PADI4
-
Official Full Name
peptidyl arginine deiminase, type IV -
Overview
This gene is a member of a gene family which encodes enzymes responsible for the conversion of arginine residues to citrulline residues. This gene may play a role in granulocyte and macrophage development leading to inflammation and immune response. -
Synonyms
PADI4;peptidyl arginine deiminase, type IV;PADI5, peptidyl arginine deiminase, type V;protein-arginine deiminase type-4;PAD;PDI4;PDI5;EC 3.5.3.15;HL 60 PAD;PAD 4;PADI 4;PADI 5;PADI H protein;PADI5;PDI 4;PDI 5;Peptidyl arginine deiminase type IV;Peptidyl arginine deiminase type V;Peptidylarginine deiminase IV;Protein arginine deiminase;Protein arginine deiminase type 4;Protein arginine deiminase type IV;HL-60 PAD;PADI-H protein;OTTHUMP00000002482;protein-arginine deiminase type IV;peptidyl arginine deiminase, type V;PAD4
Recombinant Proteins
- Human
- Cynomolgus
- Mouse
- Rat
- E.coli
- Sf9 Insect Cell
- N-His
- Mammalian Cell
- Insect Cell
- Baculovirus-Insect cells
- Insect cell
- HEK293
- Insect cells
- Mammalian cells
- HEK293T
- His
- Flag
- Non
- GST
- His&GST
- Twin Strep
- His&Fc&Avi
- Myc&DDK
- Strep
- His&Myc
Background
What is PADI4 protein?
PADI4 gene (peptidyl arginine deiminase 4) is a protein coding gene which situated on the short arm of chromosome 1 at locus 1p36. PADI4 is found in a variety of cells and tissues, including macrophages, monocytes, granulocytes, and cancer cells. PADI4 is a calcium-dependent enzyme that catalyzes the conversion of arginine residues in specific proteins (such as histones) to citcitline in the human body. PADI4 regulates chromatin structure and gene expression through citrolination of histones H1, H3 and H4, thereby affecting the pluripotency and maintenance of stem cells. In addition, PADI4 also plays a role in the innate immune response by promoting the deaggregation of chromatin to help neutrophils form extracellular traps (NETs), a structure made of DNA fibers that neutrophils release during inflammation to trap pathogens. The PADI4 protein is consisted of 663 amino acids and PADI4 molecular weight is approximately 74.1 kDa.
What is the function of PADI4 protein?
PADI4 can catalyze the conversion of arginine residues in histones to citcitline, and PADI4 leads to the dissociation of H1 from chromatin through citcitline, promoting chromatin desagglutination, thus contributing to the maintenance of pluripotency and self-renewal of stem cells. In the innate immune response of neutrophils, PADI4 is involved in the formation of neutrophils extracellular traps (NETs) by promoting the desagglutination of chromatin and the formation of H1R54ci, which are DNA fiber structures released by neutrophils to trap pathogens. PADI4 can also act as a coactivator or cosuppressor of a variety of transcription factors, affecting gene expression through its citrolination activity, such as inhibiting gene transcription by affecting the methylation state of histone H3.
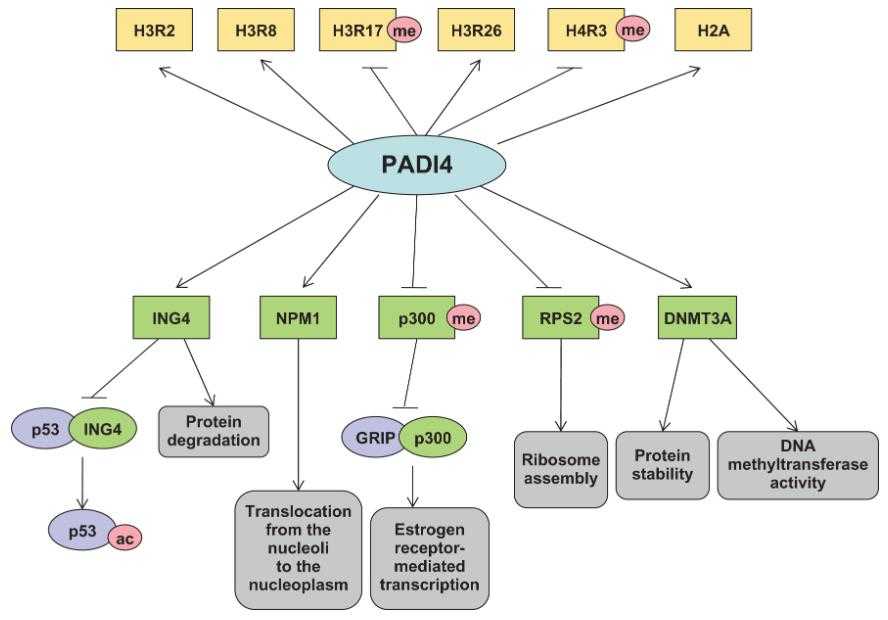
Fig1. Schematic representation of the major substrates and regulation mechanism of PADI4. (Qiaoli Zhai, 2017)
PADI4 Related Signaling Pathway
PADI4 regulates pluripotency and self-renewal of stem cells by affecting chromatin structure and gene expression through citrolination of histones. PADI4 plays a role in cell differentiation, especially when HL-60 cells differentiate into granulocytes and monocytes, and PADI4 expression is induced. PADI4 acts as a transcriptional coactivator or co-repressor that influences gene expression through its citrullination activity, for example in the estrogen receptor and p53-regulated gene promoter regions. PADI4 is involved in the regulation of apoptosis by affecting p53 signaling pathway.
PADI4 Related Diseases
PADI4 has been implicated in a variety of diseases, especially in the pathogenesis of autoimmune diseases and cancer. PADI4, through its catalytic citrullination, affects protein structure and function, and then participates in the occurrence and development of diseases. In autoimmune diseases such as rheumatoid arthritis, citrullination caused by PADI4 can produce autoantigens that trigger an immune response. In addition, PADI4 also plays a role in tumor development, and its up-regulated expression in cancers such as lung cancer is associated with tumor cell invasion, migration, and EMT processes. PADI4 is also involved in regulating stem cell pluripotency and self-renewal, affecting the function of the blood system.
Bioapplications of PADI4
As an important histone modifying enzyme, PADI4 is involved in the regulation of key biological processes such as gene expression, cell cycle, stem cell pluripotency maintenance, and cell differentiation. In terms of drug development, the research and development of PADI4 inhibitors provide new strategies for the treatment of certain autoimmune diseases such as rheumatoid arthritis, because the abnormal activity of PADI4 is closely related to the occurrence and development of these diseases. In addition, PADI4's role in tumor development makes it a potential cancer therapeutic target, and PADI4 inhibitors may help inhibit tumor cell proliferation, invasion, and metastasis.
Case Study
Case Study 1: Meiyan Liu, 2019
Lung cancer is a complex disease involving multiple genetic and phenotypic alterations. As a histone modification enzyme, protein‑arginine deiminase type‑4 (PADI4) and its downstream signaling have been studied in the progression of a variety of types of human cancer, but data on PADI4‑mediated posttranslational modification in lung cancer are lacking. The aim of present study was to evaluate the expression of PADI4 and its associated molecular signaling in lung cancer metastasis. The results of the present study indicated that PADI4 was overexpressed in lung cancer cells, while knockdown of PADI4 could lead to attenuation of the lung cancer cell invasion and migration phenotype, which was further verified by determining the epithelial‑mesenchymal transition (EMT) marker proteins. Additionally, it was demonstrated that stable knockdown of PADI4 in A549 lung cancer cells resulted in a striking reduction of the EMT‑associated Snail1/mothers against decapentaplegic homolog 3/4 transcriptional complex, which was consistent with alterations in migratory and invasive phenotypes of A549 lung cancer cells.
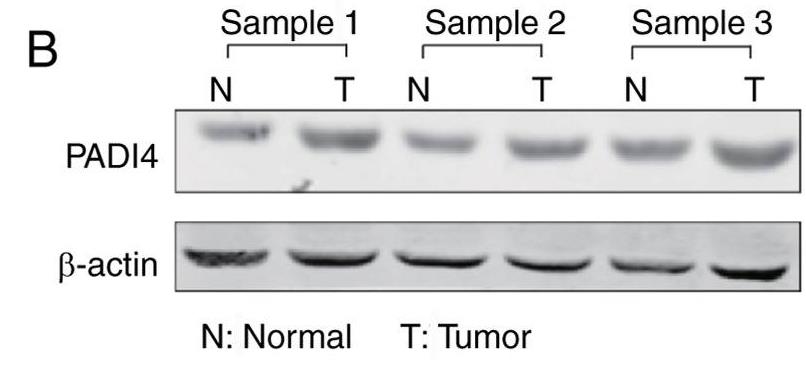
Fig1. The expression of PADI4 was detected by western blotting in lung cancer tissues and paired non-tumoral tissues.

Fig2. The invasion potential of A549 cells and shPADI4 A549 cells assessed by Transwell assay.
Case Study 2: Bongkyun Park, 2015
Cell adhesion molecules play a critical role in inflammatory processes and atherosclerosis. In this study, researchers investigated the effect of ramalin, a chemical compound from the Antarctic lichen Ramalina terebrata, on vascular cell adhesion molecule-1 (VCAM-1) expression induced by TNF-α in vascular smooth muscular cells (VSMCs). Ramalin inhibited THP-1 (human acute monocytic leukemia cell line) cell adhesion to TNF-α-stimulated VSMCs. Ramalin suppressed TNF-α-induced production of reactive oxygen species (ROS), PADI4 expression, and phosphorylation of p38, ERK, and JNK. Moreover, ramalin inhibited TNF-α-induced translocation of NF-κB and AP-1. Inhibition of PADI4 expression by small interfering RNA or the PADI4-specific inhibitor markedly attenuated TNF-α-induced activation of NF-κB and AP-1 and VCAM-1 expression in VSMCs.

Fig3. NAC significantly inhibited the expression of PADI4 induced by treatment with TNF-α in both cell types.

Fig4. MOVAS-1 cells were transiently transfected with PADI4 targeting siRNA.
Quality Guarantee
High Bioactivity
.jpg)
Fig1. Activity Data (PADI4-037H)
.
.jpg)
Fig2. Activity Data (PADI4-20H)
Involved Pathway
PADI4 involved in several pathways and played different roles in them. We selected most pathways PADI4 participated on our site, such as Chromatin modifying enzymes,Chromatin organization,protein citrullination, which may be useful for your reference. Also, other proteins which involved in the same pathway with PADI4 were listed below. Creative BioMart supplied nearly all the proteins listed, you can search them on our site.
| Pathway Name | Pathway Related Protein |
|---|---|
| Chromatin organization | BRPF3,KDM4B,SMARCB1B,MORF4L2,ATXN7,MBIP,KAT8,ING5B,TADA2B,RBBP5 |
| protein citrullination | PADI2,PADI3,PADI6,PADI1 |
| Chromatin modifying enzymes | JHDM1D,MSL1A,PHF15,SUZ12,MCRS1,ING5,BRD8,SMARCD3,C17orf81,DR1 |
Protein Function
PADI4 has several biochemical functions, for example, arginine deiminase activity,calcium ion binding,protein binding. Some of the functions are cooperated with other proteins, some of the functions could acted by PADI4 itself. We selected most functions PADI4 had, and list some proteins which have the same functions with PADI4. You can find most of the proteins on our site.
| Function | Related Protein |
|---|---|
| protein-arginine deiminase activity | PADI6,PADI3,PADI2,PADI1 |
| calcium ion binding | NECAB3,PCDHA10,MAN1A,TBC1D8B,PCDH1G32,RPH3AL,EGFEM1,THBS3A,EFCAB5,PCDH1G30 |
| protein binding | DHX16,THBS4,TIMM10,TMCO6,PDE1B,UBAC1,CWC22,RIT1,IGFBP7,MFN1 |
Interacting Protein
PADI4 has direct interactions with proteins and molecules. Those interactions were detected by several methods such as yeast two hybrid, co-IP, pull-down and so on. We selected proteins and molecules interacted with PADI4 here. Most of them are supplied by our site. Hope this information will be useful for your research of PADI4.
ANXA4;LRRK2;DNPEP
Resources
Related Services
Related Products
References
- Kochi, Y; Suzuki, A; et al. Genetic basis of rheumatoid arthritis: A current review. BIOCHEMICAL AND BIOPHYSICAL RESEARCH COMMUNICATIONS 452:254-262(2014).
- Guzman-Guzman, IP; Reyes-Castillo, Z; et al. Polymorphisms and functional haplotype in PADI4: Further evidence for contribution on rheumatoid arthritis susceptibility and anti-cyclic citrullinated peptide antibodies in a western Mexican population. IMMUNOLOGY LETTERS 163:214-220(2015).


