Cd99
-
Official Full Name
CD99 molecule -
Overview
CD99, or MIC2 gene product, or E2 antigen is expressed on the cell membrane of some lymphocytes, cortical thymocytes, and granulosa cells of the ovary. The antigen is also expressed by most pancreatic islet cells, Sertoli cells of the testis, and some endothelial cells. Mature granulocytes express very little or no CD99. MIC2 is strongly expressed on Ewing’s sarcoma cells and primitive peripheral neuroectodermal tumors. -
Synonyms
CD99;CD99 molecule;antigen identified by monoclonal antibodies 12E7, F21 and O13 , CD99 antigen , MIC2;CD99 antigen;E2 antigen;surface antigen MIC2;T-cell surface glycoprotein E2;MIC2 (monoclonal 12E7);antigen identified by monoclonal 12E7, Y homolog;antigen identified by monoclonal antibodies 12E7, F21 and O13;MIC2;HBA71;MIC2X;MIC2Y;MSK5X
Recombinant Proteins
- Human
- Mouse
- Chicken
- Zebrafish
- Rat
- HEK293
- E.coli
- Mammalian Cells
- Human Cells
- Wheat Germ
- Human
- HeLa
- In Vitro Cell Free System
- Fc
- GST
- His
- Non
- T7
- Avi
- DDK
- Myc
- SUMO
- rFc
- Flag
Background
What is CD99 Protein?
CD99 protein is this cool thing on the surface of our cells. It’s like a little handle that helps cells stick together and talk to each other. It’s super important for stuff like healing and keeping our immune system working right. But it also gets a lot of attention from researchers because it can act funny in diseases like cancer. They’re always trying to figure out how to use it to make better treatments. It’s pretty amazing how something so small can do so much!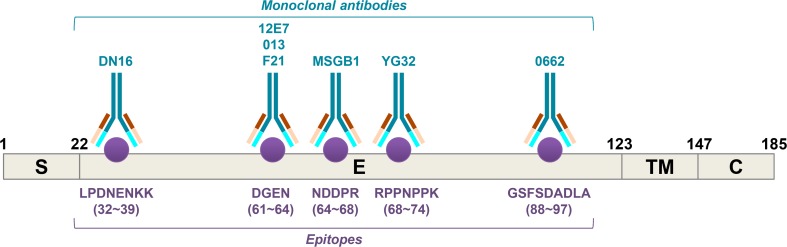
Fig1. Schematic representation of the CD99 protein (S: signal sequence
What is the Function of CD99 Protein?
CD99 is a protein you can spot on several cell types, notably on immune cells. It plays a vital role in how cells move and traverse through blood vessel walls, which is crucial for an effective immune reaction. This ability allows immune cells to quickly reach infection or injury sites. Additionally, CD99 is instrumental in the development of T-cells, which are essential for maintaining a strong immune defense. Interestingly, when it comes to cancer, CD99 can have a dual nature-it might either promote or inhibit tumor growth, and this largely depends on the cellular environment. This intriguing behavior makes CD99 a significant area of focus in cancer research. In essence, CD99 is key not only to normal physiological processes but also to our understanding of various disease mechanisms.CD99 Related Signaling Pathway
The CD99 signaling pathway is interesting because it plays numerous roles in how cells function. When CD99 is activated, it teams up with other molecules to set off a series of reactions inside the cell, involving pathways like ERK and SRC that are key to cell growth, movement, and survival. What's particularly intriguing is how CD99 can produce different results depending on the situation. In immune responses, CD99 aids T-cells and other immune cells in crossing blood vessel walls to reach areas where they're needed, boosting the body's defense against infections. In cancer, CD99's role can either help cancer cells spread or enhance the ability of T-cells to attack tumors. This dual potential makes understanding CD99 signaling crucial for developing new therapies for immune-related conditions and cancer treatments.CD99 Related Diseases
CD99 is connected to various diseases, making it a key point of interest in medical research. In the realm of cancer, CD99 can have a dual impact—it might either promote or inhibit tumor growth based on the cancer's type and environment. For instance, in Ewing's sarcoma, a bone cancer, CD99 is often found in high levels, prompting researchers to look into it as a therapeutic target. In autoimmune diseases, where the immune system wrongly attacks the body, CD99 influences the behavior of immune cells, potentially worsening the condition. Additionally, CD99 plays a part in inflammatory diseases by affecting how immune cells move, which can change the inflammation's intensity. Because it is involved in several signaling pathways, CD99 could be targeted for new treatments in conditions where cell movement and signaling go off track. By understanding CD99's diverse functions in these diseases, there's potential for developing innovative therapies that improve the management of these complex health issues.Bioapplications of CD99
CD99 shows a lot of potential in various biological applications due to its diverse roles in how cells behave. In medicine, CD99 is being looked at as a target for new cancer treatments, particularly in cancers like Ewing's sarcoma where it is often found in high amounts. By impacting cell movement and sticking, scientists are figuring out ways to alter these processes to stop tumors from growing or spreading. In the field of immunotherapy, because CD99 affects how immune cells move and activate, it could be used to strengthen the body's ability to fight off diseases and cancer. When it comes to diagnostics, CD99 could act as a marker to signal certain diseases, aiding in early disease detection and tracking treatment success. With ongoing research, CD99 might also play a role in tissue engineering and regenerative medicine by influencing cell behavior to enhance tissue repair and healing. Overall, the wide range of uses for CD99 highlights its potential in pushing forward new advances in treatment and diagnosis.Case Study
Case Study 1: Jodeleit H. et al. PLoS One. 2020
A comprehensive study on autoantibodies in ulcerative colitis (UC) has pinpointed CD99 as a key marker distinguishing UC patients. By analyzing samples from 49 patients, researchers found several indicators tied to disease activity. Autoantibodies, present even before diagnosis, appear linked to inflammation. Lab tests showed that exposure to CD99 can worsen symptoms and increase specific antibodies in a mouse model, suggesting that these autoantibodies are crucial for recognizing and understanding UC.-
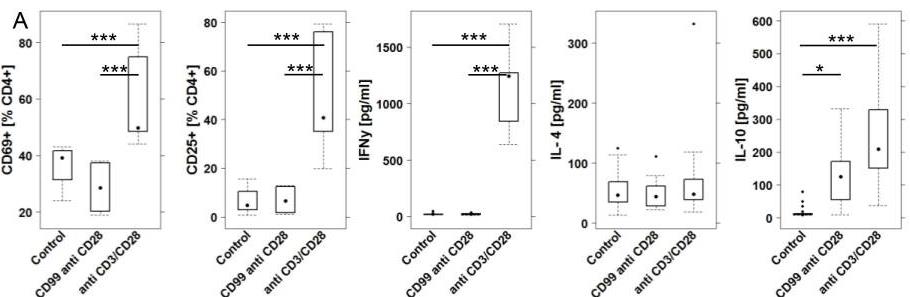 Fig1. CD99 elicits an anti-inflammatory response in vitro.
Fig1. CD99 elicits an anti-inflammatory response in vitro. -
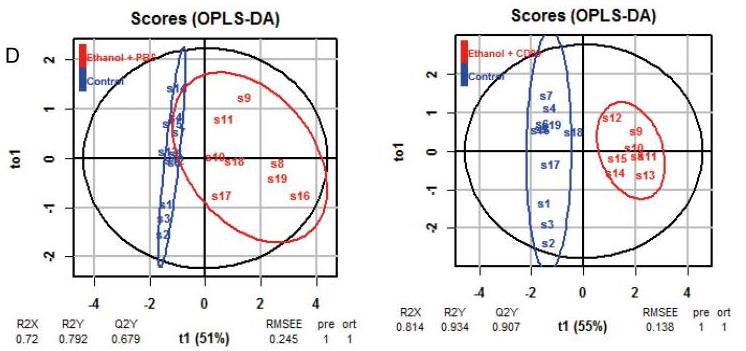 Fig2. oPLS-DA analysis of control versus the ethanol + PBS and control versus ethanol + CD99.
Fig2. oPLS-DA analysis of control versus the ethanol + PBS and control versus ethanol + CD99.
Case Study 2: Vaikari VP. et al. Haematologica. 2020
In acute myeloid leukemia (AML), the CD99 gene is often overactive, especially in cases with FLT3-ITD mutations. CD99 aids in cell movement and immune function and comes in two forms. The long form initially boosts cell growth but later leads to cell damage and death. In mice, this form slows leukemia spread. A CD99 antibody reduces leukemia cell survival and encourages cell death. The long form also temporarily boosts then decreases ERK and SRC activity, impacting disease progression.-
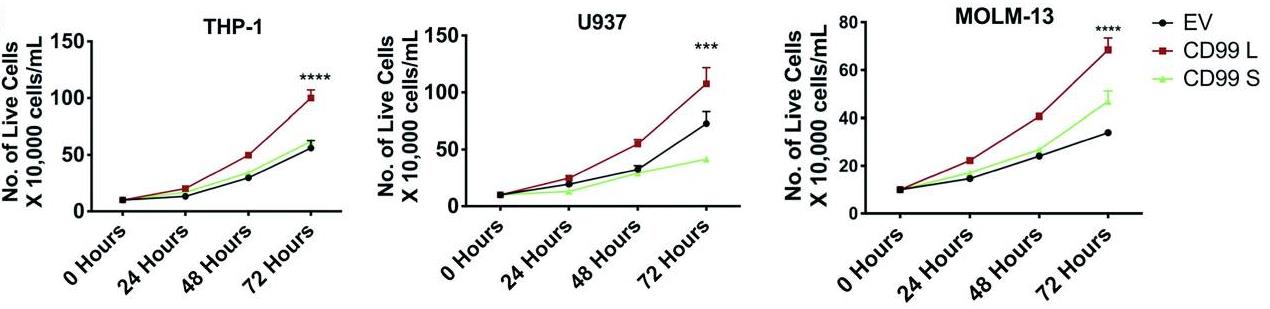 Fig3. Proliferation assay of EV, CD99-L and CD99-S measured at 24,48 and 72 h.
Fig3. Proliferation assay of EV, CD99-L and CD99-S measured at 24,48 and 72 h. -
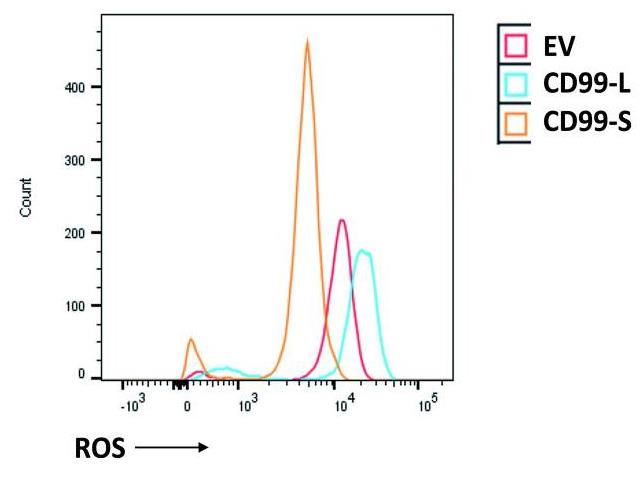 Fig4. ROS levels of EV, CD99-L and CD99-S cells determine by flow cytometry using the cell ROX reagent in THP-1 cells.
Fig4. ROS levels of EV, CD99-L and CD99-S cells determine by flow cytometry using the cell ROX reagent in THP-1 cells.
Quality Guarantee
High Purity
-
.jpg) Fig1. SDS-PAGE (CD99-473H)
Fig1. SDS-PAGE (CD99-473H) -
.jpg) Fig2. SDS-PAGE (CD99-6941H)
Fig2. SDS-PAGE (CD99-6941H)
Involved Pathway
Cd99 involved in several pathways and played different roles in them. We selected most pathways Cd99 participated on our site, such as Cell adhesion molecules (CAMs),Leukocyte transendothelial migration, which may be useful for your reference. Also, other proteins which involved in the same pathway with Cd99 were listed below. Creative BioMart supplied nearly all the proteins listed, you can search them on our site.
| Pathway Name | Pathway Related Protein |
|---|---|
| Cell adhesion molecules (CAMs) | CLDN10A,CLDN18,CNTN1,CLDNE,LRRC4B,CD8B,HLA-B,CLDN17,CLDNH,PVRL3 |
| Leukocyte transendothelial migration | MSN,CYBB,ARHGAP35,ITGAM,NIPAL1,GNAI3,MAPK12,CLDN17,PLCG2,ACTN4 |
-
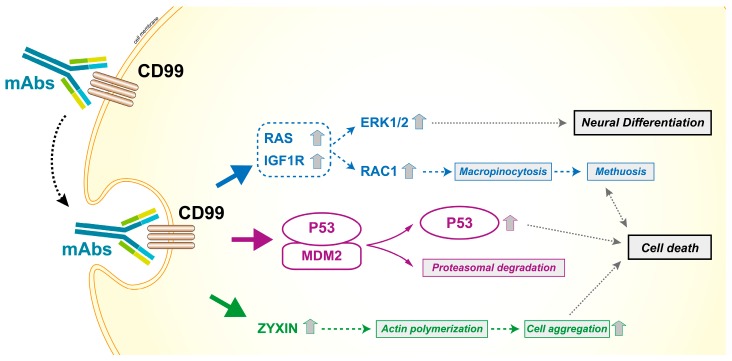 Fig1. Effects of CD99 triggering by antibodies in Ewing sarcoma cells. (Maria Cristina Manara, 2018)
Fig1. Effects of CD99 triggering by antibodies in Ewing sarcoma cells. (Maria Cristina Manara, 2018) -
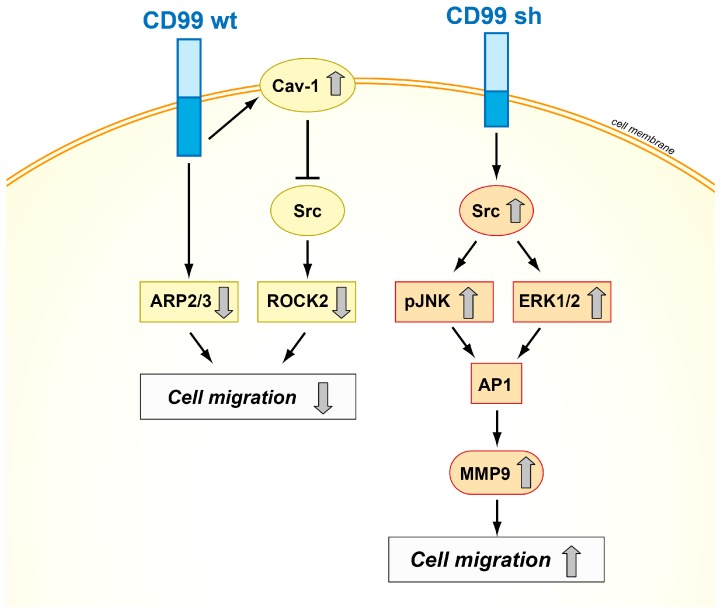 Fig2. Schematic representation of the mechanisms of action of CD99wt and CD99sh in tumor cells. (Maria Cristina Manara, 2018)
Fig2. Schematic representation of the mechanisms of action of CD99wt and CD99sh in tumor cells. (Maria Cristina Manara, 2018)
Protein Function
Cd99 has several biochemical functions, for example, . Some of the functions are cooperated with other proteins, some of the functions could acted by Cd99 itself. We selected most functions Cd99 had, and list some proteins which have the same functions with Cd99. You can find most of the proteins on our site.
| Function | Related Protein |
|---|
Interacting Protein
Cd99 has direct interactions with proteins and molecules. Those interactions were detected by several methods such as yeast two hybrid, co-IP, pull-down and so on. We selected proteins and molecules interacted with Cd99 here. Most of them are supplied by our site. Hope this information will be useful for your research of Cd99.
SGTA;UBQLN4;UBQLN1;q9wmx2-pro_0000037550
Resources
Research Area
Related Services
Related Products
References
- Shibuya, R; Matsuyama, A; et al. The combination of CD99 and NKX2.2, a transcriptional target of EWSR1-FLI1, is highly specific for the diagnosis of Ewing sarcoma. VIRCHOWS ARCHIV 465:599-605(2014).
- Urias, U; Marie, SKN; et al. CD99 is upregulated in placenta and astrocytomas with a differential subcellular distribution according to the malignancy stage. JOURNAL OF NEURO-ONCOLOGY 119:59-70(2014).




