PRG4
-
Official Full Name
proteoglycan 4 -
Overview
The protein encoded by this gene is a large proteoglycan specifically synthesized by chondrocytes located at the surface of articular cartilage, and also by some synovial lining cells. This protein contains both chondroitin sulfate and keratan sulfate glycosaminoglycans. It functions as a boundary lubricant at the cartilage surface and contributes to the elastic absorption and energy dissipation of synovial fluid. Mutations in this gene result in camptodactyly-arthropathy-coxa vara-pericarditis syndrome. Multiple transcript variants encoding different isoforms have been found for this gene. -
Synonyms
PRG4;proteoglycan 4;CACP, proteoglycan 4, (megakaryocyte stimulating factor, articular superficial zone protein, camptodactyly, arthropathy, coxa vara, pericarditis syndrome);articular superficial zone protein;bG174L6.2;bG174L6.2 (MSF: megakaryocyte stimulating factor );camptodactyly;arthropathy;coxa vara;pericarditis syndrome;FLJ32635;HAPO;Jacobs camptodactyly arthropathy pericarditis syndrome;JCAP;lubricin;megakaryocyte stimulating factor;MSF;SZP;Superficial zone proteoglycan;CACP;Camptodactyly arthropathy coxa vara pericarditis syndrome gene;Jacobs camptodactyly arthropathy pericarditis syndrome gene;PRG 4;Proteoglycan4;megakaryocyte-stimulating factor
Recombinant Proteins
- Human
- Mouse
- CHO
- Mammalian Cell
- Wheat Germ
- E.coli
- HEK293
- Yeast
- Non
- His
- GST
- His&GST
- His&Fc&Avi
| Cat.# | Product name | Source (Host) | Species | Tag | Protein Length | Price |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| PRG4-1573H |
Active Recombinant Human PRG4
|
CHO | Human | Non |
|
|
| PRG4-13339M | Recombinant Mouse PRG4 Protein | Mammalian Cell | Mouse | His |
|
|
| PRG4-1501H | Recombinant Human PRG4, GST-tagged | Wheat Germ | Human | GST |
|
|
| PRG4-361H | Recombinant Human PRG4 protein, His-tagged | E.coli | Human | His | 1151-1241 a.a. |
|
| PRG4-132M | Recombinant Mouse PRG4 protein (Met1-Pro1054), His-tagged | HEK293 | Mouse | His | 1-1054 a.a. |
|
| Prg4-1980M | Recombinant Mouse Prg4 Protein, His&GST-tagged | E.coli | Mouse | His&GST | Gly797-Pro1054 |
|
| Prg4-5499H | Recombinant Human Prg4 protein, His-tagged | Yeast | Human | His | 25-156aa |
|
| PRG4-7080M | Recombinant Mouse PRG4 Protein, His (Fc)-Avi-tagged | HEK293 | Mouse | His&Fc&Avi |
|
|
| PRG4-7080M-B | Recombinant Mouse PRG4 Protein Pre-coupled Magnetic Beads | HEK293 | Mouse |
|
Background
What is PRG4 protein?
PRG4 gene (proteoglycan 4) is a protein coding gene which situated on the long arm of chromosome 1 at locus 1q31. The protein encoded by this gene is a large proteoglycan that is synthesized by chondrocytes located at the surface of articular cartilage and by some synovial lining cells. This protein contains both chondroitin sulfate and keratan sulfate glycosaminoglycans. It functions as a boundary lubricant at the cartilage surface and contributes to the elastic absorption and energy dissipation of synovial fluid. Mutations in this gene result in camptodactyly-arthropathy-coxa vara-pericarditis syndrome. The PRG4 protein is consisted of 1404 amino acids and PRG4 molecular weight is approximately 151.1 kDa.
What is the function of PRG4 protein?
PRG4 functions as a boundary lubricant at the cartilage surface, which is crucial for reducing friction between articular cartilage surfaces during movement. It contributes to the elastic absorption and energy dissipation of synovial fluid. PRG4 has the ability to regulate inflammation. It can interact with various cell surface receptors, including CD44, TLRs (Toll-like receptors), and L-selectin, to modulate inflammatory responses within the joint. PRG4 is involved in maintaining the balance of macrophages in the synovium. PRG4 prevents protein deposition onto cartilage from synovial fluid by controlling adhesion-dependent synovial growth and inhibiting the adhesion of synovial cells to the cartilage surface. PRG4 expression can be influenced by inflammatory cytokines, and it can autoregulate native PRG4 expression in synoviocytes, which are cells found in the synovial fluid of joints. Certain isoforms of PRG4 can act as growth factors affecting primitive cells of both hematopoietic and endothelial lineages.
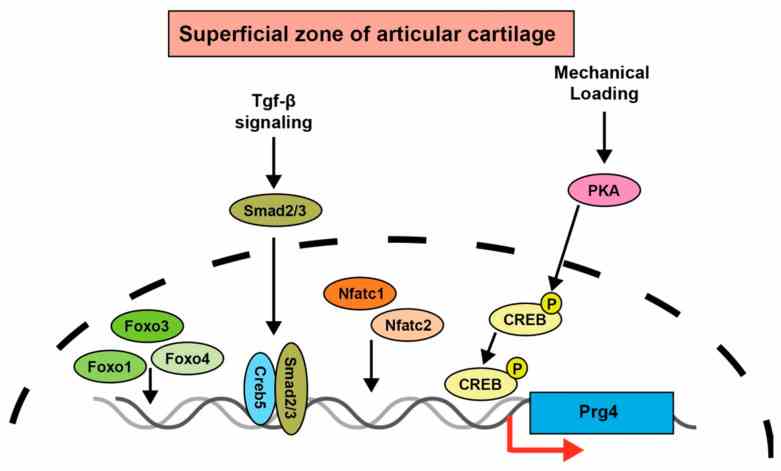
Fig1. Schematic model of upstream transcription factors of Prg4. (Yoshifumi Takahata, 2022)
PRG4 Related Signaling Pathway
PRG4 is a glycoprotein that plays a key role in joint lubrication, anti-inflammatory response, cartilage protection, and tissue repair. It's associated with a variety of signaling pathways, These include pathways that interact with the cell surface receptor CD44, the Wnt/β-catenin signaling pathway that regulates cell proliferation and differentiation, the NF-κB signaling pathway that is involved in the regulation of inflammation and immune responses, the HIF signaling pathway that influences cell response to hypoxia, and the TGFβ/βMP and FGF that play key roles in cell proliferation, differentiation, and tissue repair The signaling pathway. In addition, PRG4 may also participate in cell metabolism and biosynthesis through AMPK, mTOR and RUNX2 signaling pathways, and may play a role in the pathogenesis of osteoarthritis, regulating signaling pathways related to inflammation and articular cartilage degradation.
PRG4 Related Diseases
Its deficiency or abnormal function has been linked to a variety of joint diseases, particularly osteoarthritis (OA), a chronic degenerative disease that causes degeneration of the joint cartilage, joint pain, and dysfunction. Loss of protective effect of PRG4 may lead to accelerated wear of articular cartilage and increased inflammatory response. In addition, mutations or dysregulated expression of PRG4 have been associated with certain inherited joint diseases, such as camptodactyly-arthropathy-coxa vara-pericarditis syndrome (CACP) syndrome, a rare autoinflammatory disorder. It presents with joint contracture, joint disease and pericarditis.
Bioapplications of PRG4
As a natural joint lubricant, PRG4 is being studied for the treatment and prevention of degenerative joint diseases such as osteoarthritis, delaying disease progression by reducing joint friction and wear. In addition, due to its anti-inflammatory properties, PRG4 is also being explored as a potential therapeutic agent for regulating inflammatory responses, particularly in autoimmune and chronic inflammatory diseases. In tissue engineering and regenerative medicine, applications of PRG4 also include promoting cartilage repair and regeneration as part of biomaterials. In addition, the results of PRG4 research have facilitated the exploration of its application in sports injury recovery and military medicine to accelerate wound healing and reduce the risk of joint injury in soldiers during high-intensity training.
Case Study
Case Study 1: Nikhil G Menon, 2022
Dry Eye Disease (DED) is a complex pathology affecting millions of people with significant impact on quality of life. Corneal inflammation, including via the nuclear factor kappa B (NFκB) pathway, plays a key etiological role in DED. Recombinant human proteoglycan 4 (rhPRG4) has been shown to be a clinically effective treatment for DED that has anti-inflammatory effects in corneal epithelial cells, but the underlying mechanism is still not understood. This study aims to understand if rhPRG4 affects tumor necrosis factor α (TNFα)-stimulated inflammatory activity in corneal epithelial cells. Researchers treated hTERT-immortalized corneal epithelial (hTCEpi) cells ± TNFα ± rhPRG4 and performed Western blotting on cell lysate and RNA sequencing. Bioinformatics analysis revealed that rhPRG4 had a significant effect on TNFα-mediated inflammation with potential effects on matricellular homeostasis. rhPRG4 reduced activation of key inflammatory pathways and decreased expression of transcripts for key inflammatory cytokines, interferons, interleukins, and transcription factors. TNFα treatment significantly increased phosphorylation and nuclear translocation of p65, and rhPRG4 significantly reduced both these effects.
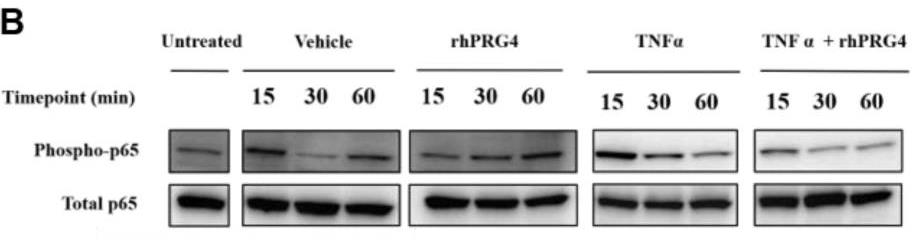
Fig1. p65 phosphorylation is stimulated by TNFα and downregulated by rhPRG4.
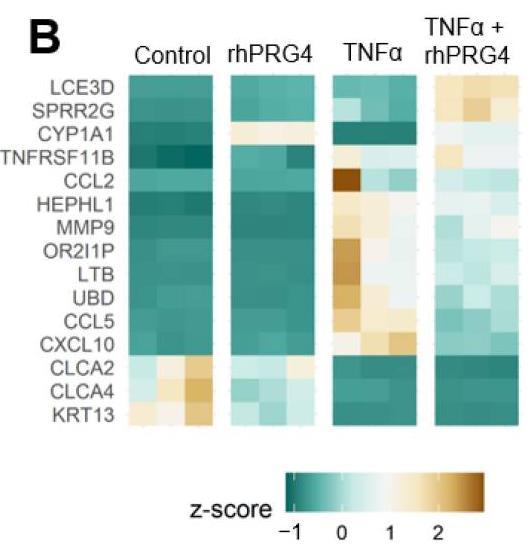
Fig2. Heatmap showing genes that were most significantly changed by TNFα and rhPRG4.
Case Study 2: Sandy ElSayed, 2021
To compare phagocytic activities of monocytes in peripheral blood mononuclear cells (PBMCs) from acute gout patients and normal subjects, examine monosodium urate monohydrate (MSU) crystal-induced IL-1β secretion ± recombinant human proteoglycan 4 (rhPRG4) or interleukin-1 receptor antagonist (IL-1RA), and study the anti-inflammatory mechanism of rhPRG4 in MSU stimulated monocytes. Acute gout PBMCs were collected from patients in the Emergency Department and normal PBMCs were obtained from a commercial source. PBMCs were incubated with IL-1RA (250ng/mL) or rhPRG4 (200μg/mL) and bead phagocytosis by monocytes was determined. THP-1 monocytes were treated with MSU crystals ± rhPRG4 and cellular levels of NLRP3 protein, pro-IL-1β, secreted IL-1β, and activities of caspase-1 and protein phosphatase-2A (PP2A) were quantified. The results showed that rhPRG4 reduced bead phagocytosis by normal and gout monocytes compared to IL-1RA and both treatments were efficacious in reducing IL-1β secretion (p<0.05). rhPRG4 reduced pro-IL-1β content, caspase-1 activity, conversion of pro-IL-1β to mature IL-1β and restored PP2A activity in monocytes. And rhPRG4 treatment reduced neutrophil accumulation and enhanced anti-inflammatory monocyte influx.

Fig3. rhPRG4 reduced IL-1β secretion by PBMCs of normal subjects.

Fig4. Representative flow cytometry histograms showing reduced ROS fluorescence intensity with rhPRG4 treatment.
Quality Guarantee
High Purity
.jpg)
Fig1. SDS-PAGE (Prg4-5499H)
Involved Pathway
PRG4 involved in several pathways and played different roles in them. We selected most pathways PRG4 participated on our site, such as , which may be useful for your reference. Also, other proteins which involved in the same pathway with PRG4 were listed below. Creative BioMart supplied nearly all the proteins listed, you can search them on our site.
| Pathway Name | Pathway Related Protein |
|---|
Protein Function
PRG4 has several biochemical functions, for example, polysaccharide binding,scavenger receptor activity. Some of the functions are cooperated with other proteins, some of the functions could acted by PRG4 itself. We selected most functions PRG4 had, and list some proteins which have the same functions with PRG4. You can find most of the proteins on our site.
| Function | Related Protein |
|---|---|
| polysaccharide binding | PRG4A,VTN,VTNA,GM106,MBL1,CD209B,TINAGL1,CLEC4G,AGL,ENPP2 |
| scavenger receptor activity | ACKR4,ENPP2,SCARA5,TMPRSS4A,DMBT1,COLEC12,CD163L1,TMPRSS4B,ABHD1,SCARF2 |
Interacting Protein
PRG4 has direct interactions with proteins and molecules. Those interactions were detected by several methods such as yeast two hybrid, co-IP, pull-down and so on. We selected proteins and molecules interacted with PRG4 here. Most of them are supplied by our site. Hope this information will be useful for your research of PRG4.
Dlg4;GRB2;MYC
Resources
Related Services
Related Products
References
- Ai, M; Cui, Y; et al. Anti-Lubricin Monoclonal Antibodies Created Using Lubricin-Knockout Mice Immunodetect Lubricin in Several Species and in Patients with Healthy and Diseased Joints. PLOS ONE 10:-(2015).
- Steele, BL; Alvarez-Veronesi, MC; et al. Molecular weight characterization of PRG4 proteins using multi-angle laser light scattering (MALLS). OSTEOARTHRITIS AND CARTILAGE 21:498-504(2013).


