RRAS
-
Official Full Name
related RAS viral (r-ras) oncogene homolog -
Overview
Regulates the organization of the actin cytoskeleton. -
Synonyms
RRAS;related RAS viral (r-ras) oncogene homolog;ras-related protein R-Ras;p23;Oncogene RRAS
Recombinant Proteins
- Human
- Mouse
- Zebrafish
- Rat
- E. coli
- E.coli
- Mammalian Cell
- Wheat Germ
- HEK293
- Mammalian cells
- HEK293T
- In Vitro Cell Free System
- GST
- His
- Non
- His&Fc&Avi
- Flag
- Myc&DDK
Background
What is RRAS protein?
RRAS (RAS related) gene is a protein coding gene which situated on the long arm of chromosome 19 at locus 19q13. RRAS protein is a member of the Ras protein family, which are small GTP-binding proteins that regulate diverse cellular functions such as proliferation, survival, and cytoskeletal dynamics. The Ras superfamily includes over 100 proteins that act as molecular switches cycling between an active GTP-bound state and an inactive GDP-bound state during signal transduction processes. RRAS, specifically, is involved in various cellular signaling pathways and has been linked to cancer and other diseases due to its role in cell growth regulation. The RRAS protein is consisted of 218 amino acids and its molecular mass is approximately 23.5 kDa.
What is the function of RRAS protein?
RRAS proteins, like other Ras proteins, are involved in signal transduction pathways that are critical for cell growth and differentiation. They are binary switches that cycle between an "ON" and "OFF" state, which is normally tightly controlled. While RRAS shares sequence homology with other Ras proteins, it has distinct functions and regulatory mechanisms. For example, R-Ras is known to antagonize H-Ras signaling in certain contexts, and it has been identified as a global regulator of vascular regeneration, highlighting its importance in development and repair processes.
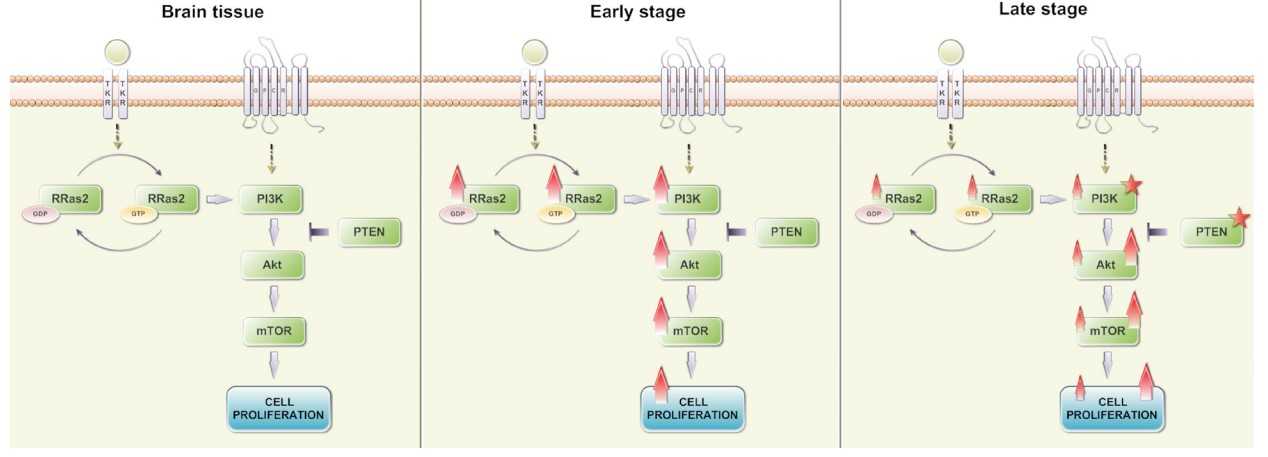
Fig1. Increased R-RAS2 expression in astrocytomas. (Sylvia Gutierrez-Erlandsson, 2013)
RRAS Related Signaling Pathway
RAS proteins, including RRAS, can activate multiple downstream signaling pathways. Three well-known RAS effector pathways are the RAF-MEK-ERK (MAPK) pathway, the PI3K-Akt pathway, and the RAL-GEF pathway. These pathways are involved in various cellular processes, including cell survival, growth, and differentiation. R-Ras has been shown to interact with other signaling molecules and affect their function. For example, the interaction between R-Ras and SIN1 can influence the activity of mTORC2 substrates and modulate insulin signaling. The Ras signaling pathway, including RRAS, is crucial for processes like cell growth, differentiation, and apoptosis. Dysregulation of this pathway, often due to mutations in RAS genes, can lead to uncontrolled cell proliferation and contribute to the development of cancer.
RRAS Related Diseases
Dysregulated R-Ras signaling has been linked to the pathogenesis of cardiovascular diseases, potentially through its effects on cellular processes like proliferation and differentiation. Altered RRAS signaling is associated with intellectual disabilities. The Ras-MAPK pathway, which RRAS is a part of, is critical for normal neurodevelopment, and its dysregulation can lead to cognitive impairments. RRAS, like other Ras proteins, plays a role in regulating cell growth and differentiation. Mutations in RRAS can lead to uncontrolled cell proliferation, which is a hallmark of cancer. RRAS has been implicated in various types of cancer, including those where RAS mutations are common, such as pancreatic and lung cancers. Beyond hematological malignancies, RAS mutations, including those affecting RRAS, are also prevalent in solid tumors, contributing to their development and progression.
Bioapplications of RRAS
Given its role in cell signaling pathways, RRAS is a potential target for therapeutic intervention in cancer. Understanding the specific pathways in which RRAS is involved could lead to the development of targeted cancer treatments. Although not directly related to RRAS, the field of organic optoelectronic materials (OOMs) for bioimaging and optical therapy might benefit from insights into how RRAS and similar proteins interact with light-sensitive molecules. This could potentially open up new avenues for the application of RRAS in biophotonics. The Ras family, including RRAS, is involved in cell growth and differentiation pathways that are crucial for tissue repair and regeneration. Understanding these pathways could be beneficial for developing regenerative medicine approaches.
Case Study
Case Study 1: Antea Talajić, 2024
The R-RAS2 is a small GTPase highly similar to classical RAS proteins at the regulatory and signaling levels. The high evolutionary conservation of R-RAS2, its links to basic cellular processes and its role in cancer, make R-RAS2 an interesting research topic. To elucidate the evolutionary history of R-RAS proteins, we investigated and compared structural and functional properties of ancestral type R-RAS protein with human R-RAS2. Bioinformatics analysis were used to elucidate the evolution of R-RAS proteins. The cell model consisted of human breast cancer cell lines MCF-7 and MDA-MB-231 transiently transfected with EsuRRAS2-like or HsaRRAS2. Biological characterization of R-RAS2 proteins was performed by Western blot on whole cell lysates or cell adhesion protein isolates, immunofluorescence and confocal microscopy, MTT test, colony formation assay, wound healing and Boyden chamber migration assays. The results showed that the single sponge R-RAS2-like gene/protein probably reflects the properties of the ancestral R-RAS protein that existed prior to duplications during the transition to Bilateria, and to Vertebrata. And the ancestral type of the R-RAS protein, sponge R-RAS2-like, enhances their oncogenic potential, similar to human R-RAS2. In addition, sponge and human R-RAS2 were not found in focal adhesions, but both homologs play a role in their regulation by increasing talin1 and vinculin.
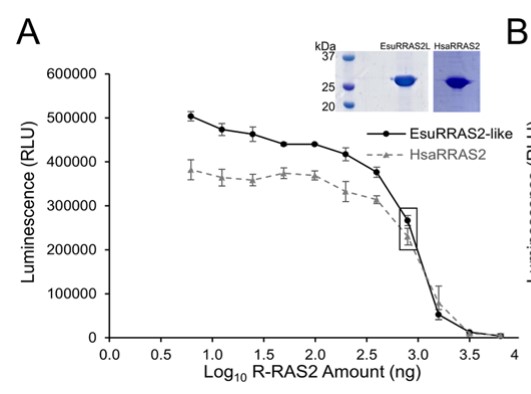
Fig1. Titration of EsuRRAS2-like and HsaRRAS2 proteins in GTPase/GAP Buffer.

Fig2. Quantification of colocalization between EsuRRAS2L or HsaRRAS2 with endosomal markers.
Case Study 2: Joanna E Gawecka, 2010
Changes in cell adhesion and migration in the tumor microenvironment are key in the initiation and progression of metastasis. R-Ras is one of several small GTPases that regulate cell adhesion and migration on the extracellular matrix, however the mechanism has not been completely elucidated. Using a yeast two-hybrid approach we sought to identify novel R-Ras binding proteins that might mediate its effects on integrins. The results showed that in M2 melanoma cells active R-Ras co-localized with FLNa but did not co-localize with FLNa lacking repeat 3. Thus, activated R-Ras binds repeat 3 of FLNa. The functional consequence of this interaction was that active R-Ras and FLNa coordinately increased cell migration. In contrast, co-expression of R-Ras and FLNaDelta3 had a significantly reduced effect on migration. While there was enhancement of integrin activation and fibronectin matrix assembly, cell adhesion was not altered. Finally, siRNA knockdown of endogenous R-Ras impaired FLNa-dependent fibronectin matrix assembly.
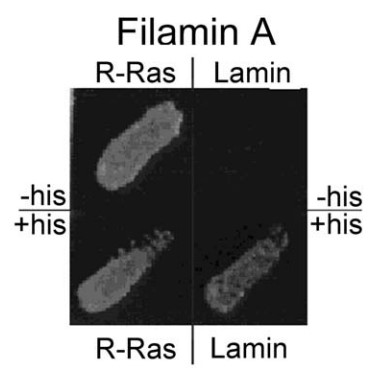
Fig3. Yeast two hybrid screen of R-Ras binding to FLNa.

Fig4. Forced expression of activated R-Ras promotes integrin activation in M2 cells.
Quality Guarantee
High Purity
.jpg)
Fig1. SDS-PAGE (RRAS-3690H)
Involved Pathway
RRAS involved in several pathways and played different roles in them. We selected most pathways RRAS participated on our site, such as MAPK signaling pathway,Ras signaling pathway,Rap signaling pathway, which may be useful for your reference. Also, other proteins which involved in the same pathway with RRAS were listed below. Creative BioMart supplied nearly all the proteins listed, you can search them on our site.
| Pathway Name | Pathway Related Protein |
|---|---|
| Tight junction | LLGL1,ACTN3A,PPP2R1B,MYHC4,PRKCZ,PPP2R2CA,MYH1B,OCLNA,PRKCA,CDC42 |
| cAMP signaling pathway | RAF1,ATP1B1,MAPK10,ARAP3,AMH,FOS,PDE3A,ATP1B4,ROCK2,FXYD2 |
| MAPK signaling pathway | HSP70,CACNA1SB,PDGFRB,MAP2K2A,CACNB1,MAX,PPM1BB,PPP3R1B,FGF12A,RAP1B |
| Rap signaling pathway | RAPGEF5,SIPA1L1,ANGPT4,FGFR2,VEGFB,ITGB3,FGF12,MAP2K2,INS2,FGF8 |
| HTLV-I infection | SLC25A5,HLA-DRA,IL1R1,IL1R2,MAP3K1,WNT10B,SMAD2,TCF3,TGFB2,CDC27 |
| Ras signaling pathway | KRAS,PRKACG,GNG13,Pdgfa&Pdgfb,MAPK9,CSF1,RALBP1,RASA3,PRKACA,PLA2G5 |
| Proteoglycans in cancer | WNT7B,HSPG2,ESR1,PIK3CA,CBLB,PRKACG,ITGAV,ANK2,TLR4,TIMP3 |
| Phospholipase D signaling pathway | HRAS,MAPK1,PDGFD,CXCR2,PPAP2A,PIK3R3,GRM2,PIK3R5,AVP,PIK3CG |
| Regulation of Actin Cytoskeleton | PAK6B,GIT1,NCKAP1L,SSH3,ITGB1B.2,DIAP1,FGF18,ITGB8,NRAS,ACTG1 |
Protein Function
RRAS has several biochemical functions, for example, GDP binding,GTP binding,GTPase activity. Some of the functions are cooperated with other proteins, some of the functions could acted by RRAS itself. We selected most functions RRAS had, and list some proteins which have the same functions with RRAS. You can find most of the proteins on our site.
| Function | Related Protein |
|---|---|
| protein binding | SLC4A1AP,SYT6,DYM,KCNJ15,RAMP1,CENPL,RAMP2,CCDC41,AP1S2,OLR1 |
| protein complex binding | TELO2,VDAC1,C8G,KAT6B,TUBB,LEPRE1,RAN,PDX1,RBX1,TRAF2 |
| GTP binding | AGAP1,TPX2,RAB5B,RAB21,EEF2A.1,ARL4AA,RAB32A,RAB35B,RAC2,ARL16 |
| GDP binding | RAB22A,KRAS,RAB7,RAP2C,RRAGC,GNAI1,MIEF1,SRP54B,PCK1,RAB5B |
| GTPase activity | RAB6A,GNB5,GBP2,TUFM,RAB1BA,RAB35,RAB23,RAB17,EFTUD1,TUBA7L |
Interacting Protein
RRAS has direct interactions with proteins and molecules. Those interactions were detected by several methods such as yeast two hybrid, co-IP, pull-down and so on. We selected proteins and molecules interacted with RRAS here. Most of them are supplied by our site. Hope this information will be useful for your research of RRAS.
FYN;SRC;NCK1;PLCG1;PIK3R1;CRK;GRB2;EEF1A1;Rassf5;q8cla8_yerpe;chbG;ACY3;MRPL36;Max;pi3p;ATP6V1A
Resources
Related Services
Related Products
References
- Imamura, S; Konnai, S; et al. Effects of anti-tick cocktail vaccine against Rhipicephalus appendiculatus. JAPANESE JOURNAL OF VETERINARY RESEARCH 56:85-98(2008).
- Ratnakumar, S; Kacherovsky, N; et al. Snf1 Controls the Activity of Adr1 Through Dephosphorylation of Ser230. GENETICS 182:735-745(2009).


