GGT1
-
Official Full Name
gamma-glutamyltransferase 1 -
Overview
The enzyme encoded by this gene catalyzes the transfer of the glutamyl moiety of glutathione to a variety of amino acids and dipeptide acceptors. The enzyme is composed of a heavy chain and a light chain, which are derived from a single precursor protein, and is present in tissues involved in absorption and secretion. This enzyme is a member of the gamma-glutamyltransferase protein family, of which many members have not yet been fully characterized and some of which may represent pseudogenes. This gene is classified as type I gamma-glutamyltransferase. Multiple alternatively spliced variants, encoding the same protein, have been identified. -
Synonyms
GGT1;gamma-glutamyltransferase 1;GGT;gamma-glutamyltranspeptidase 1;CD224;D22S672;D22S732;glutamyl transpeptidase;glutathione hydrolase 1;gamma-glutamyl transpeptidase;GTG;GGT 1;MGC96892;MGC96904;MGC96963
Recombinant Proteins
- Human
- Rat
- Mouse
- Pig
- Sus scrofa (Pig)
- N-His
- Mammalian Cell
- Wheat Germ
- E.coli
- HEK293
- Human Cell
- In Vitro Cell Free System
- Porcine Kidney
- Human Liver
- E.coli expression system
- His
- Non
- His&T7
- His&Fc&Avi
- GST
Background

Fig1. Extra- and intra-cellular effects of plasma membrane GGT ectoactivity. (Alessandro Corti, 2020)
What is GGT1 Protein?
GGT1 gene (gamma-glutamyltransferase 1) is a protein coding gene which situated on the long arm of chromosome 22 at locus 22q11. The enzyme encoded by this gene is a type I gamma-glutamyltransferase that catalyzes the transfer of the glutamyl moiety of glutathione to a variety of amino acids and dipeptide acceptors. The enzyme is composed of a heavy chain and a light chain, which are derived from a single precursor protein. It is expressed in tissues involved in absorption and secretion and may contribute to the etiology of diabetes and other metabolic disorders. The GGT1 protein is consisted of 569 amino acids and GGT1 molecular weight is approximately 61.4 kDa.
What is the Function of GGT1 Protein?
GGT1 is an extracellular enzyme that is anchored to the plasma membrane of cells, where it hydrolyzes and transfers the gamma-glutamyl portion of glutathione and other gamma-glutamyl compounds to receptors. Therefore, GGT1 plays a key role in glutathione metabolism and the conversion of leukotriene LTC4 to LTD4. In addition, GGT1 is involved in the metabolism of glutathione through the release of free glutamic acid and dipeptide cysteine-glycine, which can be hydrolyzed to cysteine and glycine by dipeptidase. In the presence of high concentrations of dipeptides and certain amino acids, GGT1 can also catalyze the transpeptide reaction, transferring the gamma-glutamyl part to the acceptor amino acid, forming a new gamma-glutamyl compound. GGT1 contributes to cysteine homeostasis, glutathione homeostasis, and the conversion of leukotriene LTC4 to LTD4.
GGT1 Related Signaling Pathway
GGT1 catalyzes the hydrolysis of gamma-glutamyl bonds of glutathione (gamma-Glu-CYS-Gly) to release free glutamic acid and dipeptide cysteine-glycine, which are further hydrolyzed to cysteine and glycine by dipeptidase. GGT1 also plays a role in the biosynthesis of leukotrienes, particularly in the conversion of leukotriene C4 (LTC4) to leukotriene D4 (LTD4). This conversion process involves the hydrolysis of γ-glutamyl groups of LTC4 by GGT1. GGT1 participates in the gamma-glutamyl cycle, a process involving multiple cell types that includes the transport and metabolism of amino acids. The activity of GGT1 is related to the proliferation and apoptosis of some cells. For example, GGT1 expression may be associated with the proliferation and metastasis of tumor cells.
GGT1 Related Diseases
GGT1 is an important biomarker in liver function tests, and elevated levels are often associated with liver diseases such as hepatitis, cirrhosis, and liver cancer. Levels of GGT1 are associated with the risk of cardiovascular disease and may play a role through mechanisms such as affecting vascular endothelial function and promoting atherosclerosis. Changes in GGT1 activity may indicate impairment of renal function, especially in the diagnosis and monitoring of chronic kidney disease and glomerular disease. The expression of GGT1 is up-regulated in some tumor types, which may be involved in the growth, proliferation and metastasis of tumor cells, and be studied as biomarkers or therapeutic targets for some cancers. GGT1 has been implicated in the pathogenesis of diabetes and other metabolic diseases and may affect glutathione metabolism, which in turn affects the antioxidant capacity and inflammatory response of cells.
Bioapplications of GGT1
Changes in levels of GGT1, an enzyme in the serum, are commonly used in the diagnosis of liver diseases, including hepatitis, cirrhosis and liver cancer. The mechanism of action of GGT1 in a variety of diseases provides potential targets for drug development, particularly in tumor therapy and metabolic disease management. The expression and activity level of GGT1 can be used as biomarkers of various disease states, which is helpful for early diagnosis and prognosis assessment of diseases. GGT1's key role in glutathione metabolism makes it an important tool for studying the relationship between nutrient intake, oxidative stress, and health. Gene therapy strategies targeting GGT1 may help treat those genetic disorders associated with abnormal GGT1 activity.
Case Study
Case Study 1: Lin Ding, 2024
Ropivacaine, a local anesthetic, exhibits anti-tumor effects in various cancer types. However, its specific functions and the molecular mechanisms involved in breast cancer cell stemness remain elusive. The effects of ropivacaine on breast cancer stemness were investigated by in vitro and in vivo assays (i.e., FACs, MTT assay, mammosphere formation assay, transwell assays, western blot, and xenograft model). RNA-seq, bioinformatics analysis, Western blot, Luciferase reporter assay, and CHIP assay were used to explore the mechanistic roles of ropivacaine subsequently. RNA-seq analysis identified GGT1 as the downstream target gene responding to ropivacaine. High GGT1 levels are positively associated with a poor prognosis in breast cancer. Ropivacaine inhibited GGT1 expression by interacting with the catalytic domain of AKT1 directly to impair its kinase activity with resultant inactivation of NF-κB. Interestingly, NF-κB can bind to the promoter region of GGT1.

Fig1. Protein levels of GGT1 and p65 in MCF-7 and MDA-MB-231 cells.

Fig2. Protein levels of GGT1, p-iκBa, iκBa, p-NF-κB and NF-κB in GGT1-depleting and GGT1-overexpressing MCF-7.
Case Study 2: Guihua Xu, 2023
The aim of this study is to elucidate the relationship between ferroptosis and glaucoma pathogenesis, and unveil the underlying mechanism. The mitochondrial morphology and autophagosomes were analysed by using transmission electron microscopy (TEM). The contents of glutathione (GSH) and malondialdehyde (MDA) were tested by a GSH assay kit and an MDA detection kit, respectively. The expression of autophagy-related proteins was detected by Western blotting. A serious cell damage, aberrant iron homeostasis, and oxidative stress was shown in RGC-5 after oxygen-glucose deprivation/reoxygenation (OGD/R) treatment and gamma-Glutamyl transpeptidase 1 (GGT1) knockdown, but these effects were significantly alleviated by overexpression of GGT1 or ferroptosis inhibitors. The TEM and immunofluorescent results indicated that mitochondria impairment and autophagosome accumulation in OGD/R-treated cells was improved after GGT1 overexpression, while the phenomenon in GGT1-silenced cells was aggravated. Furthermore, we found that GGT1 can interact with glutamate cysteine ligase catalytic subunit (GCLC) to inhibit autophagy and ferroptosis in RGC-5 cells.
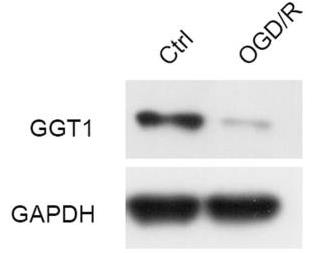
Fig3. Western blot analysis of GGT1 expression.

Fig4. The ROS level was examined in cells after GGT1 overexpression and GCLC knockdown.
Quality Guarantee
High Purity
.jpg)
Fig1. SDS-PAGE (GGT1-4876H)
.
.jpg)
Fig2. SDS-PAGE (GGT1-048H)
Involved Pathway
GGT1 involved in several pathways and played different roles in them. We selected most pathways GGT1 participated on our site, such as Taurine and hypotaurine metabolism,Cyanoamino acid metabolism,Glutathione metabolism, which may be useful for your reference. Also, other proteins which involved in the same pathway with GGT1 were listed below. Creative BioMart supplied nearly all the proteins listed, you can search them on our site.
| Pathway Name | Pathway Related Protein |
|---|---|
| Metabolic pathways | HYKK,GUSB,CYP21A2,B3GNT5A,ATP6V1E1B,NAGLU,MAN2A1,FUT8,PI4K2B,ATP6V1B2 |
| Glutathione metabolism | G6PDX,GPX3,GSTP2,GGCTA,MGST1.1,GGT1A,GPX4,ODC1,GPX5,GSR |
| Cyanoamino acid metabolism | GGT1A,SHMT1,GGT6,SHMT2,GBA3,GGT5,GGT5A,GGT7 |
| Arachidonic acid metabolism | PTGS2A,ALOX5B.3,PTGDSB,DPEP1,PTGES3B,CBR1L,ALOX5,PLA2G4D,CYP2AD2,PTGDS |
| Taurine and hypotaurine metabolism | CSAD,GAD1,ADOB,CDO1,GGT1A,GAD2,GAD1B,GGT5,BAAT,GGT5A |
Protein Function
GGT1 has several biochemical functions, for example, gamma-glutamyltransferase activity,glutathione hydrolase activity,protein binding. Some of the functions are cooperated with other proteins, some of the functions could acted by GGT1 itself. We selected most functions GGT1 had, and list some proteins which have the same functions with GGT1. You can find most of the proteins on our site.
| Function | Related Protein |
|---|---|
| protein binding | IFNAR1,NEUROD1,PARP16,GNMT,SMAD3A,BFSP1,KIF5B,TAGLN2,VPS54,TRIM16 |
| glutathione hydrolase activity | GGT6,GGT5,GGT7 |
| gamma-glutamyltransferase activity | GGT7,GGT1A,GGT5A,GGT6,GGTLC1,GGT5 |
Interacting Protein
GGT1 has direct interactions with proteins and molecules. Those interactions were detected by several methods such as yeast two hybrid, co-IP, pull-down and so on. We selected proteins and molecules interacted with GGT1 here. Most of them are supplied by our site. Hope this information will be useful for your research of GGT1.
NAMPT;potD
Resources
Related Services
Related Products
References


