ENO1
-
Official Full Name
enolase 1, (alpha) -
Overview
This gene encodes alpha-enolase, one of three enolase isoenzymes found in mammals. Each isoenzyme is a homodimer composed of 2 alpha, 2 gamma, or 2 beta subunits, and functions as a glycolytic enzyme. Alpha-enolase in addition, functions as a structural lens protein (tau-crystallin) in the monomeric form. Alternative splicing of this gene results in a shorter isoform that has been shown to bind to the c-myc promoter and function as a tumor suppressor. Several pseudogenes have been identified, including one on the long arm of chromosome 1. Alpha-enolase has also been identified as an autoantigen in Hashimoto encephalopathy. -
Synonyms
ENO1;enolase 1, (alpha);ENO1L1, MPB1;alpha-enolase;c-myc promoter-binding protein-1;MBP 1;PPH;enolase-alpha;tau-crystallin;non-neural enolase;alpha enolase like 1;phosphopyruvate hydratase;plasminogen-binding protein;MYC promot
Recombinant Proteins
- Human
- Mouse
- Rhesus macaque
- Rat
- Cynomolgus
- Chicken
- Cattle
- Candida albicans
- E.coli
- Mammalian Cells
- HEK293
- Wheat Germ
- Insect Cells
- Yeast
- In Vitro Cell Free System
- His
- GST
- Non
- MAT
- Strep
- Avi
- Fc
- Myc
- DDK
- Flag
Background
What is ENO1 protein?
ENO1 gene (enolase 1) is a protein coding gene which situated on the short arm of chromosome 1 at locus 1p36. This gene encodes alpha-enolase, one of three enolase isoenzymes found in mammals. Each isoenzyme is a homodimer composed of 2 alpha, 2 gamma, or 2 beta subunits, and functions as a glycolytic enzyme. Alpha-enolase in addition, functions as a structural lens protein (tau-crystallin) in the monomeric form. Alternative splicing of this gene results in a shorter isoform that has been shown to bind to the c-myc promoter and function as a tumor suppressor. Alpha-enolase has also been identified as an autoantigen in Hashimoto encephalopathy. The ENO1 protein is consisted of 434 amino acids and ENO1 molecular weight is approximately 47.2 kDa.
What is the function of ENO1 protein?
ENO1, also known as alpha-enolase, is a multifunctional protein that plays a crucial role in glycolysis by catalyzing the conversion of 2-phosphoglycerate into pyruvate. It also engages in cell signaling, immune responses, and is implicated in cancer development due to its upregulation in various cancers, where it influences proliferation, invasion, and metastasis. ENO1 is considered a potential therapeutic target for cancer. Additionally, it can suppress cancer cell ferroptosis by degrading the mRNA of iron regulatory protein 1 (IRP1) and enhance antitumor immunity by destabilizing PD-L1, thereby promoting T-cell-mediated immune responses against tumors. Its expression is also associated with the regulation of cell proliferation and cell cycle in hepatocellular carcinoma.
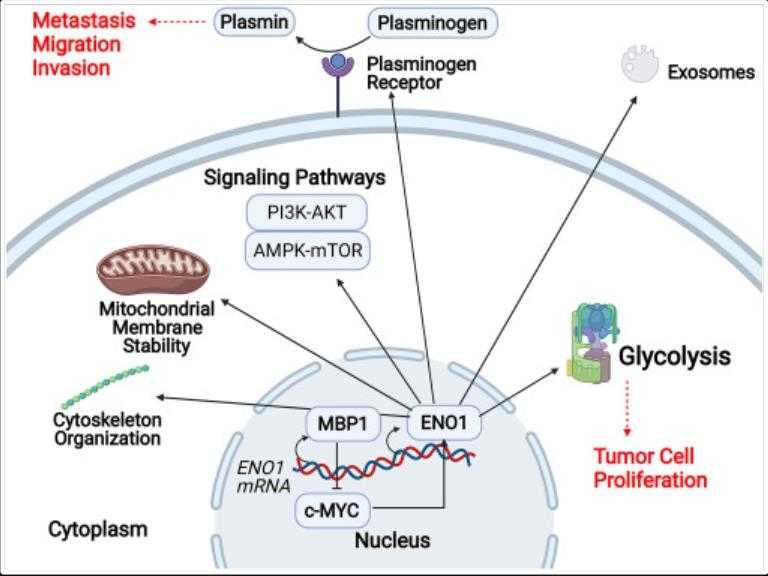
Fig1. Schematic representation of ENO1's multiple cellular functions, varied by its localization. (Chen Kai Huang, 2022)
ENO1 related signaling pathway
ENO1, or alpha-enolase, is a multifunctional protein involved in several cellular processes that are crucial to cancer development and progression. It plays a significant role in glycolysis, acting as a metabolic enzyme that helps cancer cells maintain their energy needs, thus contributing to tumor proliferation and survival. Additionally, ENO1 acts as a plasminogen receptor on the cell surface, which facilitates cancer invasion and metastasis by promoting angiogenesis and extracellular matrix degradation. Moreover, ENO1 is implicated in the activation of oncogenic signaling pathways, such as the PI3K/AKT pathway, which can lead to uncontrolled cell growth and resistance to apoptosis. It also interacts with the hepatocyte growth factor receptor (HGFR) and activates Wnt signaling, which is known to drive epithelial-to-mesenchymal transition (EMT), a process that enhances the metastatic potential of cancer cells.
ENO1 related diseases
ENO1 is a protein associated with a variety of diseases, most notably cancer. It plays a significant role in tumorigenesis and progression across different types of cancer, including liver, lung, and colon cancer. ENO1 contributes to cancer cell glycolysis, proliferation, invasion, and resistance to apoptosis. It also suppresses cancer cell ferroptosis, a form of cell death, by degrading the mRNA of iron regulatory protein 1, which is significant in cancer treatment strategies. Furthermore, ENO1 has been implicated in the regulation of arachidonic acid metabolism, which can promote liver carcinogenesis. The protein's overexpression is often correlated with poor prognosis, suggesting its potential as a diagnostic and prognostic biomarker for cancer.
Bioapplications of ENO1
ENO1 has several bioapplications in the medical field, particularly in cancer research and treatment. It is highly expressed in various solid tumors and associated with poor patient survival rates, making it a potential biomarker for early detection and prognosis in cancers such as liver, lung, and colon. Furthermore, ENO1's role in regulating PD-L1, a protein that inhibits T-cell activity and allows tumor cells to evade immune surveillance, suggests its potential in enhancing antitumor immunity by destabilizing PD-L1, thereby increasing the effectiveness of immunotherapies. Recent studies also indicate that ENO1 may be involved in myelodysplastic neoplasms and acute myeloid leukemia, with high expression levels in bone marrow biopsies and decreased levels of circulating autoantibodies to ENO1 in patients, offering a non-invasive diagnostic alternative. Additionally, ENO1's interaction with β-catenin mRNA, which influences cellular plasticity and could promote mesenchymal-to-epithelial transition in cancer cells, presents another avenue for therapeutic intervention. These applications underscore ENO1's significance in both cancer biology and clinical practice.
Case Study
Case Study 1: Linchong Sun, 2023
ENO1, a glycolytic enzyme, is implicated in cancer development, but the specific mechanisms are not fully understood. This research reveals that ENO1 binds to YAP1 mRNA, enhancing its translation and promoting cancer progression through the YAP1/PLCB1/HPGD axis, which increases arachidonic acid (AA) metabolism and prostaglandin E2 (PGE2) levels. This process can be inhibited by aspirin. Clinical samples show a link between ENO1-regulated AA metabolism and cancer, highlighting a new role for ENO1 and the potential therapeutic use of aspirin in liver cancer with ENO1 or YAP1 overexpression.
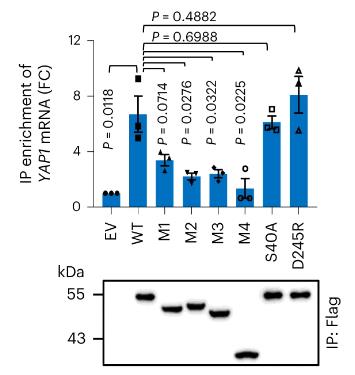
Fig1. Binding of endogenous YAP1 mRNA transcripts by Flag-tagged wild-type ENO1 and indicated ENO1 mutant variants were measured in HEK293T cells.
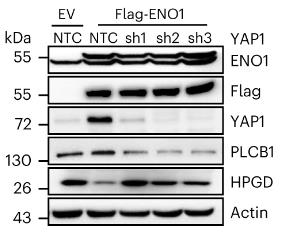
Fig2. PLC cells expressing Flag-tagged ENO1 were further infected with shRNA viruses targeting YAP1.
Case Study 2: Tong Zhang, 2021
ENO1, a key glycolytic enzyme, is overexpressed in various cancers and regulates iron homeostasis in hepatocellular carcinoma (HCC) cells by suppressing iron regulatory protein 1 (IRP1). Here ENO1 binds CNOT6 to degrade IRP1 mRNA, reducing mitoferrin-1 (Mfrn1) expression and inhibiting ferroptosis. The in vitro and in vivo studies, along with clinical data, reveal IRP1 and Mfrn1 as tumor suppressors that promote ferroptosis in HCC. This research uncovers a novel ENO1–IRP1–Mfrn1 pathway in HCC progression and its link to ferroptosis, indicating a potential therapeutic target for cancer treatment.
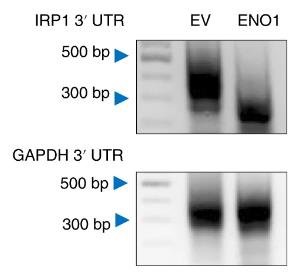
Fig3. Analysis of IRP1 poly (A) tail length in PLC cells expressing Flag-tagged ENO1 using semi-qPCR.
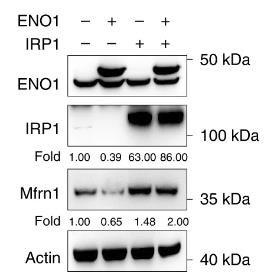
Fig4. Mfrn1 protein expression in PLC cells overexpressing ENO1 and IRP1 in the presence of ferrous iron.
Quality Guarantee
High Purity
.jpg)
Fig1. SDS-PAGE (ENO1-1814H)
.
.jpg)
Fig2. SDS-PAGE (ENO1-3309H)
Involved Pathway
ENO1 involved in several pathways and played different roles in them. We selected most pathways ENO1 participated on our site, such as Glycolysis / Gluconeogenesis,Metabolic pathways,Carbon metabolism, which may be useful for your reference. Also, other proteins which involved in the same pathway with ENO1 were listed below. Creative BioMart supplied nearly all the proteins listed, you can search them on our site.
| Pathway Name | Pathway Related Protein |
|---|---|
| Biosynthesis of amino acids | BCAT1,PHGDH,ALDOCA,PGK1,ASL,ARG2,PRPS2,TPI1A,ALDH18A1,PGK2 |
| Carbon metabolism | PFKMB,GM5506,TPI1,HIBCH,IDH3B,ACAT2,PHGDH,ALDOAA,PDHA1B,DLDH |
| Glycolysis / Gluconeogenesis | ENO3,ALDH9A1,DLDH,LDHB,PGM2,ADH7,HK1,ALDH2,ADH1,ALDH9A1B |
| Metabolic pathways | PDHX,UROD,ENO1B,POLR1A,CYP2A4,TDO2B,GLYCTK,ACO1,CYP2C70,PCXB |
| RNA degradation | ENO2,DDX6,PARN,PNPT1,PABPC5,CNOT6,CNOT4B,BTG4,CNOT3,EXOSC3 |
| HIF- signaling pathway | PFKFB3,MAPK1,ENO2,RBX1,IL6R,RPS6,PIK3R5,IFNGR2,NOX3,CAMK2B |
Protein Function
ENO1 has several biochemical functions, for example, DNA binding,GTPase binding,magnesium ion binding. Some of the functions are cooperated with other proteins, some of the functions could acted by ENO1 itself. We selected most functions ENO1 had, and list some proteins which have the same functions with ENO1. You can find most of the proteins on our site.
| Function | Related Protein |
|---|---|
| magnesium ion binding | COMT,PPM1AA,PKMA,TESC,COMTA,FARSB,GEM,CDC42BPB,MARK1,ADPRHL1 |
| GTPase binding | VPS41,BNIP3,LCP1,PTPRN,RASA1,EPRS,IARS,STOML2,GNB3,GOLGA4 |
| phosphopyruvate hydratase activity | ENO2,ENO4,ENO1A,GM5506,ENO1B,ENO3 |
| transcription factor activity, sequence-specific DNA binding | BACH1A,NME2,Trl,NKX2-1,NFATC2,CNOT8,BARX1,E2F8,FOXA,MSC |
| protein binding | MEF2C,ERCC2,CARKD,GATA5,RPS3A,EFTUD2,SPTA1,COPG,MAGEF1,STX1A |
| poly(A) RNA binding | ZFC3H1,SNRNP70,ZC3H8,SUMO2,NGDN,PTPN1,MRPL10,UTP3,SF3B4,DDX39 |
| DNA binding | ZFP541,APP,MEIS1B,CENPW,SEBOX,ZNF70,IFIH1,MCMDC2,PIN4,KDM5B |
| transcription corepressor activity | RLIM,UBP1,SAP18,DMAP1,CTCF,SSX4,JAZF1,ATF5,HIRA,RBFOX2 |
Interacting Protein
ENO1 has direct interactions with proteins and molecules. Those interactions were detected by several methods such as yeast two hybrid, co-IP, pull-down and so on. We selected proteins and molecules interacted with ENO1 here. Most of them are supplied by our site. Hope this information will be useful for your research of ENO1.
YWHAZ;PCNA;VCAM1;ACHE;Akt2;2-phospho-d-glyceric acid;PDE4DIP;MAP3K7;RIPK2;ACTB
Resources
Related Services
Related Products
References
- Petit, FM; Serres, C; et al. Moonlighting proteins in sperm-egg interactions. BIOCHEMICAL SOCIETY TRANSACTIONS 42:1740-1743(2014).
- Amedei, A; Niccolai, E; et al. Pancreatic cancer: Role of the immune system in cancer progression and vaccine-based immunotherapy. HUMAN VACCINES & IMMUNOTHERAPEUTICS 10:3354-3368(2014).



