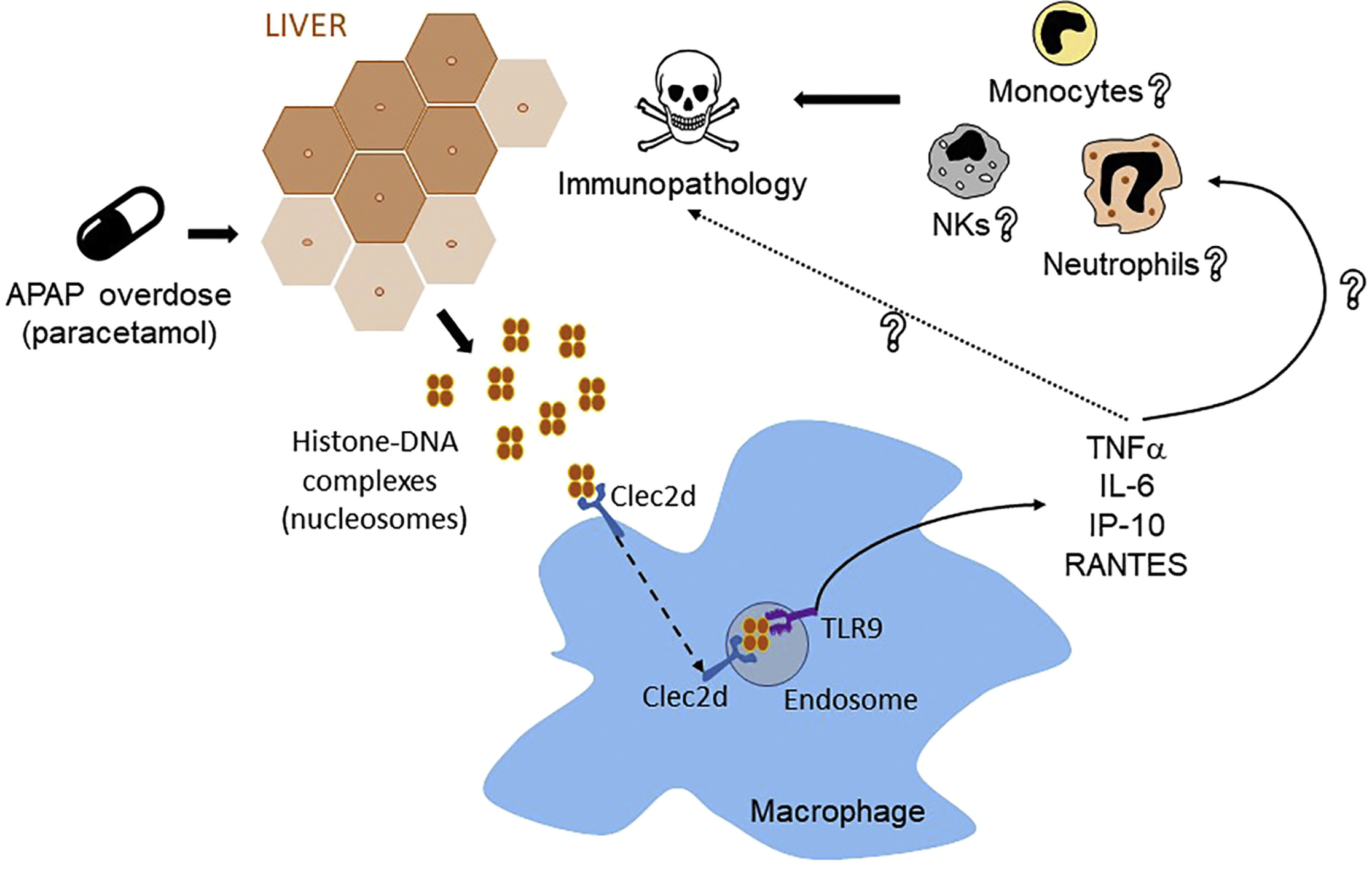
Fig1. Histones Recognition by Clec2d Contributes to Immunopathology upon Tissue-Damage Conditions. (Carlos Del Fresno, 2020)
Bioapplications of CLEC2D
The recombinant CLEC2D protein is quite the multitasker in research, industry, and medicine. Scientists are using it to dig into its roles in immune regulation, how it senses cell death, and its interactions with TLR2 signaling pathways. On the industrial side, advances in producing CLEC2D are paving the way for new bioproducts and drugs, particularly those focused on immune modulation and cancer therapies. Medically, CLEC2D’s involvement with various diseases, including cancer and pregnancy-related conditions, makes it a pivotal player in understanding disease mechanisms, validating drug targets, and developing new treatments. In short, recombinant CLEC2D is proving to be an invaluable asset in advancing both scientific research and clinical applications.Case Study
Case Study 1: Li H. et al. Heliyon. 2024
Clear cell renal cell carcinoma (ccRCC), the most common kidney cancer, has seen progress in targeted therapies. However, there’s still a need for new treatment targets due to its aggressive nature. C-type lectins, including CLEC2D, play roles in cancer, though their impact on ccRCC isn’t fully understood. We’ve noticed high levels of CLEC2D in ccRCC tissues, linking it to patient prognosis and tumor size. Moreover, CLEC2D influences immune infiltration in tumors, and reducing its expression in experiments has been shown to slow down tumor growth and affect immune behavior in ccRCC.-
 Fig1. GO and KEGG enrichment analysis of CLEC2D coexpressed genes.
Fig1. GO and KEGG enrichment analysis of CLEC2D coexpressed genes. -
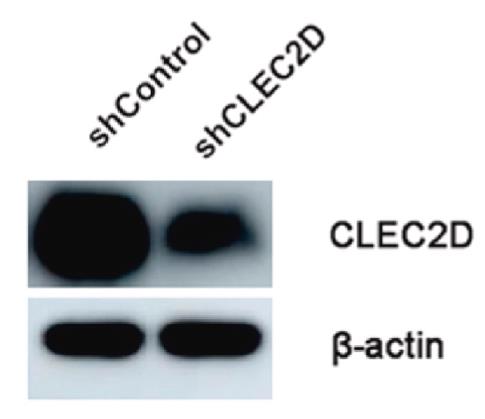 Fig2. Immunohistochemistry was performed to detect the expression of CLEC2D in tumor tissues.
Fig2. Immunohistochemistry was performed to detect the expression of CLEC2D in tumor tissues.
Case Study 2: Li F. et al. Nat Commun. 2023
When CLRs or TLRs pair up, it can affect their ability to bind with ligands and ultimately tweak immune responses, though exactly how CLRs and TLRs dimerize has been somewhat unclear. Recent findings show that CLEC2D can create both homodimers and heterodimers with TLR2. These dimer forms have a stronger affinity for fungi-derived β-glucans than TLR2 alone, leading to a suppression of the immune response by inhibiting the pathway that usually results in IL-12 production, a crucial part of the body’s defense against fungi like Candida albicans. Interestingly, females lacking Clec2d show a boosted immune response, being more resistant to Candida infections. This research uncovers that CLEC2D impacts antifungal immunity by suppressing IL-12 production through its dimer interactions.-
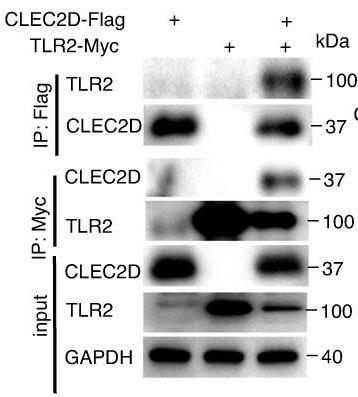 Fig3. Association analyses of human CLEC2D-Flag with human TLR2-Myc expressed in HEK293T cells.
Fig3. Association analyses of human CLEC2D-Flag with human TLR2-Myc expressed in HEK293T cells. -
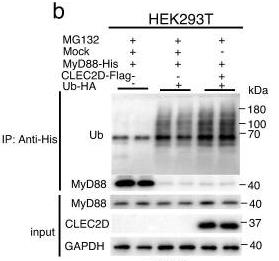 Fig4. Immunoblot analysis of the degradation of MyD88 expressed in HEK293T cells with co-expression of MyD88-his, Clec2d-Flag and Ub-HA.
Fig4. Immunoblot analysis of the degradation of MyD88 expressed in HEK293T cells with co-expression of MyD88-his, Clec2d-Flag and Ub-HA.
Quality Guarantee
High Purity
-
.jpg) Fig1. SDS-PAGE (CLEC2D-1464H)
Fig1. SDS-PAGE (CLEC2D-1464H)
-
.jpg) Fig2. SDS-PAGE (CLEC2D-329H)
Fig2. SDS-PAGE (CLEC2D-329H)
Involved Pathway
CLEC2D involved in several pathways and played different roles in them. We selected most pathways CLEC2D participated on our site, such as Adaptive Immune System,Immune System,Immunoregulatory interactions between a Lymphoid and a non-Lymphoid cell, which may be useful for your reference. Also, other proteins which involved in the same pathway with CLEC2D were listed below. Creative BioMart supplied nearly all the proteins listed, you can search them on our site.
| Pathway Name | Pathway Related Protein |
|---|---|
| Immune System | ART1,ASB9,BST2,CTSK,RNF41,RNF216,MGC174155,POLR3G,EIF4G2,NPEPPS |
| Adaptive Immune System | NCR3LG1,RACGAP1,SIGLEC7,KIF22,FRS2B,ITGB1B.1,AP2A1,KIF5B,CLTC,AP1B1 |
| Immunoregulatory interactions between a Lymphoid and a non-Lymphoid cell | CD200R1,SIGLEC5,CLEC2B,CD160,Siglece,CD96,AMICA1,LILRA1,CD226,HCST |
-
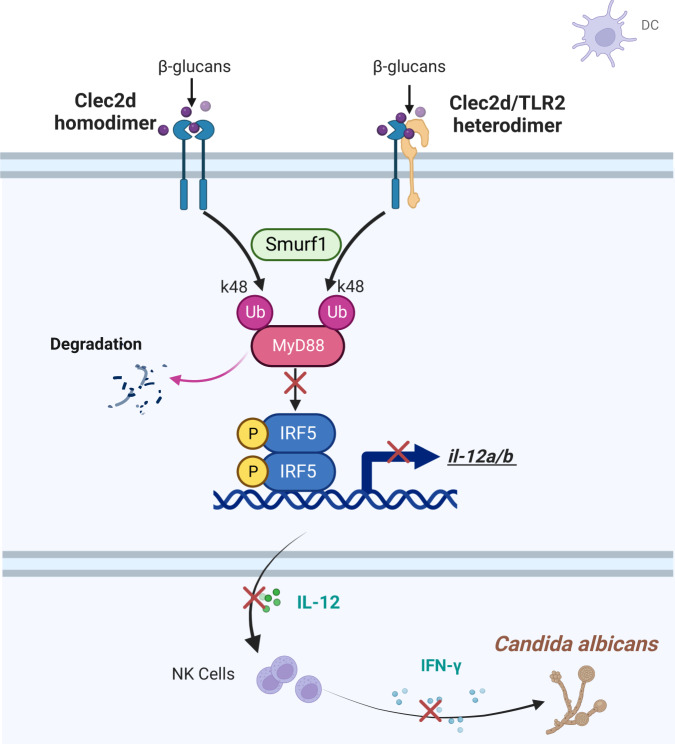 Fig1. During C. albicans infection, CLEC2D in dendritic cells forms homodimers or heterodimers with TLR2 to recognize β-glucan derived from C. albicans. (Fan Li, 2023)
Fig1. During C. albicans infection, CLEC2D in dendritic cells forms homodimers or heterodimers with TLR2 to recognize β-glucan derived from C. albicans. (Fan Li, 2023) -
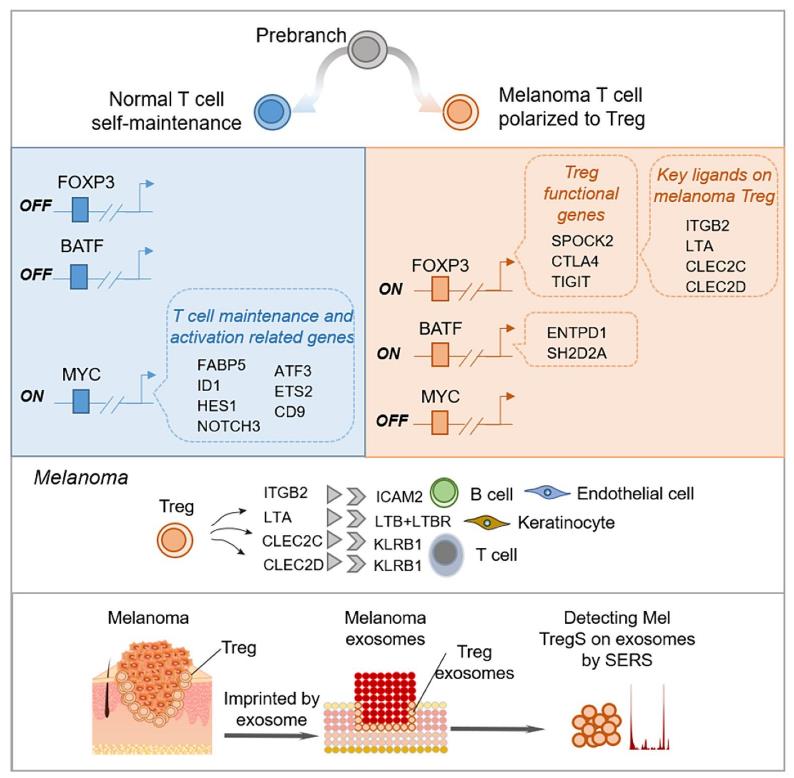 Fig2. Different transcriptional regulatory switches existed in T cells of normal and tumor tissues, with FOXP3 and BATF significantly elevated in tumor T cells. (Tengda Li, 2024)
Fig2. Different transcriptional regulatory switches existed in T cells of normal and tumor tissues, with FOXP3 and BATF significantly elevated in tumor T cells. (Tengda Li, 2024)
Protein Function
CLEC2D has several biochemical functions, for example, carbohydrate binding,transmembrane signaling receptor activity. Some of the functions are cooperated with other proteins, some of the functions could acted by CLEC2D itself. We selected most functions CLEC2D had, and list some proteins which have the same functions with CLEC2D. You can find most of the proteins on our site.
| Function | Related Protein |
|---|---|
| carbohydrate binding | G6PDX,CLEC4A,FCN3,LGALSL,HIST2H3C2,CD69,HBL4,CD209B,KLRD1,KLRC2 |
| transmembrane signaling receptor activity | EBP,GHRHRA,VIPR1B,SPN,NCR2,TNFRSF10C,CD247,TLR5,FZD9B,TRPV1 |
Interacting Protein
CLEC2D has direct interactions with proteins and molecules. Those interactions were detected by several methods such as yeast two hybrid, co-IP, pull-down and so on. We selected proteins and molecules interacted with CLEC2D here. Most of them are supplied by our site. Hope this information will be useful for your research of CLEC2D.
Resources
Related Services
Related Products
References


