FLNA
-
Official Full Name
filamin A, alpha -
Overview
The protein encoded by this gene is an actin-binding protein that crosslinks actin filaments and links actin filaments to membrane glycoproteins. The encoded protein is involved in remodeling the cytoskeleton to effect changes in cell shape and migration. This protein interacts with integrins, transmembrane receptor complexes, and second messengers. Defects in this gene are a cause of several syndromes, including periventricular nodular heterotopias (PVNH1, PVNH4), otopalatodigital syndromes (OPD1, OPD2), frontometaphyseal dysplasia (FMD), Melnick-Needles syndrome (MNS), and X-linked congenital idiopathic intestinal pseudoobstruction (CIIPX). Two transcript variants encoding different isoforms have been found for this gene. -
Synonyms
FLNA;filamin A, alpha;filamin A, alpha (actin binding protein 280) , FLN, FLN1, OPD1, OPD2;filamin-A;ABP 280;actin binding protein 280;filamin-1;alpha-filamin;non-muscle filamin;endothelial actin-binding protein;FLN;FMD;MNS;OPD;ABPX;CVD1;F
Recombinant Proteins
- Human
- Chicken
- Mouse
- Turkey
- E.coli
- Chicken Gizzard
- HEK293
- Wheat Germ
- Mammalian Cell
- HEK293T
- Mamanlian cells
- Turkey gizzard muscle
- His
- Non
- Myc&DDK
- GST
- His&Myc
- Flag
| Cat.# | Product name | Source (Host) | Species | Tag | Protein Length | Price |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| FLNA-28906TH |
Recombinant Human FLNA, His-tagged

|
E.coli | Human | His | 1730-2639 a.a. | |
| FLNA-170C |
Active Native chicken FLNA
|
Chicken Gizzard | Chicken | Non |
|
|
| FLNA-185H | Recombinant Human FLNA protein, MYC/DDK-tagged | HEK293 | Human | Myc&DDK |
|
|
| FLNA-289H | Recombinant Human FLNA, GST-tagged | Wheat Germ | Human | GST |
|
|
| FLNA-6143C | Recombinant Chicken FLNA | Mammalian Cell | Chicken | His |
|
|
| FLNA-2923H | Recombinant Human FLNA protein, His&Myc-tagged | E.coli | Human | His&Myc | 2-274aa |
|
| Flna-3038M | Recombinant Mouse Flna Protein, Myc/DDK-tagged | HEK293T | Mouse | Myc&DDK |
|
|
| FLNA-413H | Recombinant Human FLNA Protein, His-tagged | E.coli | Human | His | Ser2~Pro274 |
|
| FLNA-4155HFL | Recombinant Full Length Human FLNA protein | Mamanlian cells | Human | Flag | Full L. 1-2647 a.a. |
|
| FLNA-5086H | Recombinant Human FLNA Protein, Myc/DDK-tagged, C13 and N15-labeled | HEK293T | Human | Myc&DDK |
|
|
| FLNA-873T | Native Turkey FLNA Protein | Turkey gizzard muscle | Turkey | Non |
|
Background
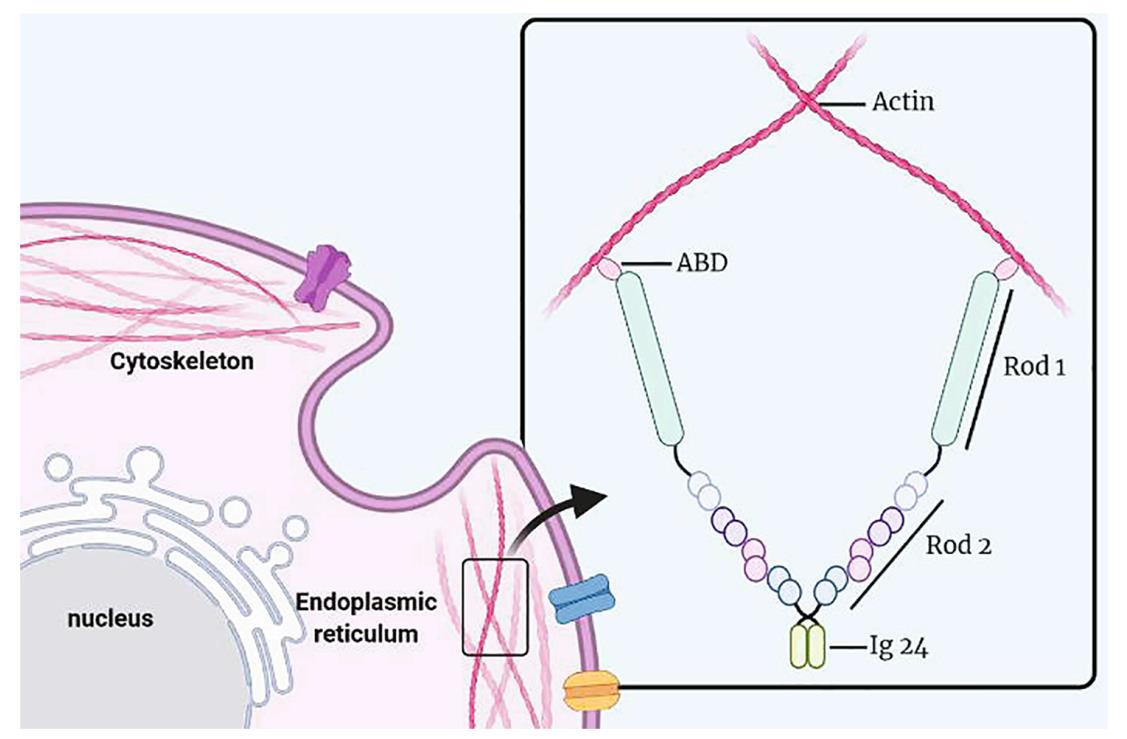
Fig1. Structure of FLNa. (Jie Zhou, 2021)
What is FLNA protein?
FLNA gene (filamin A) is a protein coding gene which situated on the long arm of chromosome X at locus Xq28. The protein encoded by this gene is an actin-binding protein that crosslinks actin filaments and links actin filaments to membrane glycoproteins. The encoded protein is involved in remodeling the cytoskeleton to effect changes in cell shape and migration. This protein interacts with integrins, transmembrane receptor complexes, and second messengers. Defects in this gene are a cause of several syndromes, including periventricular nodular heterotopias (PVNH1, PVNH4), otopalatodigital syndromes (OPD1, OPD2), frontometaphyseal dysplasia (FMD), Melnick-Needles syndrome (MNS), and X-linked congenital idiopathic intestinal pseudoobstruction (CIIPX). The FLNA protein is consisted of 2647 amino acids and FLNA molecular weight is approximately 280.7 kDa.
What is the function of FLNA protein?
It cross-links actin filaments, determining cell shape and locomotion. Filamin A anchors various proteins within the cytoskeleton and is involved in signal transduction, cell proliferation, and differentiation. Additionally, it contributes to processes such as pseudopodia formation, vesicle transport, and tumor resistance. FLNA also plays a role in protecting cells from force-induced apoptosis by enhancing matrix adhesion. Its ability to interact with a multitude of proteins makes it a key player in multiple cellular pathways and functions as a junction and intersection of various signaling pathways.
FLNA Related Signaling Pathway
FLNA plays a role in cell-cell contact and adhesion connections during the development of blood vessels, heart and brain organs. By interacting with SYK, FLNA plays a role in platelet morphology and maintains platelet cytoskeleton organization by regulating ITAM and ITAM-like receptor signaling. FLNA is associated with signaling pathways that respond to increased calcium concentrations in platelet cytoplasm. In breast cancer cells, FLNA may regulate cell proliferation through the ERK signaling pathway.
FLNA Related Diseases
In summary, the FLNA protein is associated with a spectrum of genetic disorders and pathological conditions, primarily due to its crucial roles in cytoskeletal formation, cell adhesion, migration, and various cellular processes. FLNA gene mutations can lead to a range of skeletal, cardiac, and neurological disorders, as well as certain types of cancer, such as breast cancer. The diverse functions of FLNA in the cell make it a critical protein whose dysregulation can lead to a wide array of pathological changes. On the other hand, FLNA deficiency can manifest in a range of phenotypes, including periventricular nodular heterotopia (Huttenlocher syndrome), which is characterized by abnormal migration of neurons during brain development, leading to cognitive impairment and seizures. FLNA deficiency is an X-linked disorder, predominantly affecting females, and can also lead to cardiovascular and pulmonary issues.
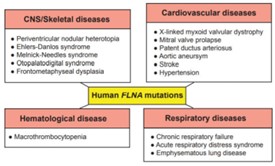
Fig2. Genetic diseases associated with mutations in the human FLNA gene. (Sashidar Bandaru, 2021)
Bioapplications of FLNA
FLNA's function in neuronal migration and other developmental processes positions it as an important factor in studies of embryonic development and organogenesis. Given the association of FLNA mutations with genetic disorders such as periventricular nodular heterotopia and others, it is a significant protein in the study and potential treatment of these conditions. FLNA's role in cell proliferation, migration, and invasion makes it relevant in cancer research, particularly in investigating the mechanisms of tumor progression and metastasis. FLNA's impact on neuronal development and function, particularly in the context of neurodevelopmental disorders, is of interest in neuroscience research.
Case Study
Case Study 1: Naphat Chantaravisoot, 2015
Glioblastoma multiforme (GBM) is one of the most highly metastatic cancers. GBM has been associated with a high level of the mechanistic target of rapamycin complex 2 (mTORC2) activity. Researchers aimed to observe roles of mTORC2 in GBM cells especially on actin cytoskeleton reorganization, cell migration and invasion, and further determine new important players involved in the regulation of these cellular processes. To further investigate the significance of mTORC2 in GBM, researchers treated GBM cells with PP242, an ATP-competitive inhibitor of mTOR, and used RICTOR siRNA to knock down mTORC2 activity. Effects on actin cytoskeleton, focal adhesion, migration, and invasion of GBM cells were examined. To gain insight into molecular basis of the mTORC2 effects on cellular cytoskeletal arrangement and motility/invasion, they affinity purified mTORC2 from GBM cells and identified proteins of interest by mass spectrometry. The results showed that mass spectrometry identified one of them as Filamin A (FLNA). Association of FLNA with RICTOR but not mTOR was demonstrated. Moreover, in vitro, purified mTORC2 can phosphorylate FLNA likewise its known substrate, AKT. In GBM cells, colocalization of FLNA with RICTOR was observed, and the overall amounts of FLNA protein as well as phosphorylated FLNA are high.
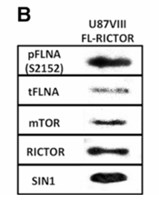
Fig1. Immunoblots of purified proteins from U87vIII cells.
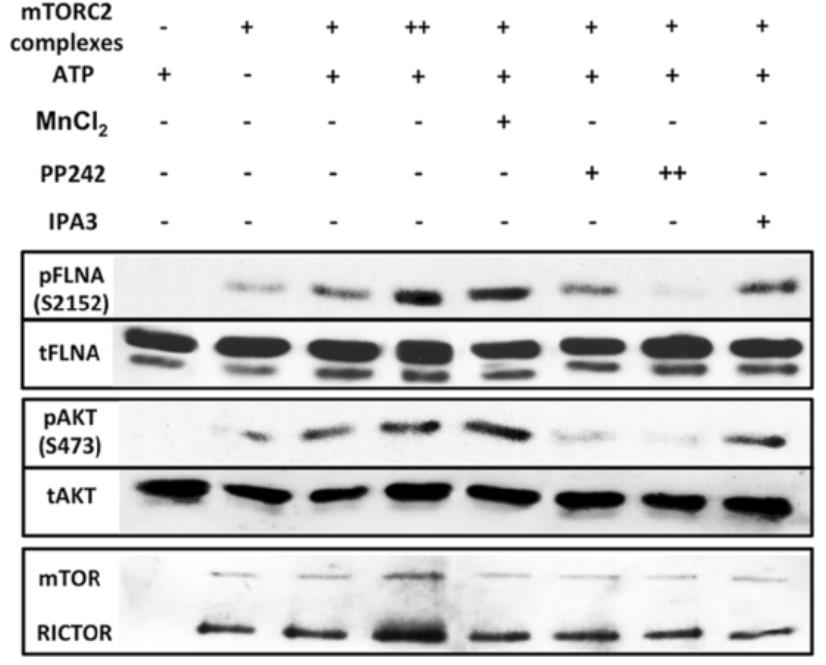
Fig2. In vitro kinase assay of mTORC2 purified from U87vIII cells with FLNA as a substrate.
Case Study 2: Yufen Wang, 2023
Autophagy is a conserved and tightly regulated intracellular quality control pathway. ULK is a key kinase in autophagy initiation, but whether ULK kinase activity also participates in the late stages of autophagy remains unknown. Here, researchers found that the autophagosomal SNARE protein, STX17, is phosphorylated by ULK at residue S289, beyond which it localizes specifically to autophagosomes. Inhibition of STX17 phosphorylation prevents such autophagosome localization. FLNA was then identified as a linker between ATG8 family proteins (ATG8s) and STX17 with essential involvement in STX17 recruitment to autophagosomes. Phosphorylation of STX17 S289 promotes its interaction with FLNA, activating its recruitment to autophagosomes and facilitating autophagosome-lysosome fusion. Disease-causative mutations around the ATG8s- and STX17-binding regions of FLNA disrupt its interactions with ATG8s and STX17, inhibiting STX17 recruitment and autophagosome-lysosome fusion.

Fig3. Mass spectrometric analysis of FLNA in Flag-STX17 immuno-precipitates.
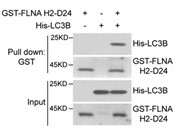
Fig4. LC3B binds FLNA H2-D24 directly.
Quality Guarantee
High Purity
.jpg)
Fig1. SDS-PAGE (FLNA-413H)
.
.jpg)
Fig2. SDS-PAGE (FLNA-5086H)
Involved Pathway
FLNA involved in several pathways and played different roles in them. We selected most pathways FLNA participated on our site, such as MAPK signaling pathway,Focal adhesion,Salmonella infection, which may be useful for your reference. Also, other proteins which involved in the same pathway with FLNA were listed below. Creative BioMart supplied nearly all the proteins listed, you can search them on our site.
| Pathway Name | Pathway Related Protein |
|---|---|
| Focal adhesion | HGF,ARHGAP5,PPP1CAB,PARVA,RAPGEF1B,ITGA6,SEPP1,CCND2,RHOAA,PIK3R5 |
| Salmonella infection | CCL3L1,PKN1,IL6,PKN3,MYD88,DYNC1LI1,PLEKHM2,RAB7A,WASLB,IL1A |
| Proteoglycans in cancer | SRC,AKT1,DROSHA,EZR,TGFB2,ITPR1,WNT3,MAPK11,PIK3R5,CBLB |
| MAPK signaling pathway | FLNB,MAPKAPK5,PPM1BB,MAP2K4B,FGF6,MAPKAPK2A,FGF19,RASGRP3,MOS,ARR3A |
Protein Function
FLNA has several biochemical functions, for example, Fc-gamma receptor I complex binding,Rac GTPase binding,Ral GTPase binding. Some of the functions are cooperated with other proteins, some of the functions could acted by FLNA itself. We selected most functions FLNA had, and list some proteins which have the same functions with FLNA. You can find most of the proteins on our site.
| Function | Related Protein |
|---|---|
| small GTPase binding | FGD1,FGD6,TSC2,PEX5L,RNF152,FGD4,ERRFI1,GDI2,PEX5,FGD5 |
| transcription factor binding | SOX8,NKX3-1,PARD6A,EPN1,DAXX,SOST,CEBPG,KAT2A,ATF7,DDIT3 |
| Rac GTPase binding | RCC2,ARHGAP4,EPS8,CAV1,FMNL1,SOD1,PKN1,PAK4,RAB7A,PAK7 |
| poly(A) RNA binding | CLTC,RPS15,PRDX1,SRP54B,CHERP,CCAR1,G3BP1,CALR,SFRS9,CCBL2 |
| glycoprotein binding | SERPINA1,BMPR1A,FBXO27,RAB14,FGFR1,BBC3,CNTN2,ITGAM,IGF2R,LCK |
| mu-type opioid receptor binding | GNAO1A,GPR177,GNAS,GNAO1B,GNAO1,WLS |
| signal transducer activity | AVP,OPN4A,PLCH1,TICAM2,STAT6,GNAS,GPR152,GPR15,RGS9,PLCD1A |
| Rho GTPase binding | INF2,ROCK2B,ROCK2A,DAPK3,AKAP13,DOCK11,DAAM1,ANTXR2A,PARD6A,FMNL2 |
| SMAD binding | BMP2,SKIA,COL3A1,SMAD2,ACVR1B,BMPR1A,HMGA2,BMPR1B,EID2,SKILB |
Interacting Protein
FLNA has direct interactions with proteins and molecules. Those interactions were detected by several methods such as yeast two hybrid, co-IP, pull-down and so on. We selected proteins and molecules interacted with FLNA here. Most of them are supplied by our site. Hope this information will be useful for your research of FLNA.
ITGB1;ITGB7;CCNB2
Resources
Related Services
Related Products
References
- Jacquemet, G; Morgan, MR; et al. Rac1 is deactivated at integrin activation sites through an IQGAP1-filamin-A-RacGAP1 pathway. JOURNAL OF CELL SCIENCE 126:4121-4135(2013).
- Noam, Y; Phan, L; et al. Distinct regional and subcellular localization of the actin-binding protein filamin a in the mature rat brain. JOURNAL OF COMPARATIVE NEUROLOGY 520:3013-3034(2012).


