SMO
-
Official Full Name
smoothened, frizzled class receptor -
Overview
The protein encoded by this gene is a G protein-coupled receptor that interacts with the patched protein, a receptor for hedgehog proteins. The encoded protein tranduces signals to other proteins after activation by a hedgehog protein/patched protein complex. [provided by RefSeq, Jul 2010] -
Synonyms
SMO;smoothened, frizzled class receptor;Gx;SMOH;FZD11;smoothened homolog;protein Gx;frizzled family member 11;seven transmembrane helix receptor;smoothened, frizzled family receptor;smoothened, seven transmembrane spanning receptor
Recombinant Proteins
- Human
- Mouse
- Rat
- Zebrafish
- Chicken
- E.coli
- Mammalian Cells
- HEK293
- Wheat Germ
- In Vitro Cell Free System
- GST
- His
- DDK
- Myc
- Non
- Flag
- Avi
- Fc
| Cat.# | Product name | Source (Host) | Species | Tag | Protein Length | Price |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| SMO-2818H | Recombinant Human SMO, GST-tagged | E.coli | Human | GST | C-242aa | |
| SMO-2700H | Recombinant Human SMO protein, His-tagged | E.coli | Human | His | 28-233 aa | |
| SMO-15631M | Recombinant Mouse SMO Protein | Mammalian Cells | Mouse | His |
|
|
| SMO-1617HCL | Recombinant Human SMO overexpression lysate | HEK293 | Human | DDK&Myc |
|
|
| SMO-31421TH | Recombinant Human SMO | Wheat Germ | Human | Non | 100 amino acids |
|
| SMO-31422TH | Recombinant Human SMO | Wheat Germ | Human | Non | 135 amino acids |
|
| SMO-31423TH | Recombinant Human SMO | Wheat Germ | Human | Non | 59 amino acids |
|
| SMO-536H | Recombinant Human SMO | Mammalian Cells | Human | His |
|
|
| SMO-5623R | Recombinant Rat SMO Protein | Mammalian Cells | Rat | His |
|
|
| SMO-8656Z | Recombinant Zebrafish SMO | Mammalian Cells | Zebrafish | His |
|
|
| RFL16147HF | Recombinant Full Length Human Smoothened Homolog(Smo) Protein, His-Tagged | E.coli | Human | His | Full L. Full Length of Mature Protein (28-787) |
|
| RFL18969RF | Recombinant Full Length Rat Smoothened Homolog(Smo) Protein, His-Tagged | E.coli | Rat | His | Full L. Full Length (31-793) |
|
| RFL28574MF | Recombinant Full Length Mouse Smoothened Homolog(Smo) Protein, His-Tagged | E.coli | Mouse | His | Full L. Full Length of Mature Protein (33-793) |
|
| RFL4256GF | Recombinant Full Length Chicken Smoothened Homolog(Smo) Protein, His-Tagged | E.coli | Chicken | His | Full L. Full Length of Mature Protein (16-794) |
|
| SMO-1110HFL | Recombinant Human SMO protein, His&Flag-tagged | HEK293 | Human | Flag&His | 1-787 aa |
|
| Smo-2084M | Recombinant Mouse Smo Protein, His-tagged | E.coli | Mouse | His | Ala33-Ile238 |
|
| SMO-2707H | Recombinant Human SMO Protein, His-tagged | E.coli | Human | His | Ala30-Ile234 |
|
| SMO-28H | Recombinant Human SMO Protein | Wheat Germ | Human | Non |
|
|
| SMO-314H | Active Recombinant Human SMO Full Length Transmembrane protein(VLPs) | HEK293 | Human | Non | Full L. Arg 28 - Phe 787 |
|
| SMO-4097H | Recombinant Human SMO Protein, His (Fc)-Avi-tagged | HEK293 | Human | Avi&Fc&His |
|
|
| SMO-4097H-B | Recombinant Human SMO Protein Pre-coupled Magnetic Beads | HEK293 | Human |
|
||
| SMO-5282R | Recombinant Rat SMO Protein, His (Fc)-Avi-tagged | HEK293 | Rat | Avi&Fc&His |
|
|
| SMO-5282R-B | Recombinant Rat SMO Protein Pre-coupled Magnetic Beads | HEK293 | Rat |
|
||
| SMO-6317H | Recombinant Human SMO Protein (Ser32-Tyr233), N-His tagged | E.coli | Human | His | Ser32-Tyr233 |
|
| SMO-6780HF | Recombinant Full Length Human SMO Protein | In Vitro Cell Free System | Human | Full L. 404 amino acids |
|
|
| SMO-8486M | Recombinant Mouse SMO Protein, His (Fc)-Avi-tagged | HEK293 | Mouse | Avi&Fc&His |
|
|
| SMO-8486M-B | Recombinant Mouse SMO Protein Pre-coupled Magnetic Beads | HEK293 | Mouse |
|
Background
What is SMO protein?
SMO gene (smoothened, frizzled class receptor) is a protein coding gene which situated on the long arm of chromosome 7 at locus 7q32. SMO protein is a G protein-coupled receptor that plays a crucial role in the Hedgehog signaling pathway. It interacts with the Patched protein, which is a receptor for Hedgehog proteins. Upon activation by a Hedgehog protein/Patched protein complex, the Smoothened protein transduces signals to other proteins, thereby influencing various cellular processes. The SMO protein is involved in the maintenance of tissue homeostasis and is crucial in embryonic development, regulating cellular differentiation by binding to sterol and Wnt ligands. It is also expressed in various tissues throughout the body, particularly in cerebellar and pituitary tissue. Abnormalities in the Hedgehog signaling pathway, which includes SMO, can lead to severe birth defects and are implicated in the pathogenesis of certain cancers, such as pediatric medulloblastoma and basal cell carcinoma. The SMO protein is consisted of 787 amino acids and SMO molecular weight is approximately 86.4 kDa.
What is the function of SMO protein?
It is known for its role in transducing signals generated when ligands of the hedgehog family bind to their immediate target, patched (PTCH1). This binding releases the inhibition that PTCH1 exerts on SMO, activating the receptor and initiating the downstream signaling events of the Hh pathway. The SMO protein contains an N-terminal extracellular segment with a cysteine-rich domain (CRD), a heptahelical transmembrane domain (TMD), and a C-terminal intracellular segment. In vertebrates, conventional SMO signaling functions in many differentiated cells and localizes to cilia, which are highly specialized surface organelles involved in developmental signaling. Beyond its role in cilia activity, SMO has also been found to be broadly localized to lipid rafts, which are regions of the cell membrane enriched in cholesterol and sphingolipids. Moreover, SMO is directly activated by oxysterols, and recent studies suggest that cholesterol, a component of lipid rafts, is the primary ligand of SMO.
SMO Related Signaling Pathway
SMO is the main signal transduction factor in the Hh signaling pathway. When Hh ligand (such as Sonic Hedgehog) binds to the PTCH1 receptor, the inhibition of PTCH1 on SMO is relieved. Activated SMO further transduces extracellular signals into the cell to activate transcription factors such as GLI. SMO also has cross-effects with the IGF1R signaling pathway, and SMO can enhance IGF1R-mediated AKT signaling independently of its function in the Hh signaling pathway. In addition to classical Hh signaling pathways, SMO may also be involved in atypical signaling pathways, such as direct activation of Oxysterols-mediated signaling that is independent of Hh ligands. As part of G protein-coupled receptors (GPCRS), SMO interacts chemically and functionally with Gi family proteins and is involved in regulating cell differentiation and embryogenesis.

Fig1. Schematic overview of SMO-SHH signaling pathway. (Saloni Rahi, 2022)
SMO Related Diseases
Abnormal activation or dysfunction of the SMO protein has been linked to a variety of diseases, especially in developmental abnormalities and cancer. The Hedgehog (Hh) signaling pathway, in which SMO is a key component, is critical for embryonic development, so anything that affects SMO function can lead to serious developmental defects. For example, certain types of congenital heart disease, neural tube defects, and other developmental disorders are associated with abnormalities in the Hh signaling pathway. In adults, abnormal activation of Hh signaling pathway is closely related to the occurrence and development of basal cell carcinoma, medulloblastoma, rhabdomyosarcoma, pancreatic cancer, lung cancer, prostate cancer, ovarian cancer and breast cancer. In addition, SMO dysfunction has also been linked to certain rare diseases such as Gorlin Syndrome, a genetic disorder characterized by abnormalities of the skin, bones, and nervous system, as well as an increased risk of developing basal cell carcinoma.
Bioapplications of SMO
Abnormal regulatory mechanisms and functions of SMO are closely associated with the occurrence of developmental diseases and cancers, making it a potential target for drug development. In drug screening and disease model studies, the development of SMO inhibitors is critical for the treatment of basal cell carcinoma and other cancers caused by abnormal activation of the Hh signaling pathway. In addition, studies on the activity and regulatory mechanisms of SMO contribute to the understanding of cell fate determination and tissue formation during embryonic development. In the field of tissue engineering and regenerative medicine, a deeper understanding of SMO's function may help promote tissue repair and regeneration. At the same time, SMO's role in cell signaling as part of the G protein-coupled receptor (GPCRS) also makes it useful in studying cell behavior and developing novel therapeutic strategies.
Case Study
Case Study 1: Yanlin Wang, 2003
The discovery of an inducible oxidase whose apparent substrate preference is spermine indicates that polyamine catabolism is more complex than that originally proposed. To facilitate the study of this enzyme, the purification and characterization of the recombinant human PAOh1/SMO polyamine oxidase are reported. Purified PAOh1/SMO oxidizes both spermine (K(m)=1.6 microM) and N(1)-acetylspermine (K(m)=51 microM), but does not oxidize spermidine. The purified human enzyme also does not oxidize eight representative antitumor polyamine analogues; however, specific oligamine analogues were found to be potent inhibitors of the oxidation of spermine by PAOh1/SMO. The results of these studies are consistent with the hypothesis that PAOh1/SMO represents a new addition to the polyamine metabolic pathway that may represent a new target for antineoplastic drug development.
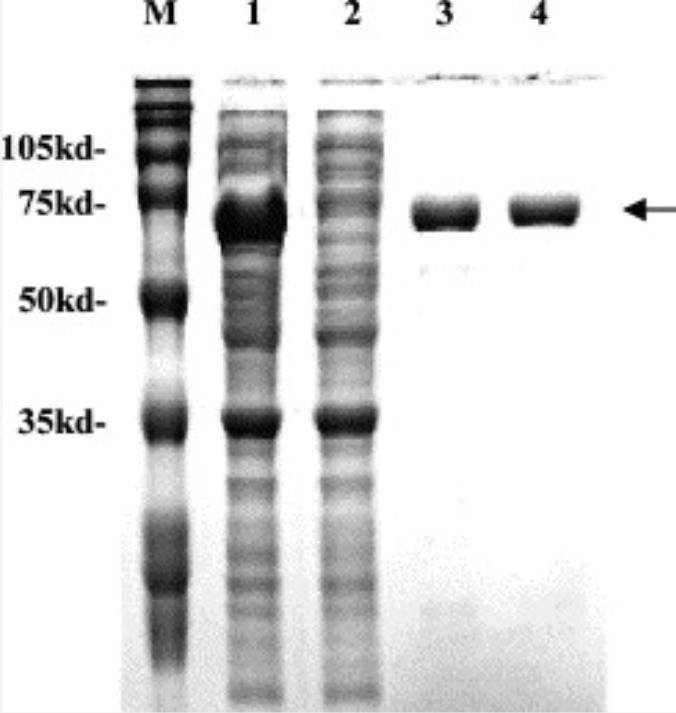
Fig1. Purification of recombinant PAOh1/SMO.
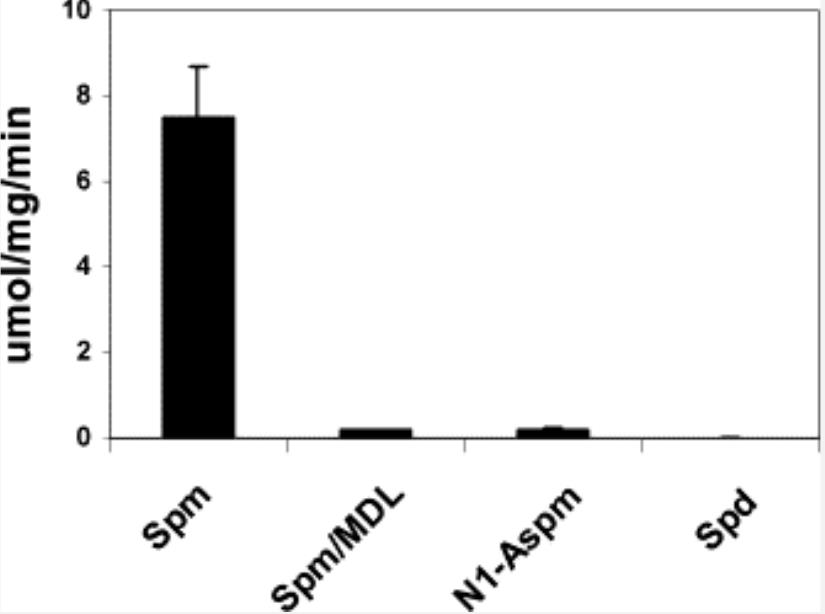
Fig2. Substrate specificity of purified recombinant PAOh1/SMO.
Case Study 2: Nitin K Agarwal, 2022
The oncoprotein Smoothened (SMO), a Frizzled-class-G-protein-coupled receptor, is the central transducer of hedgehog (Hh) signaling. While canonical SMO signaling is best understood in the context of cilia, evidence suggests that SMO has other functions in cancer biology that are unrelated to canonical Hh signaling. Herein, researchers provided evidence that elevated levels of human SMO show a strong correlation with elevated levels of insulin-like growth factor 1 receptor (IGF1R) and reduced survival in diffuse large B-cell lymphoma (DLBCL). As an integral component of raft microdomains, SMO plays a fundamental role in maintaining the levels of IGF1R in lymphoma and breast cancer cells as well IGF1R-associated activation of protein kinase B (AKT). Silencing of SMO increases lysosomal degradation and favors a localization of IGF1R to late endosomal compartments instead of early endosomal compartments from which much of the receptor would normally recycle. In addition, loss of SMO interferes with the lipid raft localization and retention of the remaining IGF1R and AKT, thereby disrupting the primary signaling context for IGF1R/AKT.

Fig3. Correlation of SMO and IGF1R levels by Immunohistochemistry in DLBCL tissue microarray sections.
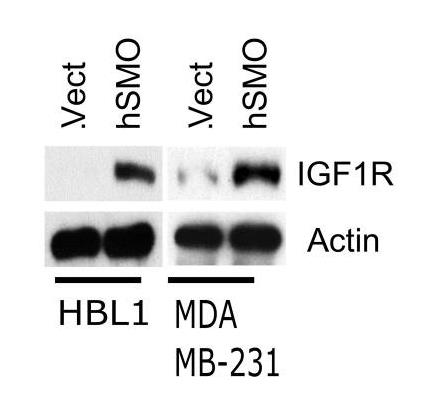
Fig4. overexpression of recombinant human SMO (hSMO) results in a very pronounced increase of IGF1R.
Quality Guarantee
High Purity
.jpg)
Fig1. SDS-PAGE (SMO-2707H)
.
.jpg)
Fig2. SDS-PAGE (SMO-6317H)
Involved Pathway
SMO involved in several pathways and played different roles in them. We selected most pathways SMO participated on our site, such as Hedgehog signaling pathway,Pathways in cancer,Proteoglycans in cancer, which may be useful for your reference. Also, other proteins which involved in the same pathway with SMO were listed below. Creative BioMart supplied nearly all the proteins listed, you can search them on our site.
| Pathway Name | Pathway Related Protein |
|---|---|
| Pathways in cancer | PIK3CA,WNT9A,HDAC2,CSF3R,HHIP,CCNE1,WNT6,PTGER1,WNT10B,KRAS |
| Basal cell carcinoma | TRP53,WNT7B,WNT2,FZD9,Shh,APC2,DVL2,WNT5B,PTCH1,STK36 |
| Hedgehog signaling pathway | WNT2,WNT5B,IHHB,GLI1,WNT11R,IHHA,PRKACG,WNT5A,DYRK1AA,PRKACAA |
| Proteoglycans in cancer | ARAF,HPSE,RHOA,TP53,CAMK2B,FZD7,ANK2,DDX5,WNT5B,MAPK13 |
Protein Function
SMO has several biochemical functions, for example, G-protein coupled receptor activity,NOT Wnt-activated receptor activity,Wnt-protein binding. Some of the functions are cooperated with other proteins, some of the functions could acted by SMO itself. We selected most functions SMO had, and list some proteins which have the same functions with SMO. You can find most of the proteins on our site.
| Function | Related Protein |
|---|---|
| Wnt-protein binding | FZD1,ROR2,LRP5,FZD9B,SFRP2,FZD10,FZD3A,APCDD1,FZD7B,WLS |
| G-protein coupled receptor activity | CXCR3.1,O3far1,OR52J3,OPN5,FZD5,GHSRA,GPR88,OR52B4,GRM1,DRD1B |
| protein binding | LATS2,SPATA7,NOTCH1,MAPK6,CARD10,PPP3CB,OSBP2,HAND1,SNX6,TWIST1 |
| drug binding | HMGB2,PDE10A,GPR30,TLR7,TLR8,HTR1B,SRP54B,GABRA1,ADH1,GLRB |
| patched binding | SETD6,Shh,BBS1,CAV1,IHH,CCNB1,PTCH1,DHH |
| NOT Wnt-activated receptor activity | SFRP1A,SZL,SFRP1,FRZB,SFRP1B,SETD6,SFRP2,TSPAN12,SFRP4 |
Interacting Protein
SMO has direct interactions with proteins and molecules. Those interactions were detected by several methods such as yeast two hybrid, co-IP, pull-down and so on. We selected proteins and molecules interacted with SMO here. Most of them are supplied by our site. Hope this information will be useful for your research of SMO.
PTCH1;ARRB2;ARRB1;ILK;BCL6
Resources
Gene Families
Research Area
Related Services
Related Products
References
- Alfaro, AC; Roberts, B; et al. Ptch2 mediates the Shh response in Ptch1(-/-) cells. DEVELOPMENT 141:3331-3339(2014).
- Kebenko, M; Drenckhan, A; et al. ErbB2 signaling activates the Hedgehog pathway via PI3K-Akt in human esophageal adenocarcinoma: Identification of novel targets for concerted therapy concepts. CELLULAR SIGNALLING 27:373-381(2015).



