GLUD2
-
Official Full Name
Glud2 glutamate dehydrogenase 2 -
Synonyms
GLUD2;glutamate dehydrogenase 2;Glud-2
Recombinant Proteins
- Human
- E.coli
- Wheat Germ
- HEK293T
- In Vitro Cell Free System
- GST
- His
- Non
- Myc&DDK
| Cat.# | Product name | Source (Host) | Species | Tag | Protein Length | Price |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| GLUD2-13320H | Recombinant Human GLUD2, GST-tagged | E.coli | Human | GST | 207-558a.a. | |
| GLUD2-27654TH | Recombinant Human GLUD2, His-tagged | E.coli | Human | His | 229-541 a.a. |
|
| GLUD2-89H | Recombinant Human GLUD2, GST-tagged | Wheat Germ | Human | GST |
|
|
| GLUD2-90H | Recombinant Human GLUD2, GST-tagged | Wheat Germ | Human | GST |
|
|
| GLUD2-716HCL | Recombinant Human GLUD2 cell lysate | Human | Non |
|
||
| GLUD2-444H | Recombinant Human GLUD2 Protein, Myc/DDK-tagged, C13 and N15-labeled | HEK293T | Human | Myc&DDK |
|
|
| GLUD2-6940HF | Recombinant Full Length Human GLUD2 Protein, GST-tagged | In Vitro Cell Free System | Human | GST | Full L. 558 amino acids |
|
| GLUD2-6941HF | Recombinant Full Length Human GLUD2 Protein, GST-tagged | In Vitro Cell Free System | Human | GST | Full L. 558 amino acids |
|
Background
What is GLUD2 Protein?
GLUD2, or glutamate dehydrogenase 2, is an enzyme found in humans that's encoded by the GLUD2 gene. This enzyme is primarily located in mitochondria and is involved in recycling glutamate during neurotransmission. It works by catalyzing the conversion of glutamate back and forth to alpha-ketoglutarate, which is a key step in managing amino acid breakdown and supporting brain function. Unlike GLUD1, its relative that is widespread in various tissues, GLUD2 is specifically expressed in neural and testicular tissues, reflecting its specialized functions in those areas.What is the Function of GLUD2 Protein?
GLUD2, or glutamate dehydrogenase 2, is a protein that primarily helps the brain efficiently recycle glutamate, a key neurotransmitter. Found in mitochondria, GLUD2 converts glutamate into alpha-ketoglutarate, aiding energy production via the TCA cycle. This process is particularly crucial during intense brain activity, as it helps meet increased energy demands and maintains neurotransmitter balance. With its unique ability to function under conditions that might limit other enzymes, GLUD2 plays a vital role in brain metabolism and communication.GLUD2 Related Signaling Pathway
GLUD2 is involved in a key signaling pathway related to neurotransmitter regulation in the brain. It functions within mitochondria, where it plays a critical role in converting glutamate into alpha-ketoglutarate. This conversion is essential for supporting the TCA cycle, which helps in energy production during neurotransmission. By assisting in maintaining glutamate levels and energy balance, GLUD2 ensures efficient signaling and proper brain function, particularly during periods of heightened neuronal activity. This pathway is crucial for managing the energy and signaling needs of brain cells.GLUD2 Related Diseases
GLUD2, linked with its function in neurotransmission and energy metabolism in the brain, has been explored in the context of several neurological conditions. Its role in recycling glutamate and supporting energy production means any imbalance or dysfunction might contribute to disorders such as neurodegenerative diseases. Changes in GLUD2 activity could potentially impact conditions like Parkinson's or Alzheimer’s, where energy metabolism and neurotransmitter balance are disrupted. Research into GLUD2 continues to uncover how its alterations might relate to these diseases.Bioapplications of GLUD2
GLUD2, with its role in managing neurotransmitter levels and energy production in the brain, shows promise in several bioapplications. Researchers are exploring how modulating this enzyme might help in treating neurological conditions linked to neurotransmission and metabolism issues, like Alzheimer's and Parkinson's diseases. Additionally, understanding GLUD2's function could contribute to strategies for boosting brain energy metabolism, especially under stress or high activity conditions. These insights could lead to new therapies aimed at enhancing brain health and addressing metabolic imbalances.Case Study
Case Study 1: Dimovasili C. et al. J Neurochem. 2021
Mammalian glutamate dehydrogenase (hGDH1 in humans) converts glutamate into α-ketoglutarate and ammonia, affecting NAD(P) levels. Humans and apes evolved hGDH2, a version better suited for expanded brain function. While hGDH1's structure was known, hGDH2's wasn't until researchers recently cracked it at 2.9 Å resolution. They used insect cells to produce it and crystallization techniques to study it. This new structure shows a unique semi-closed form, giving insights into how evolutionary changes, like Arg470His, impact its function.-
 Fig1. Comparison of the hGDH2 after superposition of their glutamate domains (red).
Fig1. Comparison of the hGDH2 after superposition of their glutamate domains (red). -
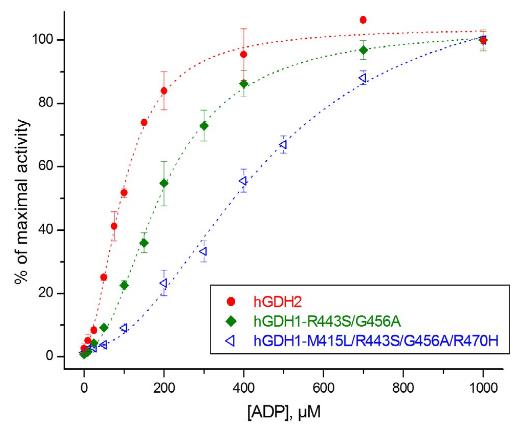 Fig2. ADP activation assays of purified wt-hGDH2 and mutant hGDH1 enzymes.
Fig2. ADP activation assays of purified wt-hGDH2 and mutant hGDH1 enzymes.
Case Study 2: Nissen JD. et al. Glia. 2017
Glutamate dehydrogenase (GDH) is key in balancing brain glutamate and connecting carbohydrate and amino acid processes. Humans have two types, GDH1 and GDH2, whereas other mammals typically just have GDH1. GDH1 is found all over the brain, but GDH2 is specific to astrocytes, where it aids in glutamate breakdown and supports the TCA cycle when the brain's really active. A study using astrocytes from GDH2-expressing mice showed that GDH2 enhances glutamate uptake and metabolism, especially when energy is scarce. It also shifts energy use from glucose to branched-chain amino acids, indicating GDH2 helps astrocytes manage energy resources better when they're low.-
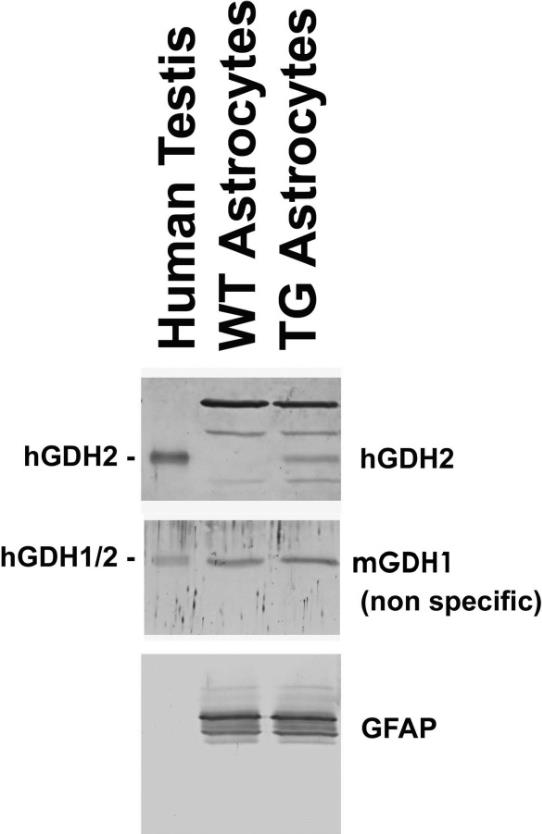 Fig3. Western blots of the glutamate dehydrogenase isoenzymes (mGDH1 and hGDH2) in astrocytes.
Fig3. Western blots of the glutamate dehydrogenase isoenzymes (mGDH1 and hGDH2) in astrocytes. -
 Fig4. Amino acid amounts in control and hGDH2-expressing astrocytes maintained in the presence of glucose.
Fig4. Amino acid amounts in control and hGDH2-expressing astrocytes maintained in the presence of glucose.
Quality Guarantee
High Purity
-
.jpg) Fig1. SDS-PAGE (GLUD2-444H)
Fig1. SDS-PAGE (GLUD2-444H)
Involved Pathway
GLUD2 involved in several pathways and played different roles in them. We selected most pathways GLUD2 participated on our site, such as Arginine biosynthesis,Alanine, aspartate and glutamate metabolism,D-Glutamine and D-glutamate metabolism, which may be useful for your reference. Also, other proteins which involved in the same pathway with GLUD2 were listed below. Creative BioMart supplied nearly all the proteins listed, you can search them on our site.
| Pathway Name | Pathway Related Protein |
|---|---|
| Proximal tubule bicarbonate reclamation | GLS,ATP1A1,AQP1,FXYD2,GLS2,Car4,CA2,SLC25A10,ATP1B3,PCK2 |
| Nitrogen metabolism | CAR7,CA9,Car9,CAHZ,CA6,CA5B,CA14,GLUD1B,CA13,Car12 |
| Carbon metabolism | PSAT1,SUCLG2,GPT2,PGAM1B,ACO1,HADHA,PFKL,PRPS1,SUCLG1,ACAT2 |
| Alanine, aspartate and glutamate metabolism | GLULA,AGXTA,GFPT1,IL4I1,ADSSL1,GPT,RIMKLB,ABAT,ASPA,AGXTB |
| Metabolic pathways | LPIN3,PAFAH2,ALG8,NDUFA7,FUT9,EPHX2,MTMR7A,PRODH2,POLR2A,LSS |
| Arginine biosynthesis | GOT2A,CPS1,NOS2A,GLUL,ASL2,ASS1,GLULB,GLUD1A,GLULC,ARG1 |
| D-Glutamine and D-glutamate metabolism | GLS2,GLUD1A,GLUD1,GLUD1B,ybaS,GLS,GLSA |
-
 Fig1. TCA cycle and anaplerotic reactions including the role of ammonia. (Leonie Drews, 2020)
Fig1. TCA cycle and anaplerotic reactions including the role of ammonia. (Leonie Drews, 2020) -
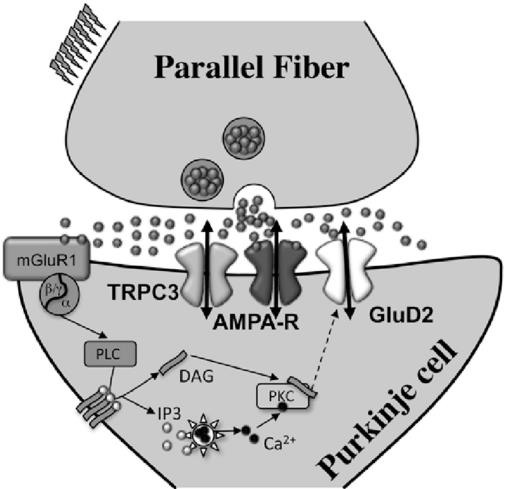 Fig2. mGlu1-induced Gq-PLC-PKC activation is required to open GluD2 channels. (Selma Dadak, 2017)
Fig2. mGlu1-induced Gq-PLC-PKC activation is required to open GluD2 channels. (Selma Dadak, 2017)
Protein Function
GLUD2 has several biochemical functions, for example, ADP binding,GTP binding,glutamate dehydrogenase (NAD+) activity. Some of the functions are cooperated with other proteins, some of the functions could acted by GLUD2 itself. We selected most functions GLUD2 had, and list some proteins which have the same functions with GLUD2. You can find most of the proteins on our site.
| Function | Related Protein |
|---|---|
| leucine binding | GLUD1,UBR2,UBR1 |
| glutamate dehydrogenase [NAD(P)+] activity | GLUD1 |
| ADP binding | MYH9,MYH10,ERN1,CYB5R3,MYO7A,ATP1A1,CHORDC1,TAP1,PKM,GCLC |
| GTP binding | IIGP1,DNM2B,GTPBP3,RHOB,RRAGD,THG1L,TUBE1,RHOT1B,GUCY1A3,RAB28 |
| glutamate dehydrogenase (NAD+) activity | GLUD1 |
Interacting Protein
GLUD2 has direct interactions with proteins and molecules. Those interactions were detected by several methods such as yeast two hybrid, co-IP, pull-down and so on. We selected proteins and molecules interacted with GLUD2 here. Most of them are supplied by our site. Hope this information will be useful for your research of GLUD2.
MYC;TRMT10C;TOM1L1;ATF2;CLPP
Resources
Related Services
Related Products
References
- Bhandage, AK; Jin, Z; et al. GABA-A and NMDA receptor subunit mRNA expression is altered in the caudate but not the putamen of the postmortem brains of alcoholics. FRONTIERS IN CELLULAR NEUROSCIENCE 8:-(2014).
- Botman, D; Tigchelaar, W; et al. Determination of Phosphate-activated Glutaminase Activity and Its Kinetics in Mouse Tissues using Metabolic Mapping (Quantitative Enzyme Histochemistry). JOURNAL OF HISTOCHEMISTRY & CYTOCHEMISTRY 62:813-826(2014).


