H3F3B
-
Official Full Name
H3 histone, family 3B (H3.3B) -
Synonyms
H3F3B;H3 histone, family 3B (H3.3B);histone H3.3;H3.3B;H3 histone, family 3A;H3F3A
Recombinant Proteins
- Human
- Chicken
- Mouse
- E.coli
- Wheat Germ
- Mammalian Cell
- HEK293
- In Vitro Cell Free System
- His
- GST
- Non
- His&Fc&Avi
| Cat.# | Product name | Source (Host) | Species | Tag | Protein Length | Price |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| H3F3B-1728H | Recombinant Human H3F3B Protein, His-tagged | E.coli | Human | His | 3-136 a.a. |
|
| H3F3B-1729H | Recombinant Human H3F3B Protein, GST-tagged | E.coli | Human | GST | 3-136 a.a. |
|
| H3F3B-4543H | Recombinant Human H3F3B Protein, GST-tagged | Wheat Germ | Human | GST |
|
|
| H3F3B-6848C | Recombinant Chicken H3F3B | Mammalian Cell | Chicken | His |
|
|
| H3F3B-7459M | Recombinant Mouse H3F3B Protein | Mammalian Cell | Mouse | His |
|
|
| H3F3B-5653HCL | Recombinant Human H3F3B 293 Cell Lysate | HEK293 | Human | Non |
|
|
| H3F3B-3411HF | Recombinant Full Length Human H3F3B Protein, GST-tagged | In Vitro Cell Free System | Human | GST | Full L. 136 amino acids |
|
| H3F3B-4048M | Recombinant Mouse H3F3B Protein, His (Fc)-Avi-tagged | HEK293 | Mouse | His&Fc&Avi |
|
|
| H3F3B-4048M-B | Recombinant Mouse H3F3B Protein Pre-coupled Magnetic Beads | HEK293 | Mouse |
|
Background
What is H3F3B Protein?
H3F3B protein is part of the histone H3 family, specifically a variant known as H3.3B. It’s actually the same kind of histone protein produced by the H3F3A gene, just differing in the untranslated regions and regulatory sequences of mRNA. The protein coded by the H3F3B gene consists of 136 amino acids, has a molecular weight of about 15.328 kDa, and generally has a globular shape, except for the disordered N-terminal tail. What sets H3.3 apart is its ability to integrate into chromatin independently of DNA replication, a process facilitated by the chaperone complexes HIRA and DAXX/ATRX. H3.3 is typically found in areas where genes are actively expressed, as well as regions near centromeres and telomeres. Additionally, mutations at certain amino acid residues in H3.3 are linked to various tumors. H3F3B mutations are relatively common in human diseases, especially in pediatric tumors and neurodevelopmental syndromes. Overall, H3F3B plays a crucial role in maintaining genome stability and organizing chromatin structure, bridging development and disease through epigenetic mechanisms.What is the Function of H3F3B Protein?
The H3F3B protein is encoded by one of the genes responsible for producing histone variant H3.3, a crucial player in chromatin architecture and gene regulation. Unlike typical histone proteins, H3.3 can be incorporated into chromatin independently of DNA replication, thanks to the chaperone proteins like HIRA, ATRX, and DAXX. This unique capability allows H3.3 to significantly influence gene expression regulation, maintain genomic stability, and organize chromatin. Mutations in the H3F3B gene have been linked to various human diseases, including pediatric tumors and neurodevelopmental syndromes, affecting brain development, structural anomalies, and neural functions. Understanding H3.3 is not only vital for grasping developmental processes but also for shedding light on the molecular mechanisms behind gene expression regulation and disease progression.H3F3B Related Signaling Pathway
The H3F3B protein, one of the genes encoding histone H3.3, plays a significant part in various signaling pathways due to its distinct properties and functions. H3.3 can be incorporated into chromatin independently of DNA replication, which makes it crucial for gene regulation and chromatin remodeling. This protein associates with active gene regions, open chromatin, telomeres, and repressive genes, showing a unique context-specific role in gene regulation and chromosomal stability. Moreover, H3.3 directly interacts with genes linked to extracellular matrices, vascular smooth muscle cell (VSMC) synthetic phenotypes, cytokine response, and TGFβ signaling, thereby influencing VSMC phenotype transitions and vascular inflammation. H3.3 is also tied to neurodevelopmental delays, facial deformities, and structural brain defects, highlighting its importance in early embryonic development and cell lineage commitment. Changes in H3F3B gene expression have been studied as potential prognostic markers for colorectal cancer. Overall, the H3F3B protein plays a pivotal role in numerous biological processes by affecting chromatin architecture and gene expression, spanning gene regulation, cell differentiation, tumor progression, and vascular inflammation across various pathways.
Fig1. RNF8/UbcH8-mediated histone H3 polyubiquitylation and degradation promotes gene expression. (Yan Xia, 2017)
H3F3B Related Diseases
The H3F3B protein is linked to various health issues, including tumors in children and young adults, neurological syndromes, and some cardiovascular diseases. Mutations in the H3F3B gene have been tied to the development of high-grade pediatric brain gliomas, chondroblastomas, and giant cell tumors of bone. Additionally, certain missense mutations in this gene are connected to neurodevelopmental syndromes, which can involve developmental delays, neurodegeneration, seizures, and facial anomalies. When it comes to heart health, H3F3B plays a role in regulating vascular smooth muscle cell transformation and inflammation, impacting aortic dissection progression. These associations highlight the critical roles of the H3F3B protein in maintaining genomic integrity, regulating gene expression, and controlling cell differentiation.Bioapplications of H3F3B
Recombinant H3F3B protein is widely used in scientific research, industrial production, and medical studies. In the research field, it’s instrumental in exploring its unique functions in regulating gene transcription and cell differentiation, particularly regarding genome stability and chromatin organization. Researchers also examine H3F3B gene mutations and their link to tumors in children and young adults, such as high-grade gliomas and chondroblastomas. Industrially, recombinant H3F3B protein aids in producing antibodies for experiments like Western Blot and ELISA, showing reactivity with human samples. Medically, it assists in understanding tumor mechanisms; for instance, research teams have found that RACK7 specifically recognizes H3.3G34R mutations in peptides and recombinant nucleosomes, offering potential therapeutic targets. Additionally, recombinant H3F3B is pivotal in developing quantitative immunohistochemistry methods to measure protein expression, a key aspect in studying diseases like breast cancer. Overall, the recombinant H3F3B protein is vital for advancing science and medicine.Case Study
Case Study 1: Chen Y. et al. Clin Transl Oncol. 2021
Liver cancer, specifically hepatocellular carcinoma (HCC), is quite lethal. Recent research has shown that circular RNA called circ_0091579 is involved in how this cancer progresses. To dig into this, scientists used several methods, like measuring how much circ_0091579, miR-624, and H3F3B mRNA were present with qRT-PCR. They also looked at how the cancer cells moved, invaded, and used energy. They discovered that circ_0091579 was more abundant in cancerous tissues and cells, and its inhibition could reduce tumor growth and increase cell death. Additionally, it was found to act like a sponge for miR-624, influencing the expression of H3F3B. Reducing miR-624 or overexpressing H3F3B could counteract these tumor-suppressing effects.-
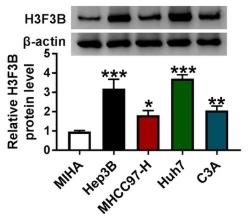 Fig1. The level of H3F3B protein in HCC cells and MIHA cells was measured by western blotting.
Fig1. The level of H3F3B protein in HCC cells and MIHA cells was measured by western blotting. -
 Fig2. Western blotting was executed to analyze the level of H3F3B protein in Hep3B cells.
Fig2. Western blotting was executed to analyze the level of H3F3B protein in Hep3B cells.
Case Study 2: Jiang H. et al. Connect Tissue Res. 2021
Osteoarthritis (OA) often hits older folks hard, causing wear and tear on the joints. Research has highlighted that long non-coding RNAs (lncRNAs), especially one called SNHG5, play important roles in how OA develops. In this study, researchers looked into how SNHG5 influences OA by using IL-1β to stimulate chondrocytes in lab tests. They checked the levels of SNHG5, miR-10a-5p, and another marker, H3F3B, using qRT-PCR and western blot. They also tested how these changes impacted cell growth and death. The findings showed that low levels of SNHG5 and H3F3B, but high levels of miR-10a-5p, were linked with OA. Lowering SNHG5 made chondrocytes more prone to die when hit by IL-1β, largely because SNHG5 usually helps soak up miR-10a-5p. MiR-10a-5p ends up promoting cell death by targeting H3F3B, and SNHG5 tries to keep everything in check by managing H3F3B levels through its interactions with miR-10a-5p.-
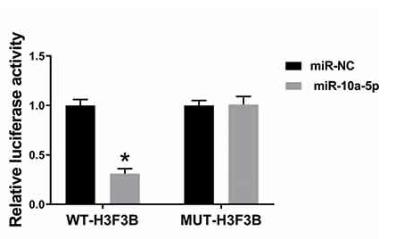 Fig3. Dual-luciferase reporter assay was performed in chondrocytes co-transfected with WT-H3F3B or MUT-H3F3B and miR-10a-5p or miR-NC.
Fig3. Dual-luciferase reporter assay was performed in chondrocytes co-transfected with WT-H3F3B or MUT-H3F3B and miR-10a-5p or miR-NC. -
 Fig4. The levels of cleaved-cas-3 and cleaved-cas-9 were detected by western blot assay.
Fig4. The levels of cleaved-cas-3 and cleaved-cas-9 were detected by western blot assay.
Quality Guarantee
High Purity
-
.jpg) Fig1. SDS-PAGE (H3F3B-4543H)
Fig1. SDS-PAGE (H3F3B-4543H)
Involved Pathway
H3F3B involved in several pathways and played different roles in them. We selected most pathways H3F3B participated on our site, such as Alcoholism,Transcriptional misregulation in cancer,Systemic lupus erythematosus, which may be useful for your reference. Also, other proteins which involved in the same pathway with H3F3B were listed below. Creative BioMart supplied nearly all the proteins listed, you can search them on our site.
| Pathway Name | Pathway Related Protein |
|---|---|
| Alcoholism | SHC4,HIST1H2AB,GRIN2C,H2AFB1,HIST1H2AL,HIST1H2BI,CREB3L1,GRIN2D,HDAC10,HIST1H3C |
| Systemic lupus erythematosus | HLA-DRB3,HLA-DRB1,CD40,HIST1H3I,HIST2H2AA2,FCGR3A,HIST2H3C1,ACTN4,GM14482,C2 |
| Transcriptional misregulation in cancer | ETV6,ELANE,CCNT1,RUNX2,GOLPH3,PFTK1,MET,ETV1,SPINT1,DEFA3 |
-
 Fig1. The flow diagram displayed the mechanism of SNHG5 regulating chondrocyte proliferation and apoptosis. (Housen Jiang, 2021)
Fig1. The flow diagram displayed the mechanism of SNHG5 regulating chondrocyte proliferation and apoptosis. (Housen Jiang, 2021) -
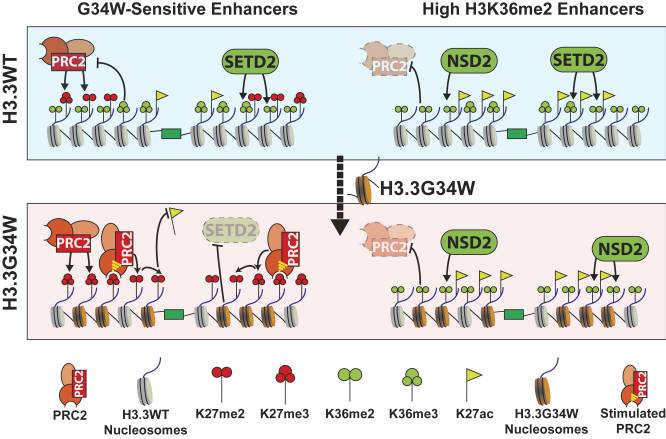 Fig2. H3.3 G34W alters enhancer landscapes by boosting the “hit-and-run” mechanism of PRC2 recruitment. (Siddhant U Jain, 2020)
Fig2. H3.3 G34W alters enhancer landscapes by boosting the “hit-and-run” mechanism of PRC2 recruitment. (Siddhant U Jain, 2020)
Protein Function
H3F3B has several biochemical functions, for example, RNA polymerase II core promoter sequence-specific DNA binding,RNA polymerase II distal enhancer sequence-specific DNA binding,histone binding. Some of the functions are cooperated with other proteins, some of the functions could acted by H3F3B itself. We selected most functions H3F3B had, and list some proteins which have the same functions with H3F3B. You can find most of the proteins on our site.
| Function | Related Protein |
|---|---|
| histone binding | TBL1XR1,PKN1,PHF21B,HIST1H3I,L3MBTL1,SNCA,PRKCBP1L,NPM2,HIST2H4,HIST1H3E |
| RNA polymerase II core promoter sequence-specific DNA binding | GATA6,TRP53,MAZ,MTF1,FOS,GBX2,SOX3,SUZ12,ZFPM1,IRF7 |
| RNA polymerase II distal enhancer sequence-specific DNA binding | GATA2,CREB1,BACH2,ARX,HOXB5,RELA,HNRNPC,PAX4,NR1H4,CDX2 |
| nucleosomal DNA binding | HNRNPC,HMGN3,NSBP1,H2AFY,H2AFZ,RCC1,HMGA2,H3F3C,HMGN4,HMGN1 |
| protein binding | CTSC,PQBP1,SLC14A2,JUB,TSGA10,KPNA1,SNRPE,EIF3G,TMEM190,PDCL3 |
| protein heterodimerization activity | ATF3,HIST1H2BF,USF2,HIST1H4K,TAS1R3,HIST1H3A,BNIP3,H2AFB1,GUCY1A3,KCNK3 |
Interacting Protein
H3F3B has direct interactions with proteins and molecules. Those interactions were detected by several methods such as yeast two hybrid, co-IP, pull-down and so on. We selected proteins and molecules interacted with H3F3B here. Most of them are supplied by our site. Hope this information will be useful for your research of H3F3B.
DNMT3A;PELP1;BPTF
Resources
Related Services
Related Products
References
- Frank, D; Doenecke, D; et al. Differential expression of human replacement and cell cycle dependent H3 histone genes. GENE 312:135-143(2003).
- Witt, O; Albig, W; et al. cAMP/phorbol ester response element is involved in transcriptional regulation of the human replacement histone gene H3.3B. BIOCHEMICAL JOURNAL 329:609-613(1998).


