RPS6KA1
-
Official Full Name
ribosomal protein S6 kinase, 90kDa, polypeptide 1 -
Overview
RSK 1 (p90-RSK 1) is a member of a family of 90 kDa ribosomal protein S6 kinases, which includes RSK 1, RSK 2 and RSK 3. These are broadly expressed serine/threonine protein kinases (1) activated in response to mitogenic stimuli, including extracellular signal-regulated protein kinases Erk1 and Erk2 (2). p90-RSK 1 is activated by MAPK in vitro and in vivo via phosphorylation (3). Active RSKs appear to play a major role in transcriptional regulation by translocating to the nucleus and phosphorylating c-Fos and CREB (2,4). -
Synonyms
RPS6KA1;ribosomal protein S6 kinase, 90kDa, polypeptide 1;ribosomal protein S6 kinase, 90kD, polypeptide 1;ribosomal protein S6 kinase alpha-1;HU 1;RSK;RSK1;RSK-1;p90S6K;p90RSK1;p90-RSK 1;MAPKAPK-1a;S6K-alpha 1;S6K-alpha-1;MAPKAP kinase 1a;ribosomal S6 kinase 1;MAPK-activated protein kinase 1a;ribosomal protein S6 kinase alpha 1;90 kDa ribosomal protein S6 kinase 1;MAP kinase-activated protein kinase 1a;dJ590P13.1 (ribosomal protein S6 kinase, 90kD, polypeptide 1);HU-1;MAPKAPK1A
Recombinant Proteins
- Human
- Chicken
- Zebrafish
- Rat
- Mouse
- E.coli
- Sf9 Insect Cell
- Mammalian Cell
- HEK293
- Insect Cell
- HEK293T
- Mammalian cells
- Insect (sf21)
- GST
- His
- Non
- His&T7
- His&Fc&Avi
- Myc&DDK
Background
What is RPS6KA1 protein?
RPS6KA1 (ribosomal protein S6 kinase A1) gene is a protein coding gene which situated on the short arm of chromosome 1 at locus 1p36. This gene encodes a member of the RSK (ribosomal S6 kinase) family of serine/threonine kinases. This kinase contains 2 nonidentical kinase catalytic domains and phosphorylates various substrates, including members of the mitogen-activated kinase (MAPK) signalling pathway. The activity of this protein has been implicated in controlling cell growth and differentiation. The RPS6KA1 protein is consisted of 735 amino acids and its molecular mass is approximately 82.7 kDa.
What is the function of RPS6KA1 protein?
RPS6KA1 promotes cell growth, proliferation and survival by activating the mTORC1 signaling pathway. RPS6KA1 can influence the process of ribosomal protein synthesis and translation, thus affecting the synthesis of proteins within the cell. RPS6KA1 plays a role in the G1 and S phases of the cell cycle and regulates cell cycle progression. RPS6KA1 maintains cell survival by inhibiting cell stress response and apoptosis pathway.

Fig1. Regulation of the cell-cycle by RSK. (Rana Anjum, 2008)
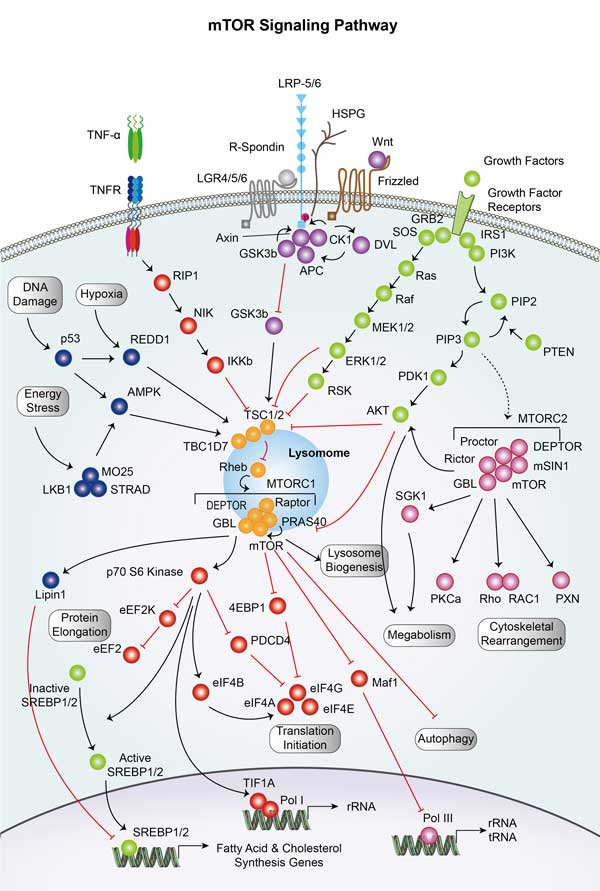
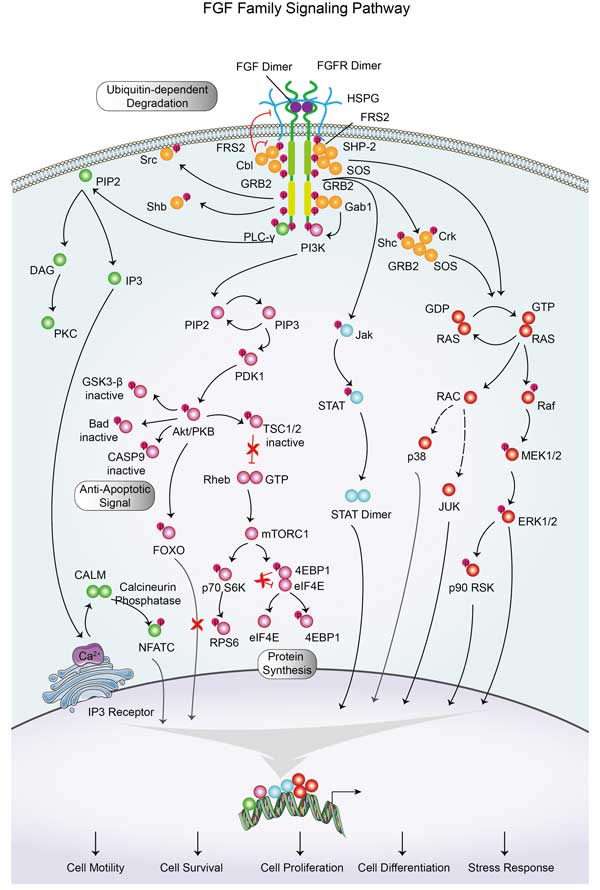
RPS6KA1 Related Signaling Pathway
RPS6KA1 is one of the key downstream effectors of the MAPK/ERK (mitogen-activated protein kinase/Extracellular signal-regulated kinase) pathway, through which it is involved in signal transduction induced by various growth factors and hormones. The PI3K/AKT signaling pathway plays a key role in cell survival, metabolism, and migration, and RPS6KA1, as a component of this pathway, responds to PI3K (phosphoinositol-3-kinase) /AKT activation, which in turn influences downstream events. RPS6KA1 is involved in regulating the G1 to S phase transition, ensuring that cells are ready before DNA replication.

Fig2. A schematic model for RSK activation. (Rana Anjum, 2008)
RPS6KA1 Related Diseases
Overactivation of RPS6KA1 plays a role in the development of many cancers, including breast cancer, pancreatic cancer, liver cancer, and neuroblastoma. The expression and activation of RPS6KA1 in cardiomyocytes is associated with cardioprotective mechanisms, but its dysregulation may also be associated with the development of cardiovascular diseases. RPS6KA1 plays a role in signaling in neurons, and abnormalities in it may be associated with neurodegenerative diseases such as Alzheimer's disease. It's also associated with diabetes.
Bioapplications of RPS6KA1
RPS6KA1 is abnormally expressed in a variety of cancers, including prostate, breast and pancreatic cancers. Therefore, it is considered a potential cancer therapeutic target, and researchers are exploring small molecule drugs that inhibit RPS6KA1 activity or its signaling pathway for tumor therapy.
Case Study
Case Study 1: Kazuhiro Katayama, 2016
P-glycoprotein (P-gp) is a critical determinant of multidrug resistance in cancer. This team previously reported that MAPK inhibition downregulates P-gp expression and that P-gp undergoes ubiquitin-proteasomal degradation regulated by UBE2R1 and SCFFbx15. Here, the researchers investigated the crosstalk between MAPK inhibition and the ubiquitin-proteasomal degradation of P-gp. Proteasome inhibitors or knockdown of FBXO15 and/or UBE2R1 cancelled MEK inhibitor-induced P-gp downregulation. RSK1 phosphorylated Thr162 on UBE2R1 but did not phosphorylate FBXO15. MEK and RSK inhibitors increased UBE2R1-WT but not UBE2R1-T162D and -T162A expression. UBE2R1-T162D showed higher self-ubiquitination and destabilisation than UBE2R1-WT and -T162A. Unlike UBE2R1-WT and -T162A, UBE2R1-T162D did not induce P-gp ubiquitination. UBE2R1-WT or -T162A downregulated P-gp expression and upregulated rhodamine 123 level and sensitivity to vincristine and doxorubicin. However, UBE2R1-T162D did not confer any change in P-gp expression, rhodamine 123 accumulation and sensitivity to the drugs.

Fig1. Binding of ERK1 and RSK1 with FBXO15.

Case Study 2: Amel Salhi, 2015
The two major melanoma histologic subtypes, superficial spreading and nodular melanomas, differ in their speed of dermal invasion but converge biologically once they invade and metastasize. Herein, the researchers tested the hypothesis that distinct molecular alterations arising in primary melanoma cells might persist as these tumors progress to invasion and metastasis. Ribosomal protein S6 kinase, 90 kDa, polypeptide 1 (RSK1; official name RPS6KA1) was significantly hyperactivated in human melanoma lines and metastatic tissues derived from nodular compared with superficial spreading melanoma. RSK1 was constitutively phosphorylated at Ser-380 in nodular but not superficial spreading melanoma and did not directly correlate with BRAF or MEK activation. Nodular melanoma cells were more sensitive to RSK1 inhibition using siRNA and the pharmacological inhibitor BI-D1870 compared with superficial spreading cells. Gene expression microarray analyses revealed that RSK1 orchestrated a program of gene expression that promoted cell motility and invasion. Differential overexpression of the prometastatic matrix metalloproteinase 8 and tissue inhibitor of metalloproteinases 1 in metastatic nodular compared with metastatic superficial spreading melanoma was observed. Finally, using an in vivo zebrafish model, constitutive RSK1 activation increased melanoma invasion.

Fig3. p-RSK1 protein expression in human metastatic melanoma tissues by Western blot analysis.

Quality Guarantee
High Purity

Fig1. SDS-PAGE (RPS6KA1-1934H) (PROTOCOL for western blot)
.

Fig2. SDS-PAGE (RPS6KA1-4414M) (PROTOCOL for western blot)
Involved Pathway
RPS6KA1 involved in several pathways and played different roles in them. We selected most pathways RPS6KA1 participated on our site, such as MAPK signaling pathway,Oocyte meiosis,mTOR signaling pathway, which may be useful for your reference. Also, other proteins which involved in the same pathway with RPS6KA1 were listed below. Creative BioMart supplied nearly all the proteins listed, you can search them on our site.
| Pathway Name | Pathway Related Protein |
|---|---|
| MAPK signaling pathway | ATF4B1,GNG12A,NFKB1,MAPK8IP3,RAC3B,MKNK1,MAP2K6,PRKCBB,CACNB2,PAK2B |
| Insulin resistance | TNFRSF1A,PPARGC1B,IKBKB,PPP1CB,INSB,RPS6KB1,PIK3CA,MLXIPL,PTPRFB,PTPN1 |
| mTOR signaling pathway | PIK3R1,TSC1,PRKCA,PRKCG,AKT2,AKT1S1,PIK3CA,MAPK1,HIF1A,RPS6KA6 |
| Neurotrophin signaling pathway | MAPK10,AKT1,CALM2,NTF3,BRAF,MAPKAPK2,PLCG2,MAP3K1,SHC1,MAP3K5 |
| Progesterone-mediated oocyte maturation | PIK3R1,ANAPC4,PIK3R2,ANAPC1,RPS6KA2,MAD2L1,MAPK11,INSB,CPEB2,PIK3CD |
| Long-term potentiation | GRIN2B,PPP3R2,HRAS,RPS6KA3,PPP3R1,MAPK1,RAF1,RAP1A,PPP1CA,PPP3CC |
| Oocyte meiosis | PRKACA,PPP2R1A,CDC23,SPDYA,IGF1R,INS2,ADCY2B,ITPR3,CUL1,PTTG2 |

Fig1. Harmonization of Ca2+, EGF, and oxidative signals. (Tsuyoshi Takata, 2020)

Fig2. Mitogen- and stress-activated kinases (MSKs). (Rana Anjum, 2008)
Protein Function
RPS6KA1 has several biochemical functions, for example, ATP binding,cysteine-type endopeptidase inhibitor activity involved in apoptotic process,magnesium ion binding. Some of the functions are cooperated with other proteins, some of the functions could acted by RPS6KA1 itself. We selected most functions RPS6KA1 had, and list some proteins which have the same functions with RPS6KA1. You can find most of the proteins on our site.
| Function | Related Protein |
|---|---|
| protein serine/threonine/tyrosine kinase activity | TTK,SGK1,CLK1,DYRK2,DYRK1AA,PRKCG,ACVR2B,TESK2,DSTYK,PRKAA2 |
| ATP binding | SIK2,TRIOA,PSMC1A,MKNK2A,CHD6,ERN1,ITM2C,SLC14A2,RPS6KA5,RAF1B |
| protein binding | MTMR14,LRCH1,FAM115A,TRAPPC6A,DCBLD2,KLRB1F,DRD1,PRMT3,CHRNB2,FAM59A |
| protein serine/threonine kinase activity | PAK6,GRK1A,DYRK2,CDK11B,PAK2A,SLC14A2,MAPK13,CDC42BPA,AKT3A,PRKAA2 |
| ribosomal protein S6 kinase activity | RPS6KB1,RPS6KA4,RPS6KA2,RPS6KA6,RPS6KA3,RPS6KA3B,RPS6KB2,RPS6KA3A,ALPK2,RPS6KB1B |
| cysteine-type endopeptidase inhibitor activity involved in apoptotic process | TFAP2B,XIAP,TNFAIP8,LEF1,CD27,GAS6,IGF1RB,PRDX5,C1QL4L,TNFSF14 |
| magnesium ion binding | NUAK2,PI4K2A,MAPK12,STK38L,ADPRH,RRAGC,SIK2,SRR,TDP2,HPGDS |
Interacting Protein
RPS6KA1 has direct interactions with proteins and molecules. Those interactions were detected by several methods such as yeast two hybrid, co-IP, pull-down and so on. We selected proteins and molecules interacted with RPS6KA1 here. Most of them are supplied by our site. Hope this information will be useful for your research of RPS6KA1.
HSP90AB1;VASP;MAPT;CREB1;EIF4B;RPS6;xmd8-92;biotin_acyl-p_probe;YWHAB;ENAH;PPM1G;DDAH2;CFL1;GBP2;TTK;CCT4
RPS6KA1 Related Signal Pathway
Resources
Related Services
Related Products
References