ALDH1A1
-
Official Full Name
aldehyde dehydrogenase 1 family, member A1 -
Overview
The protein encoded by this gene belongs to the aldehyde dehydrogenase family. Aldehyde dehydrogenase is the next enzyme after alcohol dehydrogenase in the major pathway of alcohol metabolism. There are two major aldehyde dehydrogenase isozymes in the liver, cytosolic and mitochondrial, which are encoded by distinct genes, and can be distinguished by their electrophoretic mobility, kinetic properties, and subcellular localization. This gene encodes the cytosolic isozyme. Studies in mice show that through its role in retinol metabolism, this gene may also be involved in the regulation of the metabolic responses to high-fat diet. [provided by RefSeq, Mar 2011] -
Synonyms
ALDH1A1;aldehyde dehydrogenase 1 family, member A1;ALDC;ALDH1;HEL-9;HEL12;PUMB1;ALDH11;RALDH1;ALDH-E1;HEL-S-53e;retinal dehydrogenase 1;ALHDII;RALDH 1;ALDH class 1;acetaldehyde dehydrogenase 1;epididymis luminal protein 9;epididymis luminal protein 12;retinaldehyde dehydrogenase 1;aldehyde dehydrogenase 1, soluble;aldehyde dehydrogenase, liver cytosolic;epididymis secretory sperm binding protein Li 53e
Recombinant Proteins
- Human
- Mouse
- Chicken
- Rat
- Bovine
- E.coli
- Mammalian Cells
- Wheat Germ
- HEK293
- In Vitro Cell Free System
- Yeast
- Rabbit
- His
- GST
- T7
- Non
- Flag
- Avi
- Fc
- DDK
- Myc
Background
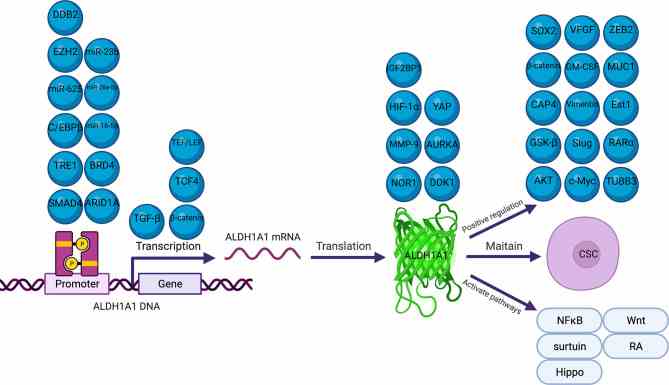
Fig1. Molecules Involved in the Regulation of ALDH1A1. (Hanxun Yue, 2022)
What is ALDH1A1 Protein?
ALDH1A1 belongs to the family of aldehyde dehydrogenases that activate when alcohol has been digested by alcohol dehydrogenase. This protein will usually be at work in the liver. You've got two incarnations: one floating in the cell's cytosol and one freezing in the mitochondria, which both hail from different genes. Apart from alcohol metabolism, ALDH1A1 also converts retinol to retinoic acid, an essential compound for several bodily processes. ALDH1A1 may also be a target for certain stem cells that are affected by cancers, such as breast cancer, although exactly what it does there is not yet known. So basically it's a part of what breakdowns and controls cells.
What is the Function of ALDH1A1 Protein?
ALDH1A1 (aldehyde dehydrogenase 1 family member A1) is the protein that is sulking in your liver and elsewhere to do its big dirty laundry. Think of it as your body's decontamination team that kicks in after alcohol dehydrogenase has scrubbed away alcohol. The ALDH1A1 works to convert the aldehydes, not so friendly if they're uncontrolled, into acids such as acetate, which are. Not only does ALDH1A1 degrade alcohol, it also participates in the synthesis of retinoic acid, which is necessary for eyesight and skin. They are also examining it in cancer research because it might have something to do with how some cancer cells grow and attack drugs.
ALDH1A1 Related Signaling Pathway
ALDH1A1 is a part of various cellular pathways, including those involved in glycine degradation and other amino acid metabolic processes. While it may not be directly listed under a singular signaling pathway like some other proteins, its role is often associated with its enzymatic activity in metabolizing aldehydes into acids. This activity is essential in processes like detoxification and cellular response to oxidative stress. The protein's function is crucial in retinoic acid biosynthesis, which has downstream effects on gene expression and development. In terms of signaling, it can influence pathways indirectly by modulating the availability of signaling molecules through its metabolic functions.
ALDH1A1 Related Diseases
ALDH1A1 is part of the aldehyde dehydrogenase family, crucial for alcohol metabolism after it's been initially processed by another enzyme. Found mainly in the liver, it exists in cytosolic and mitochondrial forms. It's also linked to various conditions, including unique responses to alcohol due to genetic variations. ALDH1A1 has a strong association with certain cancer types, where its activity can mark the presence of tumor-initiating cells (TICs), notably in breast cancer. Beyond alcohol processing, it plays a role in metabolic pathways, impacting things like fat response to a high-fat diet, and is also in a pathway that relates to dopamine neurons, which could even tie to behaviors linked to alcohol consumption.
Bioapplications of ALDH1A1
Recombinant ALDH1A1 protein finds its place mostly in research and industrial settings because of its vital role in catalysis and detoxification processes. In the lab, researchers use it to study its function in breaking down aldehydes, which are reactive compounds in the body. This protein is key for investigating metabolic processes and how they relate to diseases like cancer. It also has potential applications in developing drugs or therapies that target aldehyde metabolism. In industries, it can be a part of manufacturing processes where biochemical reactions need regulation or enhancement, making it a versatile tool in both experimental and applied sciences.
Case Study
Case Study 1: Cuicui Liu, 2021
TICs, or tumor-initiating cells, are the troublemakers that get tumors going, keep them growing, help them spread, and cause them to return. In various cancers such as breast cancer, the enzyme ALDH1A1 acts as a TIC marker. However, its role in these solid tumors is still mostly unclear. This research showed that ALDH1A1 aids breast tumor growth by dropping the pH level inside the cancer cells. This change kickstarts TAK1 phosphorylation, fires up the NFκB pathway, and boosts GM-CSF secretion. This secretion encourages immune-suppressing myeloid-derived suppressor cells to grow. Interestingly, blocking ALDH1A1 with disulfiram, combined with the cancer drug gemcitabine, managed to shrink breast tumors. This combo works by targeting ALDH+ TICs and ramping up T-cell activity. These insights show how ALDH1A1 affects the immune system to aid tumor growth and suggest new ways to tackle aggressive breast cancer.
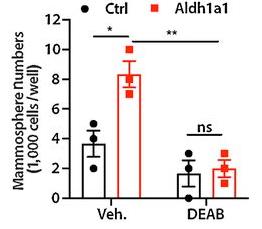
Fig1. DEAB treatment more remarkedly reduced the self-renewal ability of Aldh1a1 in 4T1 cells.
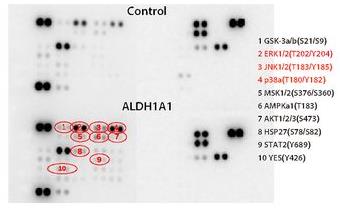
Fig2. Phosphokinases were detected with cell lysates collected from both ALDH1A1 and control MDA-MB-231 cells utilizing Human Phospho-Kinase Array.
Case Study 2: Mingyuan Wang, 2024
The main hurdle for immunotherapy is how tumors manage to dodge the immune system, leading to less than stellar success rates. Although we know this, the exact mechanics are still fuzzy. In our research with patient tissue samples, we pinpointed ALDH1A1 as crucial for cancer prognosis and tumor glycolysis. Lab tests and studies in mice showed that hitting ALDH1A1 can slow down tumor growth. Delving deeper with mouse models, it turned out that lacking ALDH1A1 boosts the immune system's ability to tackle tumors. RNA-seq, qPCR, and western blots pointed to ZBTB7B as a key player downstream of ALDH1A1, influencing the glycolysis gene LDHA. Plus, enhancing SUMOylation kept ZBTB7B stable. Both in vivo and in vitro experiments showed that combining ALDH1A1 and ZBTB7B targeting with immune checkpoint inhibitors can powerfully halt tumors. Finally, checking patient tissues confirmed the potential for targeting ALDH1A1 and ZBTB7B in cancer immunotherapy.
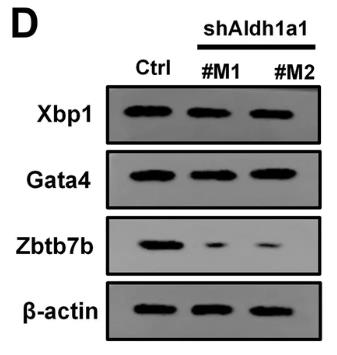
Fig3. In CT26 cells, candidate genes with significant differences in qPCR were verified by western blot of shAldh1a1.
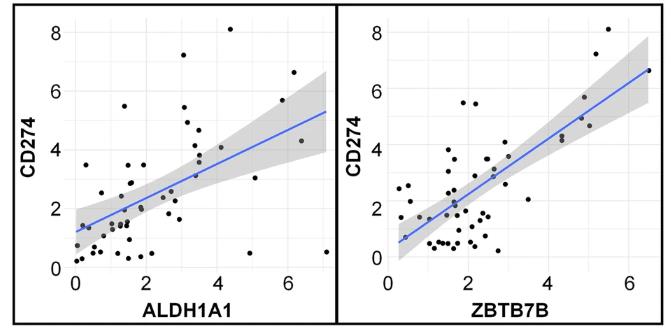
Fig4. Scatterplot of the correlation of ALDH1A1 and CD274 expression and the correlation of ZBTB7B and CD274 expression.
Quality Guarantee
High Purity
.jpg)
Fig1. SDS-PAGE (ALDH1A1-01H)
.
.jpg)
Fig2. SDS-PAGE (ALDH1A1-437H)
Involved Pathway
ALDH1A1 involved in several pathways and played different roles in them. We selected most pathways ALDH1A1 participated on our site, such as Retinol metabolism,Metabolic pathways, which may be useful for your reference. Also, other proteins which involved in the same pathway with ALDH1A1 were listed below. Creative BioMart supplied nearly all the proteins listed, you can search them on our site.
| Pathway Name | Pathway Related Protein |
|---|---|
| Metabolic pathways | CYP51A1,UPP2,C1GALT1,PNLIPRP3,LPIN1,CTPS1A,CPS1,CYP19A1,SAT1A.2,MTR |
| Retinol metabolism | RDH12,CYP2C70,UGT1A6B,CYP2C37,CYP3A41B,CYP2C54,BCO1,UGT2A3,CYP2C39,RDH11 |
Protein Function
ALDH1A1 has several biochemical functions, for example, 3-chloroallyl aldehyde dehydrogenase activity,GTPase activator activity,aldehyde dehydrogenase (NAD) activity. Some of the functions are cooperated with other proteins, some of the functions could acted by ALDH1A1 itself. We selected most functions ALDH1A1 had, and list some proteins which have the same functions with ALDH1A1. You can find most of the proteins on our site.
| Function | Related Protein |
|---|---|
| GTPase activator activity | RIN3,ADAP2,ARHGAP42,PGAM5,TBC1D22B,RAP1GAP2B,FAM13B,TBC1D30,ARHGAP12,ELMOD2 |
| benzaldehyde dehydrogenase (NAD+) activity | Aldh1a7,ALDH3A1 |
| androgen binding | SHBG,TSPO,Ar |
| aldehyde dehydrogenase (NAD) activity | ALDH8A1,ALDH3B2,ALDH1L2,ALDH1L1,Aldh1a7,ALDH1A3,ALDH6A1,ALDH3A2B,ALDH3A1,ALDH4A1 |
| retinal dehydrogenase activity | ALDH8A1,AKR1C3,AKR1C4,AKR1B8,AKR1B10,AKR1C6,Aldh1a7,ALDH1A3 |
| 3-chloroallyl aldehyde dehydrogenase activity | ALDH9A1,ALDH3A2A,ALDH3B1,ALDH3B2,Aldh1a7,ALDH3A1,ALDH2.1,ALDH3A2,ALDH3A2B |
Interacting Protein
ALDH1A1 has direct interactions with proteins and molecules. Those interactions were detected by several methods such as yeast two hybrid, co-IP, pull-down and so on. We selected proteins and molecules interacted with ALDH1A1 here. Most of them are supplied by our site. Hope this information will be useful for your research of ALDH1A1.
ALDH2;NUPR1;q5nfd5_fratt;ligA;lplJ;POT1
Resources
Research Area
Hematopoietic Stem Cell MarkersColon Cancer Stem Cell Markers
Head and Neck Cancer Stem Cell Markers
Lung Cancer Stem Cell Markers
Prostate Cancer Stem Cell Markers
Bladder Cancer Stem Cell Markers
Breast Cancer Stem Cell Markers
Glioma/Medulloblastoma Cancer Stem Cell Markers
Pancreatic Cancer Stem Cell Markers
Related Services
Related Products
References
- Thomas, AG; Henry, JJ; et al. Retinoic acid regulation by CYP26 in vertebrate lens regeneration. DEVELOPMENTAL BIOLOGY 386:291-301(2014).
- Liu, Y; Lv, DL; et al. ALDH1A1 expression correlates with clinicopathologic features and poor prognosis of breast cancer patients: a systematic review and meta-analysis. BMC CANCER 14:-(2014).


