LGR5
-
Official Full Name
leucine-rich repeat containing G protein-coupled receptor 5 -
Overview
LGR5 (leucine-rich repeat containing G protein-coupled receptor 5) An Orphan GPCR protein, contains large extracellular domain, Stem cell biomarker for small intestine, active in colon cancer; overexpressed in ovary and liver tumors. -
Synonyms
LGR5;leucine-rich repeat containing G protein-coupled receptor 5;G protein coupled receptor 49 , GPR49, GPR67, leucine rich repeat containing G protein coupled receptor 5;leucine-rich repeat-containing G-protein coupled receptor 5;FEX;HG38;G protein coupled receptor 49;G protein coupled receptor 67;G-protein coupled receptor 49;G-protein coupled receptor 67;G-protein coupled receptor HG38;GPR 49;GPR 67;GPR49;GPR67;GRP 49;GRP49;HG 38;Leucine rich repeat containing G protein coupled receptor 5;LGR 5;LGR5_HUMAN;Orphan G protein coupled receptor HG38;OTTHUMP00000241504;OTTHUMP00000241505;OTTHUMP00000241506;orphan G protein-coupled receptor HG38;leucine
Recombinant Proteins
- Human
- Cynomolgus
- Rat
- Mouse
- E. coli
- CHO
- HEK293
- C-hFc
- HEK293T
- Mammalian Cell
- Yeast
- Insect Cell
- E.coli
- Mamanlian cells
- N-His
- Fc
- His
- Non
- Myc&DDK
- His&Myc
- His&Fc&Avi
- His&Avi
- Flag
Background
What is LGR5 protein?
LGR5 gene (leucine rich repeat containing G protein-coupled receptor 5) is a protein coding gene which situated on the long arm of chromosome 12 at locus 12q21. The protein encoded by this gene is a leucine-rich repeat-containing receptor (LGR) and member of the G protein-coupled, 7-transmembrane receptor (GPCR) superfamily. The encoded protein is a receptor for R-spondins and is involved in the canonical Wnt signaling pathway. This protein plays a role in the formation and maintenance of adult intestinal stem cells during postembryonic development. The LGR5 protein is consisted of 907 amino acids and LGR5 molecular weight is approximately 100.0 kDa.
What is the function of LGR5 protein?
LGR5 acts as a stem cell marker that identifies stem cells in recesses of the small intestine and colon and helps maintain tissue homeostasis and regenerative capacity. LGR5 promotes tumor cell mobility, tumor formation, and epithelial-mesenchymal transformation in some cancers, while in other cases, LGR5 may inhibit tumor growth by inhibiting the Wnt/β-catenin signaling pathway. LGR5 is expressed in specific tissues, such as in stomach, breast, ovary, and oral mesenchymal stem cells, suggesting that it plays a role in stem cell function in these tissues. LGR5 is used as a marker to identify and study cancer stem cells, which are thought to drive tumor initiation, growth, and metastasis.
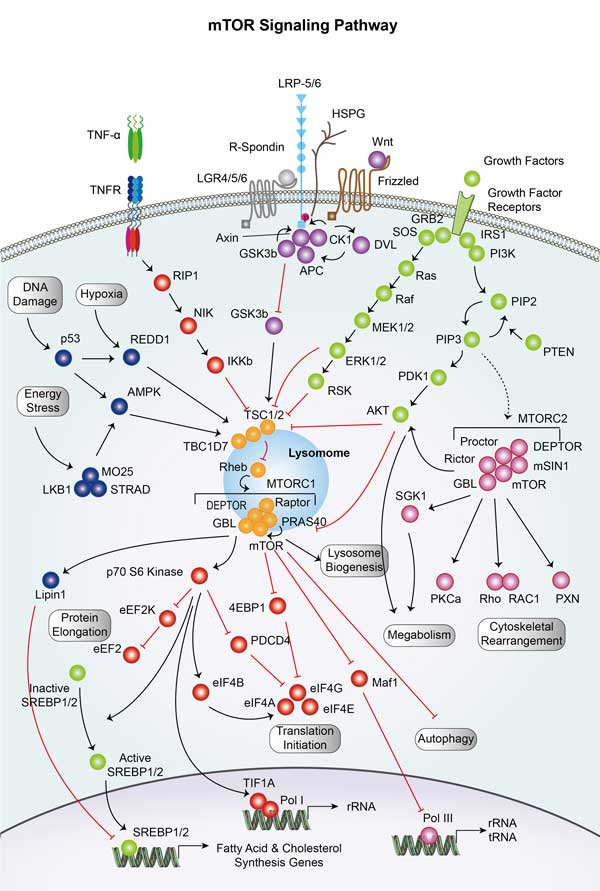
LGR5 Related Signaling Pathway
LGR5 affects the proliferation and differentiation of stem cells through its interaction with Wnt signaling pathway. After binding with the Frizzled receptor, Wnt ligand forms a complex with LRP5/6. R-spondin inhibits the activity of ZNRF3 and RNF43 by binding LGR5/6, increasing cell sensitivity to Wnt ligand, thus enhancing Wnt signal transduction. Because of its specific expression in tumor stem cells, LGR5 is considered a potential target for tumor therapy. Modulating the LGR5/Wnt/β-catenin signaling pathway may have potential for treating certain cancers. LGR5 may also be involved in atypical Wnt signaling pathways, affecting cell proliferation and differentiation. LGR5's ligand R-spondins enhances Wnt signaling by binding to it, the mechanism of which may involve interaction with LRP5/6 and Frizzled receptors to directly stimulate the Wnt pathway.

Fig1. Effect of RSPO:LGR5 complex on Wnt signaling. (Kaavya Krishna Kumar, 2014)
LGR5 Related Diseases
LGR5 expression in colorectal tumor stem cells is associated with tumor self-renewal, proliferation, and aggressiveness, and is a potential marker for tumor development and recurrence. In gastric cancer, high expression of LGR5 is associated with tumor aggressiveness and poor prognosis, and may serve as a marker for gastric cancer stem cells. LGR5 is also expressed in these tumor types and is associated with the properties of tumor stem cells and disease progression. In hepatocellular carcinoma, the expression of LGR5 may be related to the proliferation and drug resistance of tumor stem cells. The expression of LGR5 is associated with the development of skin basal cell carcinoma and may be involved in the regulation of Hedgehog signaling pathway. The role of LGR5 in other tumor types is also being studied, and its role in tumor stem cells has important implications for cancer therapy.
Bioapplications of LGR5
Due to its specific expression in a variety of tumor stem cells, LGR5 is considered an important target for the development of novel cancer therapeutic drugs that may help inhibit self-renewal and proliferation of tumor stem cells. The expression level of LGR5 in a variety of tumors is correlated with tumor aggressiveness and prognosis, and therefore can be used as a biomarker for cancer diagnosis and prognosis assessment. The role of LGR5 in normal tissue stem cells suggests that it may play a role in tissue regeneration and stem cell therapy, helping to promote tissue repair after injury. LGR5+ tumor stem cells may be associated with treatment resistance, and studying the role of LGR5 in this process could help develop new strategies to overcome resistance.
Case Study
Case Study 1: Keishi Kawasaki, 2021
LGR5 enhances Wnt-β-catenin signalling; however, involvement of LGR5 or Wnt-β-catenin signalling in ICC progression has not been reported. Functions and regulations of LGR5-mediated β-catenin activation in ICC progression were evaluated using surgical specimens collected from 61 ICC patients or 2 ICC cell lines. The results showed that LGR5 expression was increased in some cases of ICC. High LGR5 expression was an independent factor for poor prognosis in ICC after operation. In addition, LGR5 knockdown inhibited β-catenin activation, resulting in suppression of β-catenin-induced STAT3 activation through inhibition of OLFM4-GRIM19 cascade. Therefore, LGR5 was a key regulator for β-catenin activation, and β-catenin was unable to be activated without LGR5.
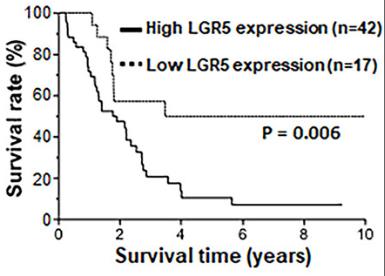
Fig1. Overall survival of ICC patients in relation to LGR5 expression was analysed by the Kaplan-Meier method.

Fig2. Effects of Wnt inhibition by IWP-2 in HuCCT1 cells were evaluated by western blotting.
Case Study 2: Jin Zhang, 2018
Tumor recurrence, the chief reason for poor prognosis of glioma, is largely attributed to glioma stem cells (GSCs) and epithelial-mesenchymal transition (EMT). However, the mechanisms among them remain unknown. Here, we determined whether leucine-rich repeat-containing G protein-coupled receptor 5 (LGR5) can serve as a novel GSC marker involved in EMT and a therapeutic target in glioma. Reported stem cell markers, EMT and the Wnt/β-catenin pathway were examined in stable LGR5 knockdown or overexpressed GSCs by Western Blot. The treatment experiment was performed in an intracranial orthotopic xenograft model by knockdown of LGR5 or by using the Wnt/β-catenin pathway inhibitor Wnt-C59. LGR5 expression was determined in 268 glioma specimens by immunohistochemistry. The results showed both LGR5 knockdown and Wnt-C59 reduced tumor invasion and migration and blocked EMT by inhibiting the Wnt/β-catenin pathway in vitro and suppressed the intracranial orthotopic xenograft growth and prolonged the survival of xenograft mice in vivo. Moreover, LGR5 was positively correlated with Ki67, N-cadherin and WHO grade and negatively correlated with IDH1. Glioma patients with high expression of LGR5 showed significantly poorer prognosis.
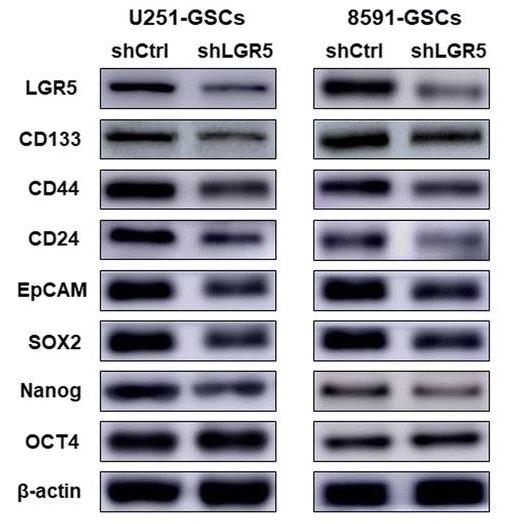
Fig3. The expression levels of LGR5 in shLGR5 and shCtrl GSCs determined by Western blot.

Fig4. LGR5 and N-cadherin staining in glioma tissues.
Quality Guarantee
.
.jpg)
Fig1. SDS-PAGE (LGR5-1947H)
.
.jpg)
Fig2. SDS-PAGE (LGR5-1441H)
Involved Pathway
LGR5 involved in several pathways and played different roles in them. We selected most pathways LGR5 participated on our site, such as Regulation of FZD by ubiquitination,Signal Transduction,Signaling by Wnt, which may be useful for your reference. Also, other proteins which involved in the same pathway with LGR5 were listed below. Creative BioMart supplied nearly all the proteins listed, you can search them on our site.
| Pathway Name | Pathway Related Protein |
|---|---|
| Regulation of FZD by ubiquitination | RSPO2,LGR6,RNF43,RSPO4,FMNL3,RSPO1,LGR4,RSPO3,ZNRF3 |
| Signaling by Wnt | PRICKLE1,TLE3B,ROR1,SOX32,LGR4,CDC73,CBY1,BCL9,RSPO1,RYK |
| TCF dependent signaling in response to WNT | WNT8-2,LGR6,TNKS2,BCL9L,RNF146,KREMEN1,RSPO3,SOX9B,RNF43,RBBP5 |
| Signal Transduction | RGS10,OPN4.1,METAP2B,TAX1BP1B,STRAP,IFT122,RGR,PYGO2,ARHGAP22,RGS20 |
Protein Function
LGR5 has several biochemical functions, for example, NOT G-protein coupled receptor activity,protein binding,transmembrane signaling receptor activity. Some of the functions are cooperated with other proteins, some of the functions could acted by LGR5 itself. We selected most functions LGR5 had, and list some proteins which have the same functions with LGR5. You can find most of the proteins on our site.
| Function | Related Protein |
|---|---|
| NOT G-protein coupled receptor activity | FRZB,LGR4,SFRP1,SZL,SFRP2,SFRP1A,LGR6,SFRP4,SFRP1B |
| protein binding | DNAJB2,DHX58,RHEBL1,GTF3C3,IGHM,RPL22,MYL6,RPP25L,CX3CL1,PPP1R2P3 |
| transmembrane signaling receptor activity | LGR6,TNFRSF11A,NRXN1,CLDN4,TLR4,CALCRLA,GIPR,LILRB5,SLAMF1,BAI2 |
Interacting Protein
LGR5 has direct interactions with proteins and molecules. Those interactions were detected by several methods such as yeast two hybrid, co-IP, pull-down and so on. We selected proteins and molecules interacted with LGR5 here. Most of them are supplied by our site. Hope this information will be useful for your research of LGR5.
pi3p
LGR5 Related Signal Pathway
Resources
Research Area
Renal MarkersIntestinal Stem Cell Markers
Colon Cancer Stem Cell Markers
Gastric Cancer Stem Cell Markers
Head and Neck Cancer Stem Cell Markers
Related Services
Related Products
References
- Baker, AM; Graham, TA; et al. Characterization of LGR5 stem cells in colorectal adenomas and carcinomas. SCIENTIFIC REPORTS 5:-(2015).
- Ying, J; Tsujii, M; et al. The effectiveness of an anti-human IL-6 receptor monoclonal antibody combined with chemotherapy to target colon cancer stem-like cells. INTERNATIONAL JOURNAL OF ONCOLOGY 46:1551-1559(2015).