EGFL7
-
Official Full Name
EGF-like-domain, multiple 7 -
Overview
This gene encodes a secreted endothelial cell protein that contains two epidermal growth factor-like domains. The encoded protein may play a role in regulating vasculogenesis. This protein may be involved in the growth and proliferation of tumor cells. Alternate splicing results in multiple transcript variants that encode the same protein. -
Synonyms
EGFL7;EGF-like-domain, multiple 7;epidermal growth factor-like protein 7;ZNEU1;EGF like domain 7;EGF like domain containing protein 7;EGF like domain multiple 7;EGF-like protein 7;EGFL 7;EGFL7_HUMAN;Epidermal growth factor like domain protein 7;MEGF 7;MEGF7;MGC111117;Multiple EGF like domain protein 7;Multiple EGF-like domains protein 7;Multiple epidermal growth factor like domain protein 7;Multiple epidermal growth factor-like domains protein 7;NEU1 protein;NOTCH4 like protein;NOTCH4-like protein;RP11 251M1.2;UNQ187/PRO1449;Vascular endothelial statin;VE statin;VE-statin;ZNEU 1;OTTHUMP00000022597;OTTHUMP00000022598;OTTHUMP00000022599;NEU1;RP11-251M1.2
Recombinant Proteins
- Human
- Mouse
- Rhesus macaque
- Rat
- Zebrafish
- Insect Cells
- Mammalian Cell
- Wheat Germ
- Insect Cell
- HEK293
- Mammalian cells
- HEK293T
- E.coli
- In Vitro Cell Free System
- His
- GST
- Non
- His&Fc&Avi
- Myc&DDK
- Flag
- His&T7
Background
What is EGFL7 Protein?
EGFL7, short for epidermal growth factor-like domain 7, is a notable protein chiefly involved in blood vessel development and maintenance. It's unique because it mostly expresses in and acts on endothelial cells, which line our blood vessels. This protein takes part in several roles, like forming blood vessels, aiding in vascular repair, regulating central nervous system inflammation, and playing a part in tumor metastasis and cancer-linked blood vessel growth. EGFL7 includes special domains allowing it to bind to the extracellular matrix and work with other proteins, featuring an elastin microfibril interface (EMI) domain and a couple of EGF-like domains. Its role in vessel formation partly involves tweaking Notch signaling. Basically, EGFL7 is crucial for our vascular system's health, and if it doesn't work right, it can contribute to diseases, especially those involving circulation and cancer.
What is the Function of EGFL7 Protein?
EGFL7, short for epidermal growth factor-like domain 7, acts like a traffic cop for our blood vessel system, directing endothelial cells in their movement and growth to build and fix blood vessels. This protein plays a big role in signaling pathways that dictate cell actions, particularly when it comes to creating new blood vessels. This process is vital for both our body's normal development and its healing response to injuries. Since EGFL7 is deeply involved in how our blood vessels form, it's tied to a bunch of vascular diseases. There's a rising buzz among researchers about using it to tackle these issues. They think EGFL7 might hold the key to fresh treatment paths, possibly helping to manage or even stave off diseases linked to our blood vessel network.
EGFL7 Related Signaling Pathway
The EGFL7 protein is known to influence various signaling pathways, especially the NOTCH pathway, which is key in cell fate decisions, blood vessel formation, and cancer growth, notably in lung cancer. EGFL7 might interfere with treatments targeting EGFR by ramping up NOTCH signaling. It also interacts with PI3K/Akt, MAPK, and Wnt pathways, crucial for cell growth, movement, and blood supply. In colorectal cancer, low EGFL7 levels might lead to more lymph node involvement and vessel invasion, linked to higher VEGF2 levels that boost lymphangiogenesis. EGFL7 is also tied to the RAP1 pathway, affecting cell stickiness and movement, and promotes blood vessel growth via ERK/MAPK signaling. These pathways are often involved when tumors spread and grow, marking EGFL7 as a central player in angiogenesis and cancer dynamics.
EGFL7 Related Diseases
EGFL7 is a protein that's pretty important when it comes to our blood vessels and certain diseases, especially those linked to the vascular system and cancer. It's involved in making and fixing blood vessels, which ties it to issues like atherosclerosis and heart disease. In cancer, EGFL7 might show up more in tumors and could help cancer spread by letting cells become more invasive. Plus, because it's involved in how brain blood vessels develop, EGFL7 might have some connections to conditions like Alzheimer's or Parkinson's. So, researchers see EGFL7 as a potential target for new treatments aimed at vascular problems and cancer.
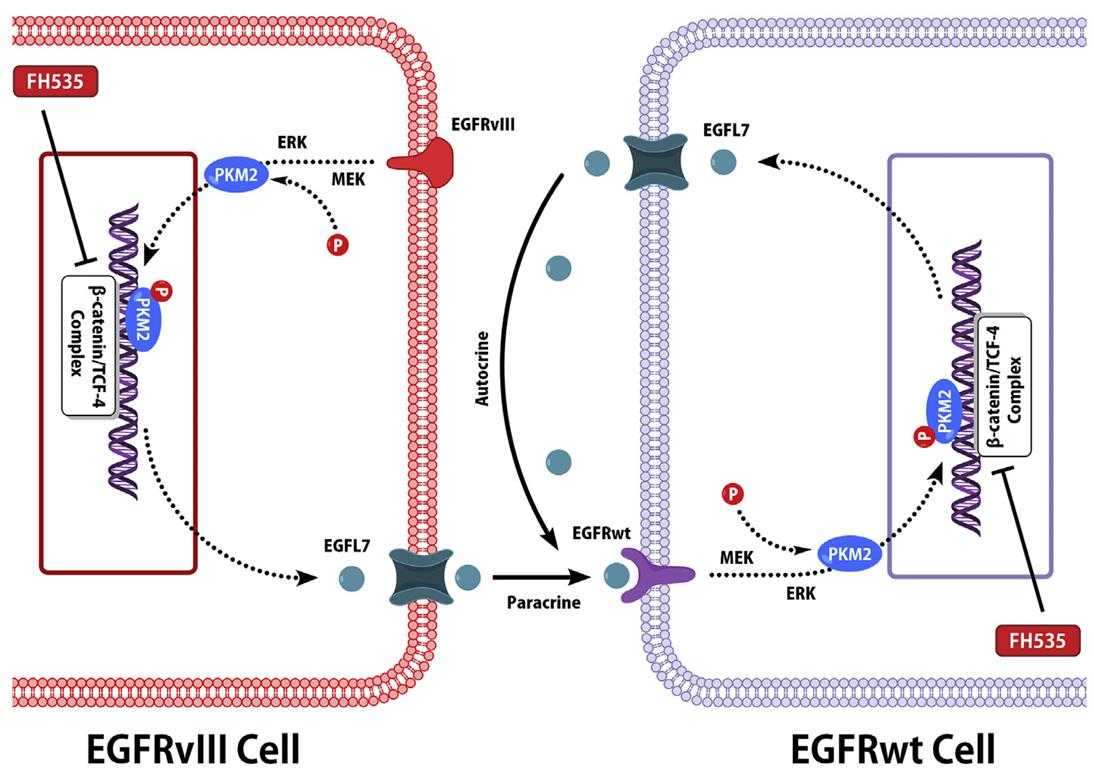
Fig1. A diagram of the mechanism indicating that EGFL7 is an intercellular EGFR signal messenger playing an oncogenic role in glioma. (Haoyu Sun, 2024)
Bioapplications of EGFL7
Recombinant EGFL7 proteins have shown promising applications in scientific research, industrial production, and clinical studies. In the lab, they are used to explore vascular formation and repair mechanisms due to EGFL7's role in blood vessel development. This has broad implications in creating tissue engineering solutions and advancing regenerative medicine. In the biotech world, recombinant EGFL7 can play a role in processes dealing with blood vessel challenges. On the medical front, EGFL7 is eyed as a possible target for treating diseases tied to blood vessels and some cancers, thanks to its role in forming new blood vessels and aiding tumor growth. Scientists are optimistic that tapping into EGFL7 could lead to fresh approaches for tackling cancer and heart-related diseases.
Case Study
Case Study 1: Mirko H.H. Schmidt, 2009
Epidermal growth factor-like domain 7 (EGFL7) is a protein that's known to play a role in how cells move and how blood vessels form, but we don't fully get the mechanics of how it works yet. Research has shown that EGFL7 interacts with Notch family receptors, essentially working against Notch signaling. When EGFL7 is expressed in lab-grown neural stem cells, it seems to dial down Notch signaling, which leads to less cell growth and self-renewal. This shift nudges these cells to become more like neurons and oligodendrocytes rather than other cell types. Moreover, neurons in the brain produce EGFL7, implying it naturally tempers Notch signaling, affecting how adult stem cells in the brain's subventricular zone grow and change.
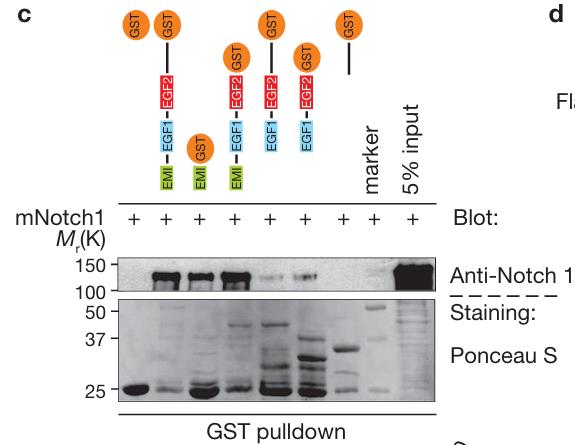
Fig1. Various EGFL7 constructs fused to GST were produced in bacteria and coupled to sepharose beads.
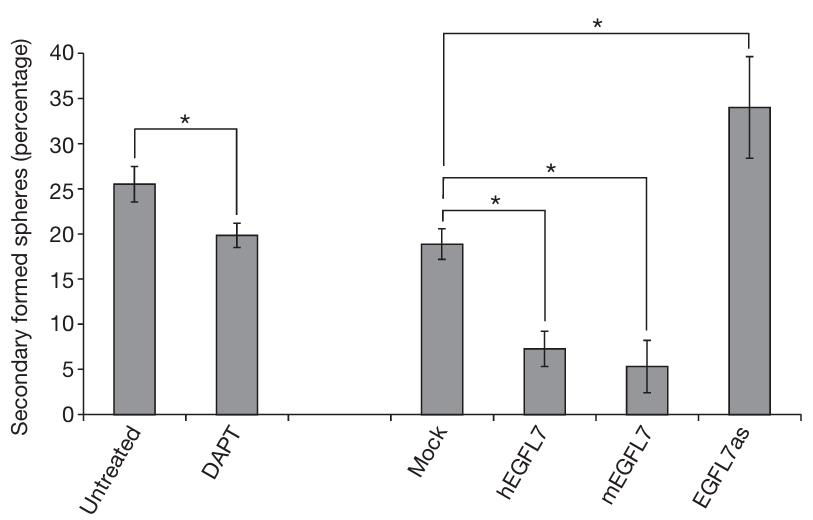
Fig2. Infection of neurospheres with adenovirus encoding human and mouse EGFL7, or application of DAPT.
Case Study 2: Fei-Yi-Fan Wang, 2017
EGFL7, which stands for Epidermal Growth Factor-like domain 7 and also goes by Vascular Endothelial-statin (VE-statin), is a protein that helps form blood vessels and might be a player in cancer growth. In tough cases of brain cancer like glioblastoma multiforme (GBM), especially when tumors show the EGFRvIII mutation, there's a tendency to see higher amounts of EGFL7. This ties in with more severe tumor stages and lower patient survival rates. These tumors seem to use EGFL7 to enhance their β-catenin/TCF4 signaling, thereby promoting further EGFL7 production. This self-sustaining cycle suggests that blocking EGFL7's function could be a promising strategy for therapy against GBM.
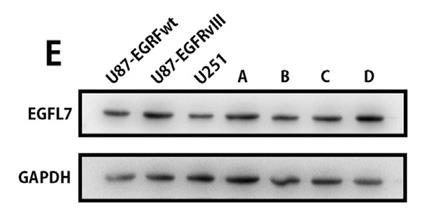
Fig3. Levels of EGFL7 in U87-EGFRwt, U87-EGFRvIII, and U251 cells compared with EGFL7 levels in glioma samples.
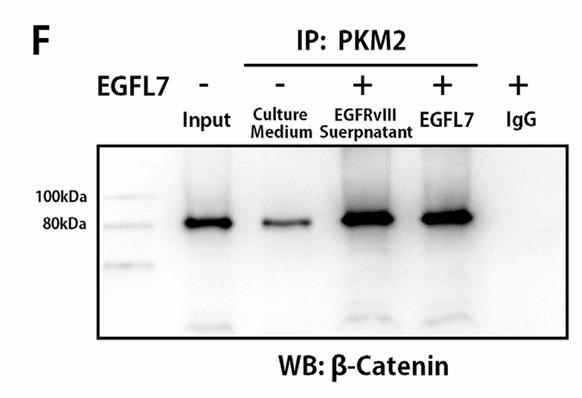
Fig4. EGFL7-mediated formation of the PKM2-β-catenin complex is demonstrated by U87EGFRwt cell-denaturing lysates and Co-IP with PKM2 antibody.
Quality Guarantee
High Purity
.jpg)
Fig1. SDS-PAGE (EGFL7-3115H)
.
.jpg)
Fig2. SDS-PAGE (EGFL7-1694H)
Involved Pathway
EGFL7 involved in several pathways and played different roles in them. We selected most pathways EGFL7 participated on our site, such as , which may be useful for your reference. Also, other proteins which involved in the same pathway with EGFL7 were listed below. Creative BioMart supplied nearly all the proteins listed, you can search them on our site.
| Pathway Name | Pathway Related Protein |
|---|
Protein Function
EGFL7 has several biochemical functions, for example, Notch binding,calcium ion binding. Some of the functions are cooperated with other proteins, some of the functions could acted by EGFL7 itself. We selected most functions EGFL7 had, and list some proteins which have the same functions with EGFL7. You can find most of the proteins on our site.
| Function | Related Protein |
|---|---|
| calcium ion binding | PADI1,PCDH1G1,AKR1C1,GALNT3,CALB1,CAPS,KIAA0494,ATP2C1,MYL9A,PROC |
| Notch binding | JAG2,GALNT11,DLL1,DLL3,JAG1,DNER,SNW1,JAG1B,CHAC1,AAK1 |
Interacting Protein
EGFL7 has direct interactions with proteins and molecules. Those interactions were detected by several methods such as yeast two hybrid, co-IP, pull-down and so on. We selected proteins and molecules interacted with EGFL7 here. Most of them are supplied by our site. Hope this information will be useful for your research of EGFL7.
LMP1;ul31_ebvb9;proS;katG;GFI1B;q81sn0_bacan;mrcA;hscA;SMARCD1;q9wmx2-pro_0000037541;Cenpe;Eef1a1;Smn1;CLTC;LOXL2
Resources
Research Area
Endothelial Cell MarkersEnzymes Secreted by Endothelial Cells
Extracellular Matrix Molecules
Epidermal Growth Factor (EGF)
EGF Ligands
Related Services
Related Products
References
- Zhang, JH; Vernes, JM; et al. Real-time immuno-polymerase chain reaction in a 384-well format: Detection of vascular endothelial growth factor and epidermal growth factor-like domain 7. ANALYTICAL BIOCHEMISTRY 463:61-66(2014).
- Poissonnier, L; Villain, G; et al. Egfl7 Is Differentially Expressed in Arteries and Veins during Retinal Vascular Development. PLOS ONE 9:-(2014).


