POLRMT
-
Official Full Name
polymerase (RNA) mitochondrial (DNA directed) -
Overview
This gene encodes a mitochondrial DNA-directed RNA polymerase. The gene product is responsible for mitochondrial gene expression as well as for providing RNA primers for initiation of replication of the mitochondrial genome. Although this polypeptide has the same function as the three nuclear DNA-directed RNA polymerases, it is more closely related to RNA polymerases of phage and mitochondrial polymerases of lower eukaryotes. [provided by RefSeq, Jul 2008] -
Synonyms
POLRMT;polymerase (RNA) mitochondrial (DNA directed);APOLMT;MTRNAP;MTRPOL;h-mtRPOL;DNA-directed RNA polymerase, mitochondrial
| Cat.# | Product name | Source (Host) | Species | Tag | Protein Length | Price |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| POLRMT-1853H | Recombinant Human POLRMT protein, His-tagged | E.coli | Human | His | 282-405 aa | |
| POLRMT-1578H | Recombinant Human POLRMT protein | E.coli | Human | Non |
|
|
| POLRMT-27748TH | Recombinant Human POLRMT, His-tagged | E.coli | Human | His | 1051-1230 a.a. |
|
| POLRMT-3019HCL | Recombinant Human POLRMT 293 Cell Lysate | HEK293 | Human | Non |
|
Background
What is POLRMT protein?
POLRMT (RNA polymerase mitochondrial) gene is a protein coding gene which situated on the short arm of chromosome 19 at locus 19p13. This gene encodes a mitochondrial DNA-directed RNA polymerase. The gene product is responsible for mitochondrial gene expression as well as for providing RNA primers for initiation of replication of the mitochondrial genome. Although this polypeptide has the same function as the three nuclear DNA-directed RNA polymerases, it is more closely related to RNA polymerases of phage and mitochondrial polymerases of lower eukaryotes. The POLRMT protein is consisted of 1230 amino acids and its molecular mass is approximately 138.6 kDa.
What is the function of POLRMT protein?
POLRMT protein, also known as RNA polymerase mitochondria, plays a crucial role in mitochondrial transcription. It catalyzes the transcription of mitochondrial DNA (mtDNA) into RNA using the four ribonucleoside triphosphates as substrates. POLRMT is a component of the mitochondrial transcription initiation complex, which is composed of at least TFB2M, TFAM, and POLRMT itself. This complex is necessary for basal transcription of mitochondrial DNA. Additionally, POLRMT has DNA primase activity, catalyzing the synthesis of short RNA primers necessary for the initiation of lagging-strand DNA synthesis from the origin of light-strand DNA replication (OriL). It is an essential part of the mitochondrial machinery, contributing to the cell's energy production and other vital functions.
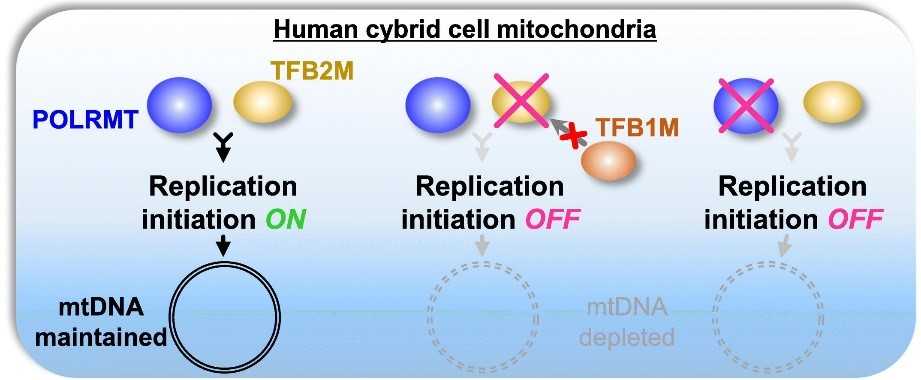
Fig1. TFB2M and POLRMT are crucial for the priming of not only strand-asynchronous but also strand-coupled replication. (Teppei Inatomi, 2022)
POLRMT Related Signaling Pathway
POLRMT is essential for the transcription of mitochondrial DNA (mtDNA) and is involved in the replication process as the sole mitochondrial primase. It works in conjunction with mitochondrial transcription factors A (TFAM) and B2 (TFB2M) to initiate transcription from light-strand and heavy-strand promoters (LSP and HSP). POLRMT is a key regulator in the communication between the nucleus and mitochondria, influencing mitochondrial function and cellular metabolism. There is evidence suggesting that high expression levels of POLRMT are linked to the activation of the WNT/β-catenin signaling pathway, which plays a role in cell proliferation, differentiation, and tumorigenesis. POLRMT has been implicated in the Akt-mTOR pathway, which is significant in the development and progression of certain diseases, including osteosarcoma.
POLRMT Related Diseases
POLRMT mutations can lead to a spectrum of mitochondrial disorders characterized by multi-organ involvement and varied clinical features. These disorders can manifest as mtDNA depletion or deletions and are associated with impaired mitochondrial function. POLRMT mutations have been associated with a range of neurological presentations, including developmental delay, intellectual disabilities, hypotonia, muscle weakness, and speech delay. POLRMT depletion impairs mitochondrial functions in prostate cancer cells, leading to mitochondrial depolarization, oxidative stress, and ATP depletion, which can inhibit cancer cell viability, proliferation, and migration. POLRMT has been implicated in the development and progression of osteosarcoma, where mitochondrial hyperfunction and the Akt-mTOR signaling pathway are known to play significant roles. POLRMT knockout mice exhibit severe mitochondrial dysfunction and dilated cardiomyopathy, suggesting a potential link between POLRMT function and heart disease.
Bioapplications of POLRMT
Medically, POLRMT is an important biomarker and potential therapeutic target because it has been linked to a variety of diseases, such as prostate cancer, neurological diseases, and certain types of cancer. By studying the function and regulatory mechanisms of POLRMT, scientists can develop diagnostic methods and treatment strategies for these diseases. For example, by detecting POLRMT expression levels in prostate cancer tissue, doctors can assess disease progression and patient prognosis. In the field of biotechnology, the understanding of POLRMT contributes to the development of new tools for studying mitochondrial function and disease mechanisms, as well as applications in drug screening and toxicity testing.
Case Study
Case Study 1: Yongkang Huang, 2023
Mitochondrial RNA polymerase (POLRMT) is essential for the expression of mitochondrial genes. In recent studies, POLRMT expression promoted non-small cell cancer cell proliferation in cell lines and xenografts. The present study investigated the impact of POLRMT expression and function on lung adenocarcinoma (LUAD) patients. Multi-omics data (genomics, transcriptomics, and proteomics) from publicly available databases were used to assess the role of POLRMT expression and function in LUAD. These findings were further verified using cancer tissues from clinical samples. POLRMT was over-expressed in LUADs, with mutation frequencies ranging from 1.30% to 5.71%. Over-expression of POLRMT was associated with an abnormal clinicopathological condition resulting in a decreased lifespan. Furthermore, gene sets enrich analysis revealed that POLRMT expression was linked to WNT/beta-catenin signaling; the expression of downstream target genes was positively correlated with POLRMT expression. Also, POLRMT expression was positively correlated with immunosuppressive genes, thereby affecting immune infiltration.

Fig1. POLRMT protein expression in CPTAC LUAD samples.

Fig2. Alteration frequency of POLRMT in LUAD.
Case Study 2: Jessica Nouws, 2016
To translate the 13 mtDNA-encoded mRNAs involved in oxidative phosphorylation (OXPHOS), mammalian mitochondria contain a dedicated set of ribosomes comprising rRNAs encoded by the mitochondrial genome and mitochondrial ribosomal proteins (MRPs) that are encoded by nuclear genes and imported into the matrix. In addition to their role in the ribosome, several MRPs have auxiliary functions or have been implicated in other cellular processes like cell cycle regulation and apoptosis. For example, we have shown that human MRPL12 binds and activates mitochondrial RNA polymerase (POLRMT), and hence has distinct functions in the ribosome and mtDNA transcription. Here we provide concrete evidence that there are two mature forms of mammalian MRPL12 that are generated by a two-step cleavage during import, involving efficient cleavage by mitochondrial processing protease and a second inefficient or regulated cleavage by mitochondrial intermediate protease. We also show that knock-down of MRPL12 by RNAi results in instability of POLRMT, but not other primary mitochondrial transcription components, and a corresponding decrease in mitochondrial transcription rates. Knock-down of MRPL10, the binding partner of MRPL12 in the ribosome, results in selective degradation of the mature long form of MRPL12, but has no effect on POLRMT.

Fig3. Western blot analysis of POLRMT in HeLa cells.
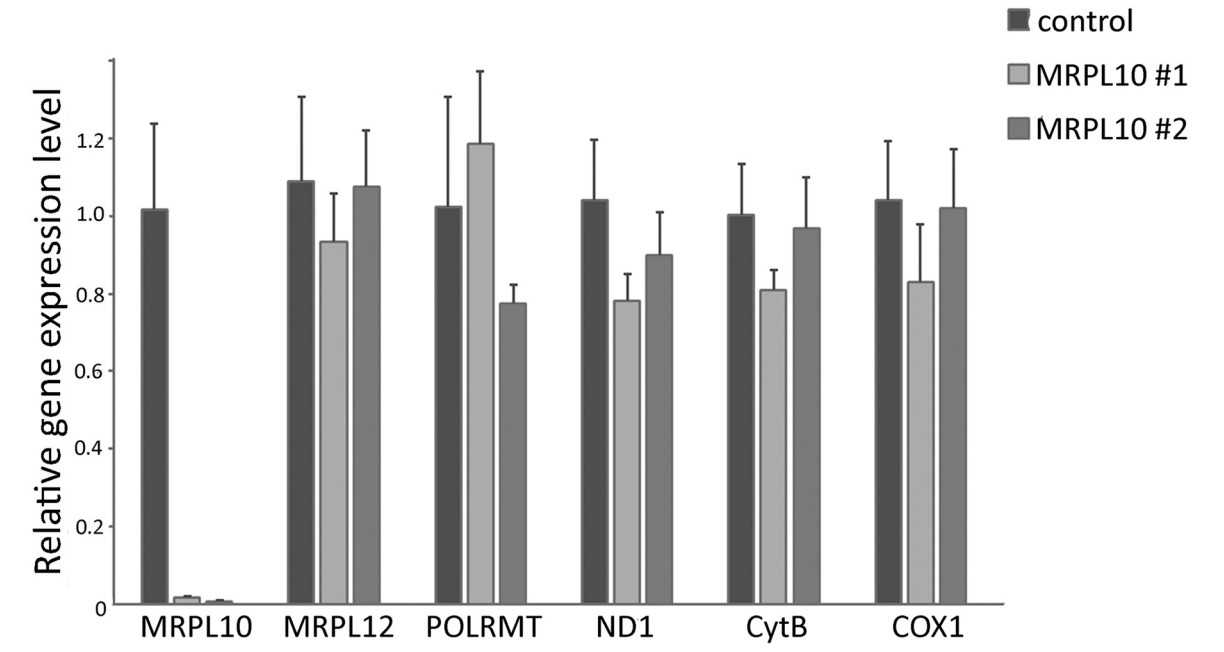
Fig4. Results of quantitative RT-PCR of POLRMT in HEK293T cells.
Quality Guarantee
High Purity
.jpg)
Fig1. SDS-PAGE (POLRMT-1853H)
Involved Pathway
POLRMT involved in several pathways and played different roles in them. We selected most pathways POLRMT participated on our site, such as Gene Expression,Mitochondrial Gene Expression,Mitochondrial biogenesis, which may be useful for your reference. Also, other proteins which involved in the same pathway with POLRMT were listed below. Creative BioMart supplied nearly all the proteins listed, you can search them on our site.
| Pathway Name | Pathway Related Protein |
|---|---|
| Transcriptional activation of mitochondrial biogenesis | MTERF,GABPA,C10orf2,PPRC1,GABPB1,TFB1M,POLG2 |
| Transcription from mitochondrial promoters | TFB2M,MTERF |
| Mitochondrial transcription initiation | TFB2M |
| Gene Expression | MADD,ZNF791,MED25,TH1L,NR1H3,COX6C,AGO3B,NR2F6,POLR3H,GTF3A |
| RNA Polymerase I, RNA Polymerase III, and Mitochondrial Transcription | PTRF,NFIC,ZNF143,NFIA,GTF3A,GATAD2A,ZFP143,NFIB,SNAPC2,SNAPC5 |
| Organelle biogenesis and maintenance | MRPL45,PKD2,MRPS35,TUFM,MARK4,MRPL52,ARL3,MRPS36,EXOC3,TTBK2 |
| Mitochondrial biogenesis | TFB1M,GABPA,ESRRA,TFB2M,C10orf2,GABPB1,MTERF,PPRC1,PPARGC1B,POLG2 |
| Mitochondrial Gene Expression | TFB2M,ESRRA,TFB1M,PPRC1,PPARGC1B,MTERFD1 |
Protein Function
POLRMT has several biochemical functions, for example, DNA binding,DNA-directed RNA polymerase activity,poly(A) RNA binding. Some of the functions are cooperated with other proteins, some of the functions could acted by POLRMT itself. We selected most functions POLRMT had, and list some proteins which have the same functions with POLRMT. You can find most of the proteins on our site.
| Function | Related Protein |
|---|---|
| DNA-directed RNA polymerase activity | RPAP1,POLR2EB,POLR3B,POLR3K,CD3EAP,POLR2GL,POLR3H,POLR2A,POLR3F,POLR1C |
| protein binding | MYBPC3,EVLA,EXOC4,TBC1D5,MRPL1,ATRNL1,GP9,ARHGAP1,YAF2,RB1 |
| poly(A) RNA binding | KTN1,PLEC,LRRC47,RPS6,ATP5C1,EIF2C3,EIF1,ZNF638,MBNL3,THUMPD1 |
| DNA binding | TFEC,CREB3,DACH1,ZSCAN10,RAD51D,PAX6B,ATOH8,RFXANK,DNAJC2,POLR2I |
Interacting Protein
POLRMT has direct interactions with proteins and molecules. Those interactions were detected by several methods such as yeast two hybrid, co-IP, pull-down and so on. We selected proteins and molecules interacted with POLRMT here. Most of them are supplied by our site. Hope this information will be useful for your research of POLRMT.
TFB1M;NFKBIA;NFKB2;KBTBD7;ssrna_ug
Resources
Related Services
Related Products
References


