PDCD4
-
Official Full Name
programmed cell death 4 (neoplastic transformation inhibitor) -
Overview
This gene is a tumor suppressor and encodes a protein that binds to the eukaryotic translation initiation factor 4A1 and inhibits its function by preventing RNA binding. Alternative splicing results in multiple transcript variants. [provided by RefSeq, Dec 2010] -
Synonyms
PDCD4;programmed cell death 4 (neoplastic transformation inhibitor);H731;programmed cell death protein 4;protein 197/15a;nuclear antigen H731;neoplastic transformation inhibitor protein
Recombinant Proteins
- Human
- Mouse
- Rhesus macaque
- Chicken
- E.coli
- Mammalian Cell
- Wheat Germ
- Rabbit
- HEK293
- In Vitro Cell Free System
- GST
- His
- Non
- His&Fc&Avi
Background
What is PDCD4 protein?
PDCD4 (programmed cell death 4) gene is a protein coding gene which situated on the long arm of chromosome 10 at locus 10q25. This gene is a tumor suppressor and encodes a protein that binds to the eukaryotic translation initiation factor 4A1 and inhibits its function by preventing RNA binding. The protein encoded by this gene is a tumor suppressor. And it inhibits tumor promoter-induced neoplastic transformation. The PDCD4 protein is consisted of 469 amino acids and its molecular mass is approximately 51.7 kDa.
What is the function of PDCD4 protein?
PDCD4 is restricted to the nucleus in proliferating cells. Expression of PDCD4 is modulated by cytokines in natural killer and T cells. PDCD4 takes part in apoptosis. PDCD4 is a translation inhibitor targeted for degradation during tumor promotion. PDCD4 promotes colonic neoplastic transformation and tumor invasion. PDCD4 is an important target for microrna R-21 in breast cancer cells. PDCD4 is a proapoptotic protein involved in TGF-beta1-induced apoptosis in human HCC cells, and a tumor suppressor in hepatocarcinogenesis. PDCD4 restraines tumor progression in colon carcinoma cells by the novel mechanism of down-regulating MAP4K1 transcription, with consequent inhibition of c-Jun activation and AP-1-dependent transcription.

Fig1. PDCD4 regulates cell apoptosis, proliferation, invasion, and metastasis apoptosis. (Kaikai Lu, 2020)
PDCD4 Related Signaling Pathway
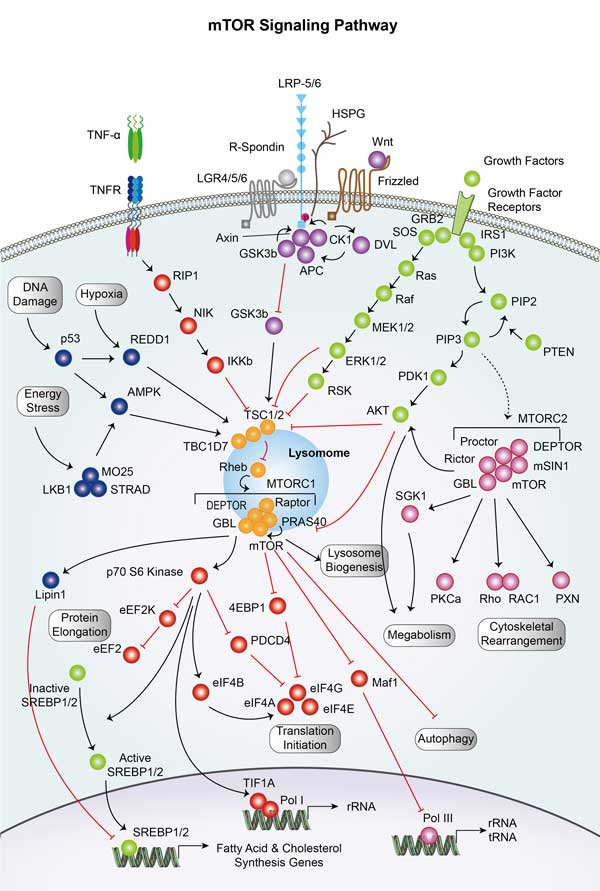
1. Akt/mTOR signaling pathway: PDCD4 is a negative regulator of mTOR (mammalian target protease), involved in the regulation of cell growth, proliferation and apoptosis.
2. MAPK/ERK signaling pathway: PDCD4 is also associated with the MAPK (mitogen-activated protein kinase) /ERK (Extracellular signal-regulated kinase) signaling pathway, which plays a key role in cell proliferation, differentiation, and survival.
3. Transcriptional regulation: PDCD4 can affect the activity of some transcription factors and thus participate in the regulation of gene expression. Also, PDCD4 inhibits protein translation process by competitively binding eIF4A with eIF4G.
PDCD4 Related Diseases
In cancer, PDCD4 has been found to be expressed at reduced levels in tumor tissue, and its dysfunction promotes tumor cell growth and metastasis. In addition, PDCD4 has also been found to be associated with inflammation-related diseases such as rheumatoid arthritis and inflammatory bowel disease. In addition, the role of PDCD4 in cardiovascular diseases has also been concerned, and studies have shown that PDCD4 is associated with diseases such as heart muscle disease and atherosclerosis.
Bioapplications of PDCD4
PDCD4 protein can improve the response of tumor cells to therapeutic drugs, which has important significance in treatment regimens such as chemotherapy. In addition, PDCD4 transgenic mice were found to be resistant to malignant transformation of skin cancer, indicating its potential in preventing tumor progression. At the same time, PDCD4 protein is also involved in the induction of inflammation, which may provide a new research direction for the treatment of inflammatory diseases in the future.
Case Study
Case study 1: Ekaterina Shuvalova, 2021
Programmed cell death 4 protein (PDCD4) regulates many vital cell processes, although is classified as a tumor suppressor because it inhibits neoplastic transformation and tumor growth. PDCD4 is known to inhibit translation initiation by binding to eukaryotic initiation factor 4A and elongation of oncogenic c- and A-myb mRNAs. Additionally, PDCD4 has been shown to interact with poly(A)-binding protein (PABP), which affects translation termination, although the significance of this interaction is not fully understood.
Using in vitro translation systems, the researchers revealed that PDCD4 directly activates translation termination. PDCD4 stimulates peptidyl-tRNA hydrolysis induced by a complex of eukaryotic release factors, eRF1-eRF3. PDCD4 regulates translation termination by facilitating the binding of release factors to the ribosome, increasing the GTPase activity of eRF3, and dissociating eRF3 from the posttermination complex.

Fig1. GTPase activity of eRF3a or eRF3c mixed with 80S and eRF1 in presence/absence of PDCD4.

Case study 2: Yue Li, 2018
Endometriosis (EM) is a kind of estrogen-dependent disease in reproductive-age women. Ovarian EM is the most common type. Although EM is a benign disease, it shares many similar features with cancers. Programmed cell death 4 (PDCD4), a newly identified tumor suppressor, plays an important role in inhibiting tumorigenesis and tumor progression at the transcriptional and translational levels.
To explore the roles of PDCD4 in EM, the researchers detected the expression of PDCD4 in control endometrium and eutopic/ectopic endometrium of ovarian EM patients, and analyzed the effects of PDCD4 on the biological behaviors of endometrial cell lines and primary endometrial cells. PDCD4 effectively inhibited the proliferation and colony-forming ability of endometrial cells maybe by inhibiting cell autophagy. In addition, PDCD4 also suppressed the migration and invasion ability of endometrial cells, the mechanism may be related to NF-κB/MMP2/MMP9 signal pathway.

Fig3. PDCD4 overexpression in HEC-1-A cells had no significant effect on the cell cycle of endometrial cells.

Quality Guarantee
High Purity

Fig1. SDS-PAGE (PDCD4-4201H) (PROTOCOL for western blot)
Involved Pathway
PDCD4 involved in several pathways and played different roles in them. We selected most pathways PDCD4 participated on our site, such as Proteoglycans in cancer,MicroRNAs in cancer, which may be useful for your reference. Also, other proteins which involved in the same pathway with PDCD4 were listed below. Creative BioMart supplied nearly all the proteins listed, you can search them on our site.
| Pathway Name | Pathway Related Protein |
|---|---|
| Proteoglycans in cancer | MAP2K1,SLC9A1,LUM,WNT7B,ANK2,IGF1,PLAUR,VAV2,ESR1,HRAS |
| MicroRNAs in cancer | BMF,CCND2,CCNE1,NOTCH1,BMPR2,SIRT1,TP63,ABCB1A,PRKCA,Abcb1b |

Fig1. mTOR signaling pathway.

Fig2. PDCD4 inhibits tumorigenesis through multiple pathways. (Kaikai Lu, 2020)
Protein Function
PDCD4 has several biochemical functions, for example, RNA binding,protein binding. Some of the functions are cooperated with other proteins, some of the functions could acted by PDCD4 itself. We selected most functions PDCD4 had, and list some proteins which have the same functions with PDCD4. You can find most of the proteins on our site.
| Function | Related Protein |
|---|---|
| protein binding | CXCL9,HYAL3,MAVS,SMARCAD1,SEC61B,SPA17,EXOC8,MED6,SPDYE2,CLDN18 |
| RNA binding | A1CF,CPSF2,ALYREF,QKIA,ZFP346,RPL22,EIF4G2A,NOL9,RAE1,RC3H2 |
Interacting Protein
PDCD4 has direct interactions with proteins and molecules. Those interactions were detected by several methods such as yeast two hybrid, co-IP, pull-down and so on. We selected proteins and molecules interacted with PDCD4 here. Most of them are supplied by our site. Hope this information will be useful for your research of PDCD4.
EIF4A2;EIF4A1;RELA;EIF4A3;RPS13
PDCD4 Related Signal Pathway
Resources
Related Services
Related Products
References