NOS2
-
Official Full Name
nitric oxide synthase 2, inducible -
Overview
Nitric oxide synthase, inducible is an enzyme that in humans is encoded by the NOS2 gene. Nitric oxide is a reactive free radical which acts as a biologic mediator in several processes, including neurotransmission and antimicrobial and antitumoral activities. This gene encodes a nitric oxide synthase which is expressed in liver and is inducible by a combination of lipopolysaccharide and certain cytokines. Three related pseudogenes are located within the Smith-Magenis syndrome region on chromosome 17. Alternative splicing of this gene results in two transcript variants encoding different isoforms. -
Synonyms
NOS2;nitric oxide synthase 2, inducible;HEP-NOS;NOS;nitric oxide synthase 2A (inducible, hepatocytes);Hepatocyte NOS;Inducible NO synthase;Peptidyl-cysteine S-nitrosylase NOS2;NOS type II;EC 1.14.13.39;INOS;nitric oxide synthase, inducible;nitric oxide synthase, macrophage;NOS, type II;inducible NOS;OTTHUMP00000163279;NOS2A
Recombinant Proteins
- Human
- Mouse
- Rat
- Chicken
- E.coli
- Mammalian Cell
- Insect Cell
- HEK293
- HEK293T
- E. coli
- Wheat Germ
- Mammalian cells
- His
- Non
- His&T7
- His&Fc&Avi
- Myc&DDK
- GST
- Flag
Background
What is NOS2 Protein?
NOS2 gene (nitric oxide synthase 2) is a protein coding gene which situated on the long arm of chromosome 17 at locus 17q11. Nitric oxide is a reactive free radical which acts as a biologic mediator in several processes, including neurotransmission and antimicrobial and antitumoral activities. This gene encodes a nitric oxide synthase which is expressed in liver and is inducible by a combination of lipopolysaccharide and certain cytokines. The NOS2 protein is consisted of 1153 amino acids and NOS2 molecular weight is approximately 131.1 kDa.
What is the Function of NOS2 Protein?
It is mainly responsible for catalyzing the oxidation of L-arginine to nitric oxide (NO), which requires the participation of NADPH, oxygen, heme, FAD, FMN and calmodulin. In immune response, NOS2 plays an important role in both innate and adaptive immune phases. Especially in the early stages of infection, NOS2 expression not only has antibacterial effects, but also regulates the function of natural killer cells and the expression of cytokines such as interferon-γ (IFN-γ) or transforming growth factor-β (TGF-β). In addition, NOS2 is involved in inflammatory responses, enhancing the synthesis of pro-inflammatory mediators such as interleukin 6 (IL6) and interleukin 8 (IL8). NOS2 activity is regulated by a variety of factors, including intracellular calcium ion levels, pH, and substrate availability.
NOS2 Related Signaling Pathway
NF-κB/iNOS-NO signaling pathway is a highly conserved signaling pathway, which is involved in many biological processes such as immunoinflammatory response, apoptosis and tumorigenesis. The activation of NF-κB/iNOS-NO signaling pathway is related to the occurrence and development of many clinical diseases. The NOS family includes several different subtypes, such as endothelial (eNOS), inducible (iNOS), and neural (nNOS). These subtypes catalyze the production of nitric oxide (NO), which plays a messenger role in a variety of functions such as vasodilation, neurotransmission, anti-tumor and anti-pathogenic activity. Different NOS subtypes may be involved in different regulatory processes, for example, during pain, nNOS is mainly observed at the spinal cord level or in neuropathic pain models, while iNOS is upregulated in inflammatory tissues and is involved in the development of hyperanalgesia, inflammation and neuropathic pain.
NOS2 Related Diseases
When NOS2 is overexpressed or abnormally active, it can lead to a range of diseases. In terms of autoimmune diseases, NOS2 has been linked to diseases such as rheumatoid arthritis and multiple sclerosis. In infectious diseases, abnormalities in NOS2 may be related to the severity and duration of infection, since NOS2 is involved in regulating the immune response. In terms of cardiovascular diseases, excessive activation of NOS2 is associated with hypertension and atherosclerosis. In neurodegenerative diseases such as Parkinson's disease and Alzheimer's disease, abnormal NOS2 activity may affect the function of neurons. In addition, the development of cancer is also related to the expression level and activity of NOS2, which can affect the growth and metastasis of tumors by promoting angiogenesis and other mechanisms. Finally, the occurrence and development of some inflammatory diseases are also related to the abnormal activity of NOS2.
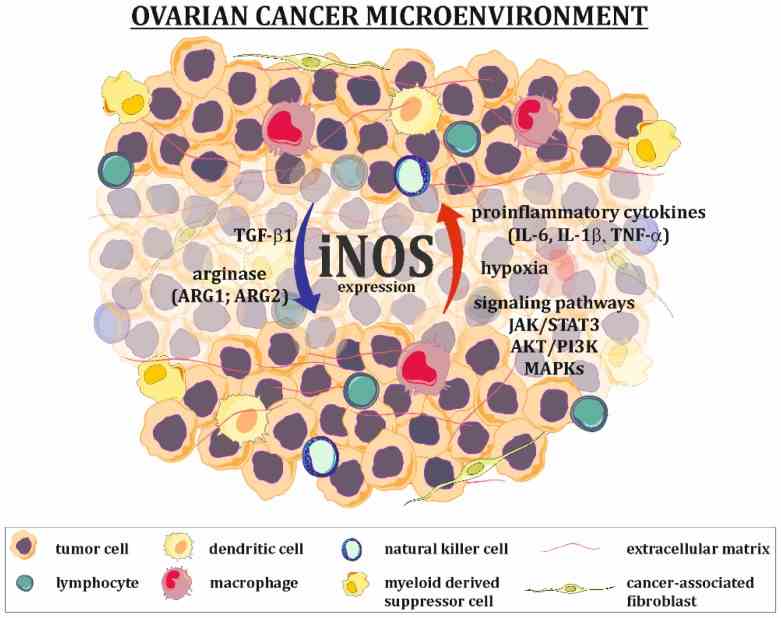
Fig1. Regulation of iNOS expression in ovarian cancer microenvironment. (Michal Kielbik, 2019)
Bioapplications of NOS2
Because NOS2 is associated with a variety of diseases, inhibiting NOS2 activity or reducing its expression is a potential therapeutic strategy. For example, specific inhibitors or gene regulation are used to reduce the expression of NOS2, thereby slowing tumor growth and metastasis. As an important immune effector molecule, NOS2 is induced to be expressed in macrophages to fight pathogens by catalyzing the synthesis of nitric oxide. In addition, by regulating the activity of NOS2, blood vessel function can be improved and diseases such as hypertension and atherosclerosis can be alleviated.
Case Study
Case Study 1: Paige C Arneson-Wissink, 2021
Muscle stem cells (MuSCs) are the cellular compartment responsible for muscle regeneration, which makes MuSCs an intriguing target in the context of wasting muscle. Molecular studies investigating MuSCs and skeletal muscle wasting largely focus on transcriptional changes, but our group and others propose that metabolic changes are another layer of cellular regulation underlying MuSC dysfunction in cancer cachexia. In the present study, researchers combined gene expression and non-targeted metabolomic profiling of myoblasts exposed to wasting conditions (cancer cell conditioned media, CC-CM) to derive a more complete picture of the myoblast response to wasting factors. Notably, arginine metabolism was a highly enriched pathway in combined metabolomic and transcriptomic data. Arginine catabolism generates nitric oxide (NO), an important signaling molecule known to have negative effects on mature muscle. They hypothesize that tumor-derived disruptions in Nitric Oxide Synthase (NOS)2-regulated arginine catabolism impair differentiation of MuSCs. The work presented here further investigates the effect of NOS2 overactivity on myoblast proliferation and differentiation.

Fig1. NOS2 total protein, detected by antibody-based flow cytometry.

Fig2. Eccentricity scores for myosin heavy chain-positive objects, binned into 3 sizes.
Case Study 2: Qiyue Gao, 2016
Prior to this study, it was not known whether inducible nitric oxide synthase (iNOS or NOS2), a signature molecule of inflammation, could be intensified by IL-17 when combined with IFN-γ. Thus, researchers explored the roles and underlying mechanisms of IL-17 and IFN-γ in the regulation of NOS2 expression in RAW 264.7 cells using qPCR, western blot analysis, colorimetric analysis, ChIP assay and statistical analysis. Although IL-17 alone did not induce NOS2 expression or nitric oxide (NO) production, as shown by western blot analysis and colorimetric analysis, it intensified IFN-γ-induced NOS2 upregulation and NO production in RAW 264.7 cells. The alteration of relevant transcription factors demonstrated that a combination of IFN-γ and IL-17 enhanced Tyr701-phosphorylated signal transducer and activator of transcription 1 [p-STAT1(Y701)] and nuclear factor-κB (NF-κB) activation, nuclear translocations and their binding to the NOS2 promoter, compared with IFN-γ alone, as illustrated by the results of the western blot analysis and ChIP assay. In addition, IFN-γ increased phosphorylated (p-)p38 mitogen-activated protein kinase (MAPK), and accelerated the activation of the NF-κB pathway and the expression of NOS2, but phosphorylated extracellular signal-regulated kinase 1/2 (p-ERK1/2) was reduced by treatment with IFN-γ and IL-17. Taken together, these results suggest that IL-17 intensified IFN-γ-induced NOS2 upregulation and NO production by increasing the transcription activity of p-STAT1(Y701) and NF-κB in RAW 264.7 cells.
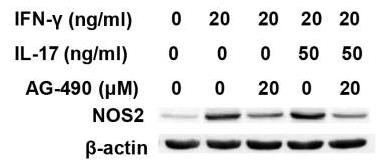
Fig3. Representative western blot analysis of NOS2 in RAW 264.7 cells.
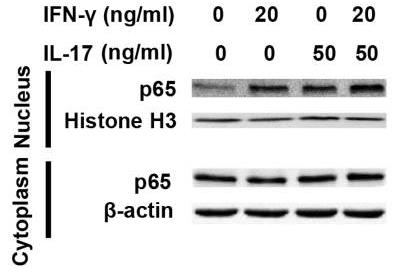
Fig4. Representative western blot analysis of nuclear translocation of p65 in RAW 264.7 cells.
Quality Guarantee
High Purity
.jpg)
Fig1. SDS-PAGE (NOS2-7795H)
.
.jpg)
Fig2. SDS-PAGE (NOS2-986HFL)
Involved Pathway
NOS2 involved in several pathways and played different roles in them. We selected most pathways NOS2 participated on our site, such as Arginine biosynthesis,Arginine and proline metabolism,Metabolic pathways, which may be useful for your reference. Also, other proteins which involved in the same pathway with NOS2 were listed below. Creative BioMart supplied nearly all the proteins listed, you can search them on our site.
| Pathway Name | Pathway Related Protein |
|---|---|
| Arginine and proline metabolism | ALDH2.1,CKMT2B,P4HA2,ODC1,SAT1,CKBB,NOS2B,SAT2,L3HYPDH,SMOX |
| Amoebiasis | IL12B,LAMA2,SERPINB13,LAMC2,SERPINB1B,COL24A1,CSF2,CD14,COL5A2,ACTN2 |
| Small cell lung cancer | BIRC3,LAMA5,RARB,PTGS2,LAMB1,TRAF4,PIK3R3,LAMA2,ITGB1,CYCS |
| HIF- signaling pathway | MKNK1,CAMK2A,PLCG2,IFNGR1,PDHB,ENO2,ERBB2,HIF1A,ENO1,TCEB2 |
| Salmonella infection | CDC42,DYNC1I2A,MYH9,RAC1A,MAPK12B,MAPK8A,RILP,WASF1,MAPK1,KLC2 |
| Tuberculosis | CASP9,IFNGR2,TGFB2,IL18,HLA-DRB3,Pla2r1,FADD,IFNA12,MAPK13,CALM2 |
| Arginine biosynthesis | ARG2,GLS,GLUD2,GLULA,NOS2A,GLSA,GLS2,GOT2B,GLUD1,ACY1 |
| Chagas disease (American trypanosomiasis) | CCL5,IKBKG,GNAL,PLCB3,FADD,PLCB2,PIK3CD,PLCB4,MAPK3,PIK3R1 |
| Calcium signaling pathway | VDAC1,PRKACA,SLC25A4,PTGER3,SPHK1,CACNA1B,PPIAA,TRHR,GRM5,PTK2BB |
Protein Function
NOS2 has several biochemical functions, for example, FMN binding,NADP binding,NADPH-hemoprotein reductase activity. Some of the functions are cooperated with other proteins, some of the functions could acted by NOS2 itself. We selected most functions NOS2 had, and list some proteins which have the same functions with NOS2. You can find most of the proteins on our site.
| Function | Related Protein |
|---|---|
| FMN binding | NOS3,HAO1,POR,CREG1,TYW1B,NOS2A,DHODH,TYW1,CREG2,HAO2 |
| protein homodimerization activity | XPNPEP1,VEGFB,SRR,FZD9,CRYBA2,CAT,HMOX1,HPS4,SYT14,G6PDX |
| receptor binding | CXCL10,A2M,TMEM38A,SNX17,ANGPTL1,C1QTNF2,NRG2B,HSPA1A,CD86,SRMS |
| nitric-oxide synthase activity | NOS1,NOS2B,NOS2A,NOS3 |
| NADP binding | FMO1,GSR,NOX1,G6PD,GAPDH,NDOR1,GAPDHS,NNT,DHFRL1,PGD |
| flavin adenine dinucleotide binding | ACAD9,NOS1,FOXRED2,FMO3,KDM1B,DMGDH,ACOX3,GSR,AOX4,AIFM4 |
| NADPH-hemoprotein reductase activity | NDOR1,POR,MTRR,NOS2A,NOS1,NOS3,NOS2B,CYP2J6 |
| tetrahydrobiopterin binding | TH,NOS3,NOS1 |
| calmodulin binding | TRPV6,KCNN2,SLC8A2,CNN2,CAMK1GA,TRPM4,MYO1C,MYH1B,MARCKSL1B,SLC9A1 |
Interacting Protein
NOS2 has direct interactions with proteins and molecules. Those interactions were detected by several methods such as yeast two hybrid, co-IP, pull-down and so on. We selected proteins and molecules interacted with NOS2 here. Most of them are supplied by our site. Hope this information will be useful for your research of NOS2.
GAPDH;S100A8;S100A9;arginine
Resources
Related Services
Related Products
References
- Niedbala, W; Besnard, AG; et al. Nitric oxide enhances Th9 cell differentiation and airway inflammation. NATURE COMMUNICATIONS 5:-(2014).
- Giordano, D; Draves, KE; et al. Nitric Oxide Regulates BAFF Expression and T Cell-Independent Antibody Responses. JOURNAL OF IMMUNOLOGY 193:1110-1120(2014).


