HLA-DMA
-
Official Full Name
major histocompatibility complex, class II, DM alpha -
Overview
HLA-DMA belongs to the HLA class II alpha chain paralogues. This class II molecule is a heterodimer consisting of an alpha (DMA) and a beta chain (DMB), both anchored in the membrane. It is located in intracellular vesicles. DM plays a central role in the peptide loading of MHC class II molecules by helping to release the CLIP molecule from the peptide binding site. Class II molecules are expressed in antigen presenting cells (APC: B lymphocytes, dendritic cells, macrophages). The alpha chain is approximately 33-35 kDa and its gene contains 5 exons. Exon one encodes the leader peptide, exons 2 and 3 encode the two extracellular domains, exon 4 encodes the transmembrane domain and the cytoplasmic tail. -
Synonyms
HLA-DMA;major histocompatibility complex, class II, DM alpha;HLA class II histocompatibility antigen, DM alpha chain;D6S222E;RING6;MHC class II antigen DMA;really interesting new gene 6 protein;class II histocompatibility antigen, M alpha chain;DM
| Cat.# | Product name | Source (Host) | Species | Tag | Protein Length | Price |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| HLA-DMA-27713TH | Recombinant Human HLA-DMA | Wheat Germ | Human | Non | 261 amino acids |
|
| HLA-DMA-4836H | Recombinant Human HLA-DMA Protein, GST-tagged | Wheat Germ | Human | GST | 1-261 a.a. |
|
| HLA-DMA-5499HCL | Recombinant Human HLA 293 Cell Lysate | HEK293 | Human | Non |
|
|
| HLA-DMA-230HF | Recombinant Full Length Human HLA-DMA Protein | In Vitro Cell Free System | Human | Full L. 261 amino acids |
|
|
| HLA-DMA-3561HF | Recombinant Full Length Human HLA-DMA Protein, GST-tagged | In Vitro Cell Free System | Human | GST | Full L. 261 amino acids |
|
| HLA-DMA-4026H | Recombinant Human HLA-DMA protein, His-tagged | E.coli | Human | His | 27-233aa |
|
Background
What is HLA-DMA protein?
HLA-DMA gene (major histocompatibility complex, class II, DM alpha) is a protein coding gene which situated on the long arm of chromosome 6 at locus 6p21. HLA-DMA belongs to the HLA class II alpha chain paralogues. This class II molecule is a heterodimer consisting of an alpha (DMA) and a beta chain (DMB), both anchored in the membrane. It is located in intracellular vesicles. DM plays a central role in the peptide loading of MHC class II molecules by helping to release the CLIP molecule from the peptide binding site. Class II molecules are expressed in antigen presenting cells (APC: B lymphocytes, dendritic cells, macrophages). The alpha chain is approximately 33-35 kDa and its gene contains 5 exons. The HLA-DMA protein is consisted of 261 amino acids and HLA-DMA molecular weight is approximately 29.2 kDa.
What is the function of HLA-DMA protein?
HLA-DMA proteins are located in vesicles within cells, especially those associated with the endoplasmic reticulum and Golgi apparatus, and are involved in protein synthesis and processing. HLA-DMA proteins act as molecular chaperones that contribute to the correct folding and assembly of MHC Class II molecules. HLA-DMA proteins play a key role in catalyzing the release of Class II-associated invariant chains (clips) on newly synthesized MHC Class II molecules, thereby emptying peptide binding sites for acquisition of antigenic peptides. The interaction of HLA-DMA with MHC Class II molecules is regulated by HLA-DO, especially in B cells, and is essential for the regulation of immune responses.
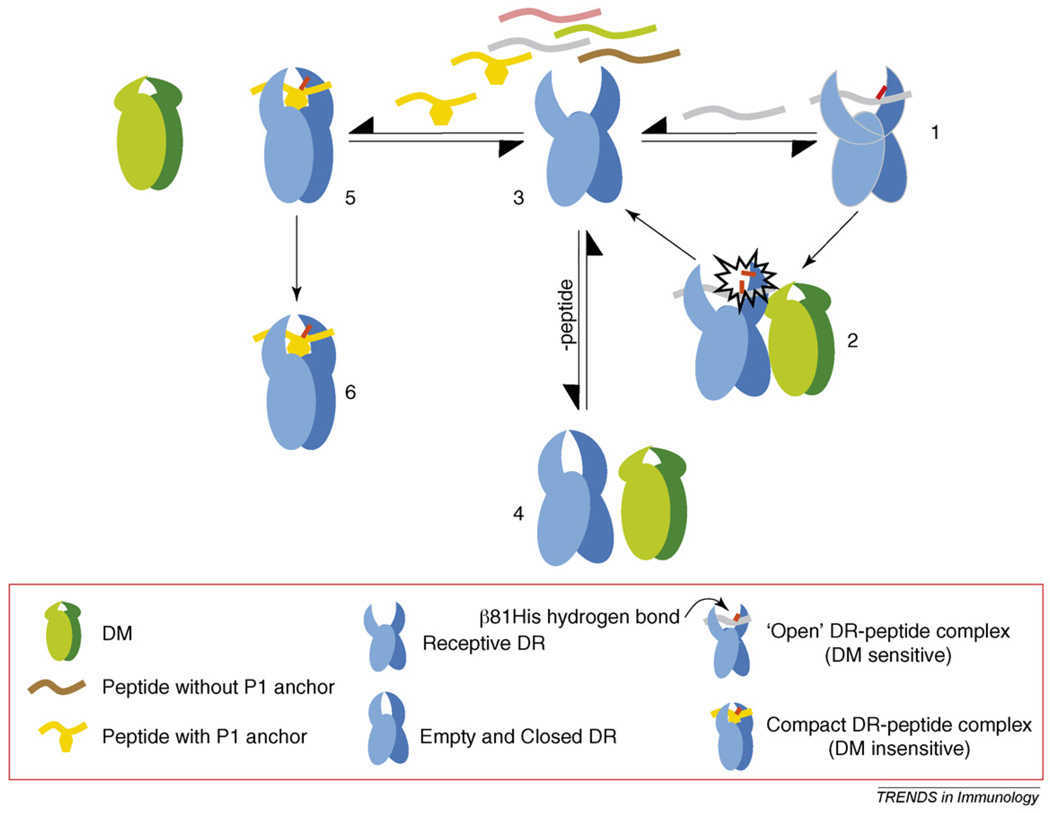
Fig1. A model for DM recognition of a MHC class II molecule and its effector function. (Scheherazade Sadegh-Nasseri, 2008)
HLA-DMA Related Signaling Pathway
HLA-DMA plays a key role in catalyzing the release of Class II-associated invariant chains (clips) on newly synthesized MHC Class II molecules, clearing peptide binding sites for acquisition of antigenic peptides. HLA-DMA is involved in adaptive immune responses, particularly with MHC Class II protein complexes involved in antigen processing and presentation to T cells. HLA-DMA is localized to intracellular vesicles, such as those associated with the endoplasmic reticulum and Golgi apparatus, and is involved in protein synthesis and processing. The interaction of HLA-DMA with MHC Class II molecules is regulated by HLA-DO, especially in B cells, and is essential for the regulation of immune responses.
HLA-DMA Related Diseases
Variations or abnormalities in the function of HLA-DMA proteins are associated with a variety of immune-mediated diseases. As a key regulator of MHC Class II molecular assembly and antigen presentation, alterations in HLA-DMA may affect the immune system's recognition and response to pathogens and abnormal cells. Specifically, HLA-DMA is associated with the following types of diseases: autoimmune diseases such as rheumatoid arthritis, systemic lupus erythematosus, allergic diseases, immune deficiency diseases. It may also be related to tumor immune escape and immune rejection.
Bioapplications of HLA-DMA
The role of HLA-DMA in antigen processing and presentation makes it potentially valuable in designing vaccine strategies, especially in enhancing vaccine-induced immune responses. The functional study of HLA-DMA facilitates the development of drugs targeting its activity for the treatment of diseases associated with MHC Class II molecular dysfunction. HLA-DMA plays a role in the immune response during transplantation, and its research helps to improve transplant compatibility and reduce rejection. The expression level or specific variation of HLA-DMA may be used as a biomarker of disease state for disease diagnosis and prognosis assessment.
Case Study
Case Study 1: Liusong Yin, 2015
Ag presentation by MHC class II (MHC II) molecules to CD4(+) T cells plays a key role in the regulation of the adaptive immune response. Loading of antigenic peptides onto MHC II is catalyzed by HLA-DM (DM), a nonclassical MHC II molecule. The mechanism of DM-facilitated peptide loading is an outstanding problem in the field of Ag presentation. In this study, researchers systemically explored possible kinetic mechanisms for DM-catalyzed peptide association by measuring real-time peptide association kinetics using fluorescence polarization assays and comparing the experimental data with numerically modeled peptide association reactions. The results showed that DM does not facilitate peptide association by stabilizing peptide-free MHC II against aggregation. Moreover, DM does not promote transition of an inactive peptide-averse conformation of MHC II to an active peptide-receptive conformation. Instead, DM forms an intermediate with MHC II that binds peptide with faster kinetics than MHC II in the absence of DM. In the absence of peptides, interaction of MHC II with DM leads to inactivation and formation of a peptide-averse form.
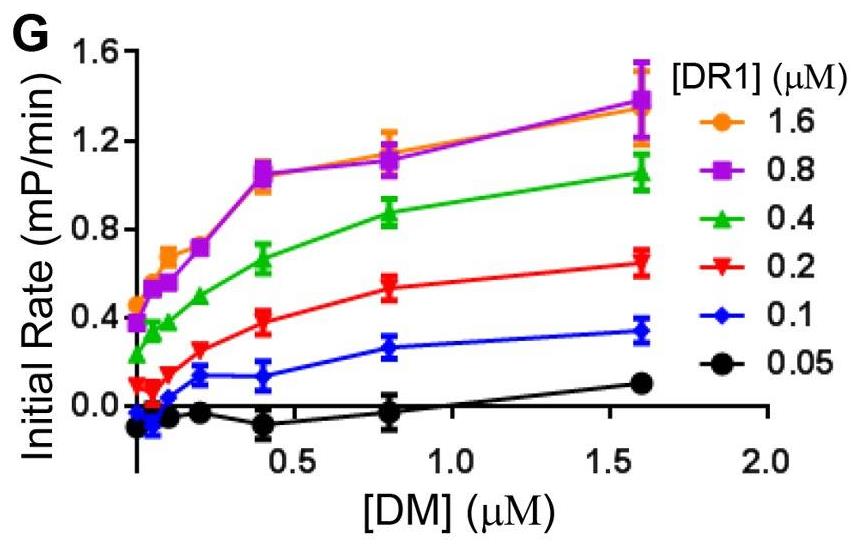
Fig1. Initial rate versus DM concentration for various DR1 concentrations.
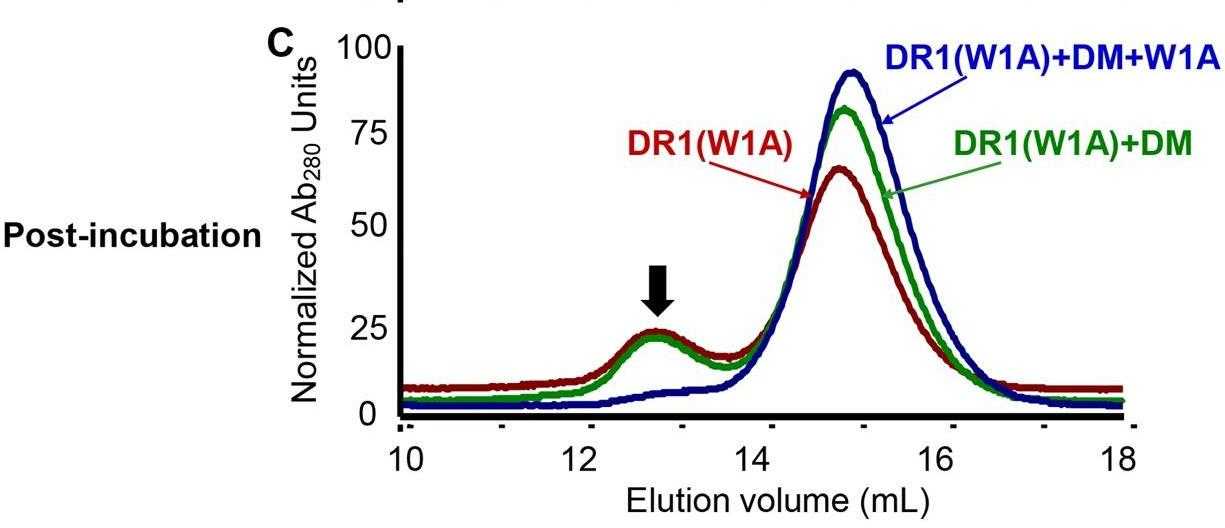
Fig2. Stabilization of DR1 loaded with a weakly binding peptide W1A by DM or peptides was monitored by gel filtration.
Case Study 2: Liusong Yin, 2012
HLA-DM (DM) is a nonclassical MHC class II (MHC II) protein that acts as a peptide editor to mediate the exchange of peptides loaded onto MHC II during Ag presentation. Although the ability of DM to promote peptide exchange in vitro and in vivo is well established, the role of DM in epitope selection is still unclear, especially in human response to infectious disease. In this study, researchers addressed this question in the context of the human CD4 T cell response to vaccinia virus. They measured the IC(50), intrinsic dissociation t(1/2), and DM-mediated dissociation t(1/2) for a large set of peptides derived from the major core protein A10L and other known vaccinia epitopes bound to HLA-DR1 and compared these properties to the presence and magnitude of peptide-specific CD4(+) T cell responses. MHC II-peptide complex kinetic stability in the presence of DM distinguishes T cell epitopes from nonrecognized peptides in A10L peptides and also in a set of predicted tight binders from the entire vaccinia genome.
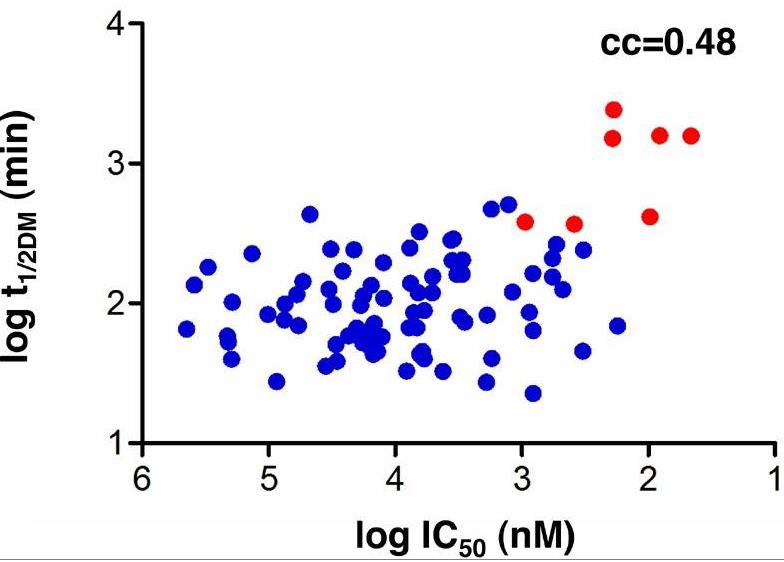
Fig3. Correlation between DM-mediated half-life and IC50.
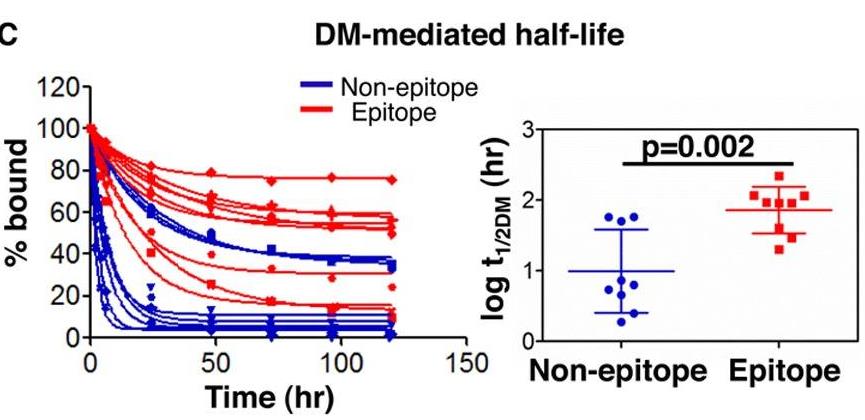
Fig4. DM-mediated half-lives.
Quality Guarantee
High Purity
.jpg)
Fig1. SDS-PAGE (HLA-DMA-4836H)
Involved Pathway
HLA-DMA involved in several pathways and played different roles in them. We selected most pathways HLA-DMA participated on our site, such as Phagosome,Cell adhesion molecules (CAMs),Antigen processing and presentation, which may be useful for your reference. Also, other proteins which involved in the same pathway with HLA-DMA were listed below. Creative BioMart supplied nearly all the proteins listed, you can search them on our site.
| Pathway Name | Pathway Related Protein |
|---|---|
| Toxoplasmosis | BCL2L1,HLA-DQA1,STAT3,TYK2,MAP2K3,STAT1,MAPK1,LAMB4,MAP2K6,IFNGR2 |
| Herpes simplex infection | SRSF5A,HCFC1,GLTSCR2,IFNA12,NFKBIB,GTF2IRD1,Ifna11,ABCB3L1,HLA-DOA,PER1B |
| Inflammatory bowel disease (IBD) | STAT6,TBX21,IL13,IL12RB1,HLA-DPB1,H2-AA,HLA-DOA,NFATC1,RELA,HLA-DQA2 |
| Antigen processing and presentation | HLA-DMB,LGMN,HLA-DOB,KIR2DS4,Ctsl,TAP2,HLA-G,KIR2DL4,TAPBP,CD8B |
| Tuberculosis | HSPA9,IFNG,IL1B,NOS2,MAPK10,ATP6V0A4,CAP18,HLA-DRB1,HLA-DRB5,IFNA6 |
| Staphylococcus aureus infection | cgr2b,HLA-DRB1,FCGR3,CFI,ITGB2,HLA-DOA,ICAM1,C3AR1,HLA-DOB,ITGAL |
| Phagosome | CTSSB.2,TUBB1,ATP6V1C1B,BF2,ATP6V0E2,DYNC2H1,ITGB5,MPO,SEC61A1,M6PR |
| Rheumatoid arthritis | CD86,IL17A,TLR4,CCL3,ATP6V0B,HLA-DRA,CTLA4,ATP6AP1,TGFB3,HLA-DRB4 |
| Viral myocarditis | CD86,ABL1,ACTG1,SGCB,LAMA2,RAC1,CD28,CD80,HLA-DMB,RAC3 |
Protein Function
HLA-DMA has several biochemical functions, for example, MHC class II protein complex binding. Some of the functions are cooperated with other proteins, some of the functions could acted by HLA-DMA itself. We selected most functions HLA-DMA had, and list some proteins which have the same functions with HLA-DMA. You can find most of the proteins on our site.
| Function | Related Protein |
|---|---|
| MHC class II protein complex binding | HLA-DMB,PKM,YWHAE,HLA-DRB1,CD74,CD81,HLA-DRA,HSPA8,ANXA11,HSP90AB1 |
Interacting Protein
HLA-DMA has direct interactions with proteins and molecules. Those interactions were detected by several methods such as yeast two hybrid, co-IP, pull-down and so on. We selected proteins and molecules interacted with HLA-DMA here. Most of them are supplied by our site. Hope this information will be useful for your research of HLA-DMA.
HLA-DRB1;HLA-DMB
Resources
Related Services
Related Products
References



