XRCC1
-
Official Full Name
X-ray repair complementing defective repair in Chinese hamster cells 1 -
Overview
The X-ray repair cross complementing protein 1 (XRCC1) is a DNA repair protein important in both single strand break repair and base excision repair following damage from ionizing radiation and alkylating agents. XRCC1 acts as a scaffold protein to coordi -
Synonyms
XRCC1;X-ray repair complementing defective repair in Chinese hamster cells 1;RCC;DNA repair protein XRCC1;X-ray repair cross-complementing protein 1;X-ray-repair, complementing defective, repair in Chinese hamster
Recombinant Proteins
- Human
- Zebrafish
- Rat
- Mouse
- E.coli
- Mammalian Cell
- HEK293
- HEK293T
- Mammalian cells
- His
- Non
- Myc&DDK
- His&Fc&Avi
- Flag
Background
What is XRCC1 protein?
XRCC1 gene (X-ray repair cross complementing 1) is a protein coding gene which situated on the long arm of chromosome 19 at locus 19q13. The protein encoded by this gene is involved in the efficient repair of DNA single-strand breaks formed by exposure to ionizing radiation and alkylating agents. This protein interacts with DNA ligase III, polymerase beta and poly (ADP-ribose) polymerase to participate in the base excision repair pathway. It may play a role in DNA processing during meiogenesis and recombination in germ cells. A rare microsatellite polymorphism in this gene is associated with cancer in patients of varying radiosensitivity. The XRCC1 protein is consisted of 633 amino acids and XRCC1 molecular weight is approximately 69.5 kDa.
What is the function of XRCC1 protein?
XRCC1 is involved in several specialized functions within the DNA repair process:
It helps organize specific DNA repair functions by recruiting additional enzymes whose contributions are dependent on the details of the damaged site.
It has a bipartite nuclear localization signal (NLS) that supports its own nuclear localization as well as that of other XRCC1-binding repair proteins like LIG3 and APLF.
XRCC1 is involved in the base excision repair pathway by facilitating the transfer of DNA damage to more appropriate enzymes in the DNA repair pathway.
It interacts with PARP1, playing a critical role in preventing hereditary neurodegenerative diseases by protecting transcription from toxic PARP1 activity.
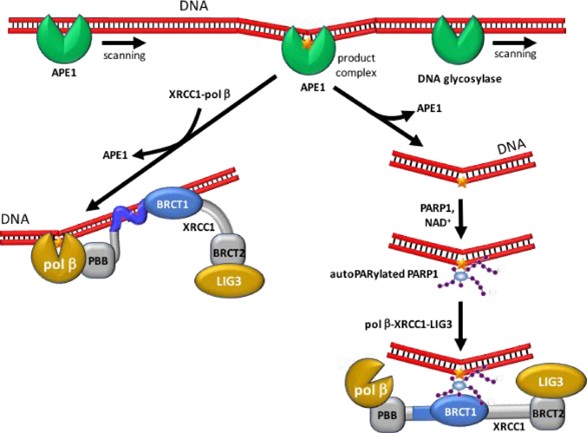
Fig1. MXRCC1 participates in BER by facilitating transfer of DNA damage. (Robert E London, 2020)
XRCC1 Related Signaling Pathway
XRCC1 plays a central role in base excision repair. As a molecular scaffold protein, XRCC1 interacts with a variety of enzyme components, including DNA polymerase β and DNA Ligase III (LIG3), to jointly accelerate the repair of DNA single strand breaks. XRCC1 is also involved in the repair of single strand breaks, responding to damage signals from PARP1 through its central region and supporting single strand break repair activities with long and short patches. XRCC1 contains a two-part nuclear localization signal (NLS), which supports not only the nuclear localization of XRCC1 itself, but also the nuclear localization of repair proteins that bind to it, such as LIG3 and APLF. XRCC1 also protects the transcriptional process from the toxic activity of PARP1, suggesting that it may be involved in regulating gene expression related to DNA damage response.
XRCC1 Related Diseases
The XRCC1 protein has been implicated in a variety of diseases, particularly those related to the repair of DNA damage. It plays a decisive role in cell proliferation, cancer occurrence and cancer treatment. Abnormal expression or loss of function of XRCC1 is associated with an increased risk of certain types of cancer, such as down-regulated XRCC1 expression in melanoma, glioma, renal cell carcinoma, bladder cancer, and stomach cancer, and up-regulated expression in ovarian cancer and head and neck squamous cell carcinoma. In addition, some polymorphisms of XRCC1 are associated with tumor chemotherapy sensitivity, radiotherapy efficacy and patient survival. XRCC1 has also been associated with neurodegenerative diseases such as spin cerebellar ataxia.
Bioapplications of XRCC1
Because of its central role in DNA repair, the XRCC1 protein has multiple potential applications, especially in the fields of cancer therapy and biomedical research. In cancer treatment, the expression level and functional status of XRCC1 can be used as biomarkers to predict a patient's response to certain chemotherapy drugs, contributing to the development of personalized medicine and precision treatment strategies. In addition, polymorphic studies of XRCC1 can help to understand the differences in response to treatment among different patient groups, so as to optimize treatment options. In biomedical research, XRCC1 serves as an important tool for studying DNA repair mechanisms, helping to reveal the molecular mechanisms involved in DNA damage and repair, driving a deeper understanding of cancer and other diseases associated with defective DNA damage repair.
Case Study
Case Study 1: Griffin M Wright, 2022
Dysregulation of DNA repair is a hallmark of cancer, though few cancer-specific mechanisms that drive the overexpression of DNA repair proteins are known. Researchers previously identified STAT3 as a novel transcriptional regulator of X-ray cross-complementing group 1 (XRCC1). They also identified an inducible response to IL-6 and epidermal growth factor stimulation in the non-tumorigenic embryonic kidney cell line HEK293T. As IL-6 and EGF signaling are growth and inflammatory-inducible responses, they examined if glucose challenge can increase STAT3 activation, promoting adaptive changes in XRCC1 expression in different cell types. Acute high glucose exposure promoted XRCC1 expression through STAT3 activation, increasing the repair of methyl methanesulfonate-induced DNA damage in HEK293T cells and the osteosarcoma cell line U2OS. Sustained exposure to high glucose promoted the overexpression of XRCC1, which can be reversed upon glucose restriction and down-regulation of STAT3 activation.

Fig1. XRCC1 protein expression in HEK293T normalized to control.
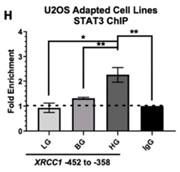
Fig2. ChIP analysis of STAT3 occupancy of the XRCC1 promoter.
Case Study 2: María José Peña-Gómez, 2022
Because very little is known about the toxicity of these cytosine analogues when they incorporate during replication. Here, researchers report a role of the base excision repair factor XRCC1 in protecting replication fork upon incorporation of 5-hydroxymethyl-2'-deoxycytosine (5hmC) and its deamination product 5-hydroxymethyl-2'-deoxyuridine (5hmU) during DNA synthesis. In the absence of XRCC1, 5hmC exposure leads to increased genomic instability, replication fork impairment and cell lethality. Moreover, the 5hmC deamination product 5hmU recapitulated the genomic instability phenotypes observed by 5hmC exposure, suggesting that 5hmU accounts for the observed by 5hmC exposure. Remarkably, 5hmC-dependent genomic instability and replication fork impairment seen in Xrcc1-/- cells were exacerbated by the trapping of Parp1 on chromatin, indicating that XRCC1 maintains replication fork stability during processing of 5hmC and 5hmU by the base excision repair pathway.

Fig3. Immunofluorescence showing the chromatin retention of HsXRCC1-RFP and EdU co-staining.

Fig4. Western blot of PARP1, histone H3 and tubulin levels.
Quality Guarantee
High Purity
.jpg)
Fig1. SDS-PAGE (XRCC1-778HFL)
.
.jpg)
Fig2. SDS-PAGE (XRCC1-6578H)
Involved Pathway
XRCC1 involved in several pathways and played different roles in them. We selected most pathways XRCC1 participated on our site, such as Base excision repair, which may be useful for your reference. Also, other proteins which involved in the same pathway with XRCC1 were listed below. Creative BioMart supplied nearly all the proteins listed, you can search them on our site.
| Pathway Name | Pathway Related Protein |
|---|---|
| Base excision repair | POLD4,APEX2,UNG,HMGB1B,xthA,POLD2,HMGB1A,NTHL1,POLD1,POLE3 |
Protein Function
XRCC1 has several biochemical functions, for example, damaged DNA binding,enzyme binding,protein binding. Some of the functions are cooperated with other proteins, some of the functions could acted by XRCC1 itself. We selected most functions XRCC1 had, and list some proteins which have the same functions with XRCC1. You can find most of the proteins on our site.
| Function | Related Protein |
|---|---|
| damaged DNA binding | RAD18,RBBP8,OGG1,HMGB1,RAD1,CRY2,UNG,RPA3,RAD23AB,TRP63 |
| protein binding | BIN2,TCHP,ATF4,ZEB1,SOCS5,NUAK2,PAGE1,EIF5B,TIMP1,TGS1 |
| enzyme binding | EHHADH,IL6R,UGT1A3,ATP6AP2,NOXO1,EGFR,CCDC99,CYB5A,PHKG1,LAMB1 |
Interacting Protein
XRCC1 has direct interactions with proteins and molecules. Those interactions were detected by several methods such as yeast two hybrid, co-IP, pull-down and so on. We selected proteins and molecules interacted with XRCC1 here. Most of them are supplied by our site. Hope this information will be useful for your research of XRCC1.
APTX;PNKP
Resources
Related Services
Related Products
References


