CES2
-
Official Full Name
carboxylesterase 2 -
Overview
This gene encodes a member of the carboxylesterase large family. The family members are responsible for the hydrolysis or transesterification of various xenobiotics, such as cocaine and heroin, and endogenous substrates with ester, thioester, or amide bonds. They may participate in fatty acyl and cholesterol ester metabolism, and may play a role in the blood-brain barrier system. The protein encoded by this gene is the major intestinal enzyme and functions in intestine drug clearance. Alternatively spliced transcript variants have been found for this gene.[provided by RefSeq, Oct 2010] -
Synonyms
CES2;carboxylesterase 2;iCE;CE-2;PCE-2;CES2A1;cocaine esterase;hCE-2;carboxylesterase 2 (intestine, liver);methylumbelliferyl-acetate deacetylase 2;intestinal carboxylesterase;liver carboxylesterase-2
Recombinant Proteins
- Human
- Zebrafish
- Rat
- BTI Insect Cell
- HEK293
- E.coli
- Wheat Germ
- Mammalian Cells
- Human Cells
- In Vitro Cell Free System
- Non
- His
- DDK
- Myc
- GST
- Flag
- Avi
- Fc
Background
What is CES2 Protein?
CES2, or carboxylesterase 2, is an enzyme that plays a big role in breaking down various substances within the body, including drugs and fats. Think of it as a cleanup crew in your liver, where it helps manage the fats by breaking down triglycerides, making it crucial for lipid metabolism. It's particularly important when you're considering how your body handles medications and processes them effectively. In the context of diseases like nonalcoholic fatty liver disease (NAFLD) and diabetes, CES2 can be a significant player. When its levels drop, it might lead to problems like fat buildup in the liver, as seen in conditions like NASH. Understanding CES2 can provide insights into tackling these metabolic issues and improving liver health.What is the Function of CES2 Protein?
CES2, short for carboxylesterase 2, is like a molecular multitasker in your body, especially hanging out in the liver. It's primarily responsible for breaking down certain compounds, including different drugs and dietary fats. Picture it as part of the body's detox team, helping to manage what comes in and ensuring it's processed smoothly. In the realm of fats, CES2 takes on the task of breaking down triglycerides, playing a vital role in fat metabolism. This function becomes particularly crucial when considering conditions like nonalcoholic fatty liver disease (NAFLD), where improper fat processing is a major issue. When CES2 is functioning well, it helps maintain a balance, preventing fat accumulation in the liver and ensuring drugs are metabolized properly, keeping both metabolism and detox processes in check.CES2 Related Signaling Pathway
The CES2-related signaling pathway is like a complex communication network within the liver, where CES2 (carboxylesterase 2) plays a crucial role. This pathway is involved in how the liver processes and breaks down fats and drugs. When CES2 is doing its job right, it helps the liver efficiently metabolize triglycerides and detoxify various substances, keeping liver function smooth. However, if something goes wrong—if CES2 levels drop, for example—this pathway can be disrupted, leading to issues like fat accumulation in the liver, seen in conditions such as nonalcoholic fatty liver disease (NAFLD). Moreover, CES2 influences pathways linked to stress responses in cells; if not managed well, this can tip the balance towards liver damage and metabolic disorders. Understanding CES2's place in these signaling pathways is key for potential therapies that target liver diseases, aiming to restore balance and health in this vital organ.CES2 Related Diseases
CES2, known as carboxylesterase 2, is connected to a range of health problems, particularly in the liver. When CES2 isn't working properly, the liver has a tough time breaking down fats. This can result in fat build-up and lead to nonalcoholic fatty liver disease (NAFLD). CES2 is also linked to nonalcoholic steatohepatitis (NASH), which is a more severe liver issue. Beyond the liver, CES2 is crucial in processing medications. If it's not working well, it might affect how effectively the body can handle different drugs. If CES2 isn't doing its job, it might lead to drugs not working well or causing bad reactions. Changes in CES2 activity have also been seen in conditions like diabetes, where fat management is key. Getting a handle on how CES2 affects these diseases is crucial for finding better treatment paths and understanding metabolic health.Bioapplications of CES2
CES2, or carboxylesterase 2, is paving the way for new uses in biotech and medicine. In drug development, CES2 helps break down medications in the liver, so understanding it can lead to better drugs and more personalized dosages, reducing side effects. Its role in fat metabolism makes it a key player in tackling liver issues like nonalcoholic fatty liver disease (NAFLD) and nonalcoholic steatohepatitis (NASH). By tweaking CES2 activity, we might boost liver health and manage these metabolic problems. In cancer treatment, CES2 might enhance the effectiveness of certain chemotherapy drugs, making it a useful tool in fighting cancer. Overall, CES2 holds potential for improving health outcomes and creating more personalized treatment options.Case Study
Case Study 1: Chen Y. et al. Proc Mol Metab. 2022
In pancreatic ductal adenocarcinoma (PDAC), the serine hydrolase carboxylesterase 2 (CES2) plays a role in activating the drug irinotecan. The researchers are looking into how CES2 affects tumor growth. Using data from The Cancer Genome Atlas, they found that high CES2 mRNA levels in tumors are linked to lower survival rates in PDAC patients. In lab tests and with a mouse model, reducing CES2 made cancer cells less viable and slowed tumor growth. CES2 promotes phospholipid breakdown, activating HNF4α through a pathway involving soluble epoxide hydrolase (sEH). Blocking CES2 with siRNA or inhibitors decreased HNF4α levels and shifted gene expression, lowering cell viability.-
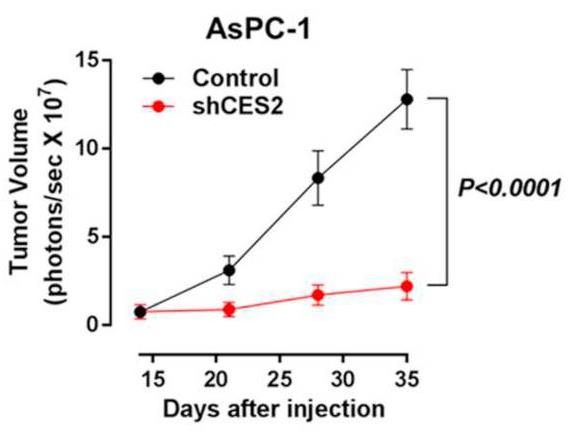 Fig1. The growth of AsPC-1 cells expressing high (control) or low (shCES2) level of CES2 in nude mice was monitored every week.
Fig1. The growth of AsPC-1 cells expressing high (control) or low (shCES2) level of CES2 in nude mice was monitored every week. -
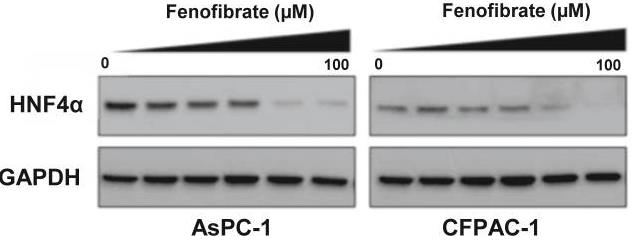 Fig2. Western blots for HNF4α in AsPC-1 and CFPAC-1 cells treated with variable concentrations of CES2 inhibitor fenofibrate for 48 h.
Fig2. Western blots for HNF4α in AsPC-1 and CFPAC-1 cells treated with variable concentrations of CES2 inhibitor fenofibrate for 48 h.
Case Study 2: Li Y. et al. Hepatology. 2016
Nonalcoholic fatty liver disease (NAFLD) can start with just extra fat in the liver and advance to a more severe condition called NASH. The reasons behind this progression aren't fully known yet. The research showed that in cases like NASH, as well as in diabetic and high-fat diet mice, the level of hepatic carboxylesterase 2 (CES2) drops significantly. Restoring CES2 improved liver fat and insulin resistance, while reducing it caused liver problems. CES2 helps break down triglycerides, enhancing fat burning and reducing fat creation. Without CES2, fat production increases due to endoplasmic reticulum stress, involving SREBP-1. Hepatocyte nuclear factor 4 alpha (HNF-4α) plays a crucial role in controlling CES2 in diabetes, obesity, or NASH.-
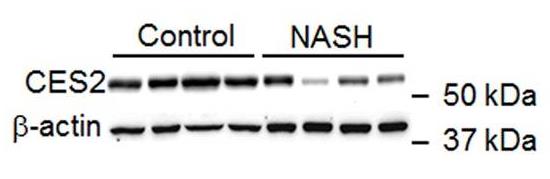 Fig3. Hepatic protein level in NASH patients (left panel) and relative CES2 protein level.
Fig3. Hepatic protein level in NASH patients (left panel) and relative CES2 protein level. -
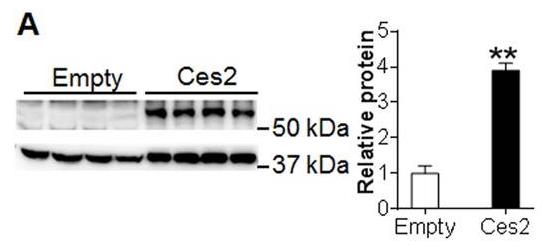 Fig4. Hepatic protein levels (left panel) and relative CES2 protein level.
Fig4. Hepatic protein levels (left panel) and relative CES2 protein level.
Quality Guarantee
High Purity
-
.jpg) Fig1. SDS-PAGE (CES2-749H)
Fig1. SDS-PAGE (CES2-749H) -
.jpg) Fig2. SDS-PAGE (CES2-1149H)
Fig2. SDS-PAGE (CES2-1149H)
Involved Pathway
CES2 involved in several pathways and played different roles in them. We selected most pathways CES2 participated on our site, such as Drug metabolism - other enzymes, which may be useful for your reference. Also, other proteins which involved in the same pathway with CES2 were listed below. Creative BioMart supplied nearly all the proteins listed, you can search them on our site.
| Pathway Name | Pathway Related Protein |
|---|---|
| Drug metabolism - other enzymes | XDH,TPMT.1,UGT2A3,TPMT,TYMP,Nat3,UCK1,NAT1,UGT1A2,PNAT10 |
-
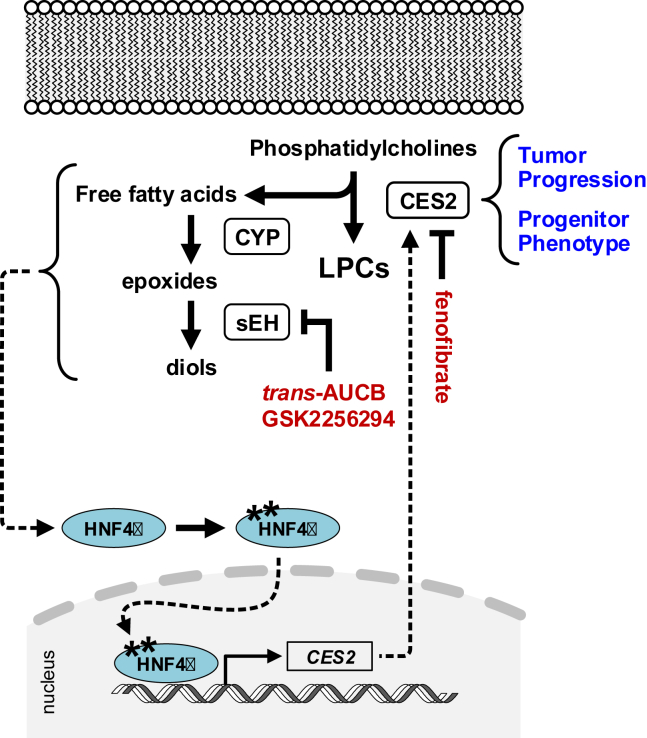 Fig1. Diagram of reciprocal regulation between CES2 and HNF4α. (Yihui Chen, 2022)
Fig1. Diagram of reciprocal regulation between CES2 and HNF4α. (Yihui Chen, 2022) -
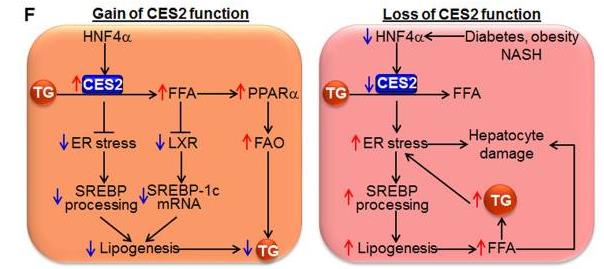 Fig2. A central role for hepatic CES2 in regulating TG homeostasis. CES2 is a TG hydrolase and is regulated by HNF4α. (Jung Gi Kim, 2021)
Fig2. A central role for hepatic CES2 in regulating TG homeostasis. CES2 is a TG hydrolase and is regulated by HNF4α. (Jung Gi Kim, 2021)
Protein Function
CES2 has several biochemical functions, for example, carboxylic ester hydrolase activity,methylumbelliferyl-acetate deacetylase activity. Some of the functions are cooperated with other proteins, some of the functions could acted by CES2 itself. We selected most functions CES2 had, and list some proteins which have the same functions with CES2. You can find most of the proteins on our site.
| Function | Related Protein |
|---|---|
| carboxylic ester hydrolase activity | CES1C,ABHD2A,NCEH1A,ACOT8,ACOT7,LIPCA,NOTUM1A,AADACL4,LYPLA2,PNPLA7 |
| methylumbelliferyl-acetate deacetylase activity | CES1,ESD |
Interacting Protein
CES2 has direct interactions with proteins and molecules. Those interactions were detected by several methods such as yeast two hybrid, co-IP, pull-down and so on. We selected proteins and molecules interacted with CES2 here. Most of them are supplied by our site. Hope this information will be useful for your research of CES2.
ispH;1-phosphatidyl-1d-myo-inositol 4,5-bisphosphate
Resources
Related Services
Related Products
References


