CYP46A1
-
Official Full Name
cytochrome P450, family 46, subfamily A, polypeptide 1 -
Overview
This gene encodes a member of the cytochrome P450 superfamily of enzymes. The cytochrome P450 proteins are monooxygenases which catalyze many reactions involved in drug metabolism and synthesis of cholesterol, steroids and other lipids. This endoplasmic reticulum protein is expressed in the brain, where it converts cholesterol to 24S-hydroxycholesterol. While cholesterol cannot pass the blood-brain barrier, 24S-hydroxycholesterol can be secreted in the brain into the circulation to be returned to the liver for catabolism. -
Synonyms
CYP46A1;cytochrome P450, family 46, subfamily A, polypeptide 1;CYP46, cytochrome P450, subfamily 46 (cholesterol 24 hydroxylase);cholesterol 24-hydroxylase;CH24H;cytochrome P450 46A1;cytochrome P450, subfamily 46 (cholesterol 24-hydroxylase);CP46
Recombinant Proteins
- Human
- Chicken
- E.coli
- HEK293
- Wheat Germ
- Mammalian Cell
- Mammalian cells
- Mamanlian cells
- His
- Myc&DDK
- GST
- Non
- Flag
- His&Fc&Avi
| Cat.# | Product name | Source (Host) | Species | Tag | Protein Length | Price |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| CYP46A1-11786H | Recombinant Human CYP46A1, His-tagged | E.coli | Human | His | C-term-300a.a. | |
| CYP46A1-258H | Recombinant Human CYP46A1 protein, MYC/DDK-tagged | HEK293 | Human | Myc&DDK |
|
|
| CYP46A1-259H | Recombinant Human CYP46A1 protein, GST-tagged | Wheat Germ | Human | GST | 201-300 a.a. |
|
| CYP46A1-4530C | Recombinant Chicken CYP46A1 | Mammalian Cell | Chicken | His |
|
|
| CYP46A1-7105HCL | Recombinant Human CYP46A1 293 Cell Lysate | HEK293 | Human | Non |
|
|
| CYP46A1-03H | Active Recombinant Human CYP46A1 Protein | E.coli | Human |
|
||
| CYP46A1-221HFL | Recombinant Full Length Human CYP46A1 Protein, C-Flag-tagged | Mammalian cells | Human | Flag | Full L. |
|
| CYP46A1-706H | Recombinant Human CYP46A1 Protein, His (Fc)-Avi-tagged | HEK293 | Human | His&Fc&Avi |
|
|
| CYP46A1-706H-B | Recombinant Human CYP46A1 Protein Pre-coupled Magnetic Beads | HEK293 | Human |
|
||
| CYP46A1-9798HFL | Recombinant Full Length Human CYP46A1 protein, Flag-tagged | Mamanlian cells | Human | Flag | Full L. |
|
Background
What is CYP46A1 Protein?
CYP46A1 gene (cytochrome P450 family 46 subfamily A member 1) is a protein coding gene which situated on the long arm of chromosome 14 at locus 14q32. This gene encodes a member of the cytochrome P450 superfamily of enzymes. The cytochrome P450 proteins are monooxygenases which catalyze many reactions involved in drug metabolism and synthesis of cholesterol, steroids and other lipids. This endoplasmic reticulum protein is expressed in the brain, where it converts cholesterol to 24S-hydroxycholesterol. While cholesterol cannot pass the blood-brain barrier, 24S-hydroxycholesterol can be secreted in the brain into the circulation to be returned to the liver for catabolism. The CYP46A1 protein is consisted of 500 amino acids and CYP46A1 molecular weight is approximately 56.8 kDa.
What is the Function of CYP46A1 Protein?
CYP46A1, full name cytochrome P450 family 46 subgroup A member 1, is an enzyme expressed in the brain whose primary function is to metabolize cholesterol, converting it to 24S-hydroxycholesterol (24(S)OHC). This metabolic process is crucial for regulating cholesterol levels in the brain, as cholesterol plays a key role in neurodevelopment and nerve function. The activity of CYP46A1 may be related to the pathogenesis of Alzheimer's disease (AD), as abnormal accumulation of 24S-OHC May be related to the pathological process of AD. In addition, the activity of the enzyme CYP46A1 is also associated with age-related cognitive decline, and its expression levels decline with age, which may affect the brain's cholesterol metabolism and neurological function.
CYP46A1 Related Signaling Pathway
The enzyme CYP46A1 plays a key role in cholesterol metabolism in the brain, converting cholesterol to 24S-hydroxycholesterol (24(S)OHC), which is the main pathway by which cholesterol is eliminated in the brain. This transformation is essential for the maintenance of brain cholesterol homeostasis and is associated with the regulation of neurodevelopment, synaptic function, and cognitive function. The function of the CYP46A1 enzyme is not limited to cholesterol metabolism, it may also play a role by influencing the function of neurotransmitter receptors, regulating the signaling of neurotrophic factors, and participating in the transport and distribution of cholesterol within cells. In addition, astrocytes play an important role in cholesterol metabolism in the brain, where they not only provide cholesterol to neurons, but are also involved in regulating memory formation. Lipidized apolipoprotein particles such as ApoE promote the entry of cholesterol into neurons through specific receptors, and may influence the expression of cholesterol biosynthesis genes in neurons through mirnas. ApoE isomers show different effects in regulating learning and memory, among which ApoE4 is less efficient than ApoE3 in inhibiting neuronal cholesterol synthesis and promoting memory formation.
CYP46A1 Related Diseases
CYP46A1 is a cytochrome P450 enzyme specifically expressed in the brain, which is involved in the maintenance of cerebral cholesterol homeostase by catalysing the conversion of cholesterol into 24S-hydroxyl cholesterol. Changes in its activity are closely related to the pathogenesis of various neurodegenerative diseases, including Alzheimer's disease, Huntington's disease and Niemann-Pick type C diseases. It may play a role by influencing neurotransmitter receptor function, neurotrophic factor signaling, and cholesterol transport and distribution within the cell, modulating cognitive function and neurodegenerative processes.
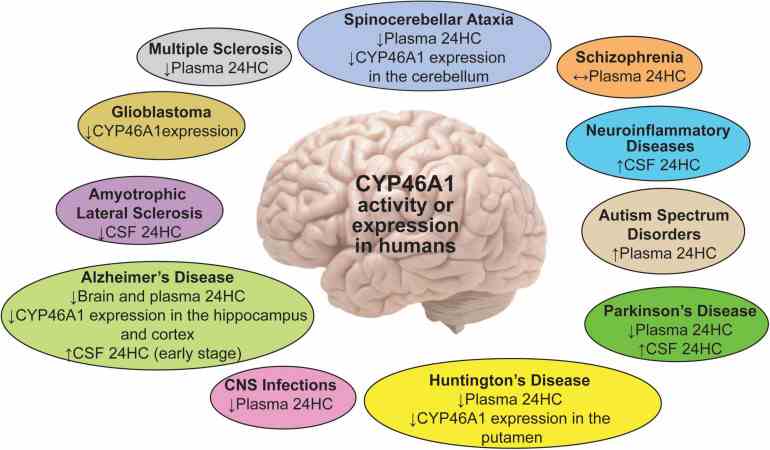
Fig1. A summary of the 24HC or CYP46A1 measurements in human plasma, CSF and brain regions in different brain disorders. (Irina A Pikuleva, 2021)
Bioapplications of CYP46A1
As a key neurocytochrome P450 enzyme, CYP46A1's role in brain cholesterol metabolism makes it a potential target for the treatment of neurodegenerative diseases. Although there are no commercial drugs directly targeting CYP46A1 at present, its role in regulating cognitive function and affecting neuropathological processes is being actively explored. To develop new therapeutic strategies, such as increasing its expression level in the brain by means of gene therapy, in the hope of improving the symptoms and pathological features of neurodegenerative diseases associated with dysregulation of cholesterol metabolism.
Case Study
Case Study 1: Mingzhi Han, 2020
Dysregulated cholesterol metabolism is a hallmark of many cancers, including glioblastoma (GBM), but its role in disease progression is not well understood. Here, researchers identified cholesterol 24-hydroxylase (CYP46A1), a brain-specific enzyme responsible for the elimination of cholesterol through the conversion of cholesterol into 24(S)-hydroxycholesterol (24OHC), as one of the most dramatically dysregulated cholesterol metabolism genes in GBM. CYP46A1 was significantly decreased in GBM samples compared with normal brain tissue. A reduction in CYP46A1 expression was associated with increasing tumour grade and poor prognosis in human gliomas. Ectopic expression of CYP46A1 suppressed cell proliferation and in vivo tumour growth by increasing 24OHC levels. RNA-seq revealed that treatment of GBM cells with 24OHC suppressed tumour growth through regulation of LXR and SREBP signalling. Efavirenz, an activator of CYP46A1 that is known to penetrate the blood-brain barrier, inhibited GBM growth in vivo.
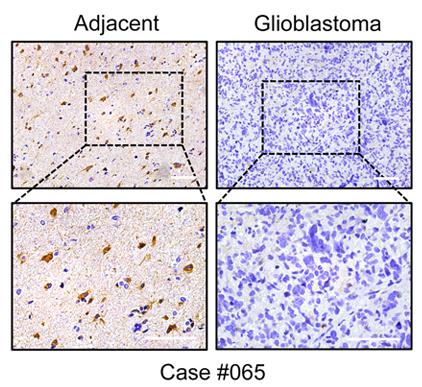
Fig1. Representative images of CYP46A1 IHC staining in GBM and adjacent brain tissues from one specific case.

Fig2. Kaplan–Meier survival curve of tumour-bearing mice injected with GBM cells infected with lenti-Ctrl or lenti-CYP46A1.
Case Study 2: Maria João Nunes, 2024
Here, researchers hypothesized that CYP46A1 could be a potential therapeutic target in Niemann-Pick type C (NPC) disease, a rare and fatal neurodegenerative disorder, characterized by cholesterol accumulation in endolysosomal compartments. Herein, CYP46A1 ectopic expression, in cellular models of NPC and in Npc1tm(I1061T) mice by adeno-associated virus-mediated gene therapy improved NPC disease phenotype. Amelioration in functional, biochemical, molecular and neuropathological hallmarks of NPC disease were characterized. In vivo, CYP46A1 expression partially prevented weight loss and hepatomegaly, corrected the expression levels of genes involved in cholesterol homeostasis, and promoted a redistribution of brain cholesterol accumulated in late endosomes/lysosomes. Moreover, concomitant with the amelioration of cholesterol metabolism dysregulation, CYP46A1 attenuated microgliosis and lysosomal dysfunction in mouse cerebellum, favoring a pro-resolving phenotype. In vivo CYP46A1 ectopic expression improves important features of NPC disease and may represent a valid therapeutic approach to be used concomitantly with other drugs.
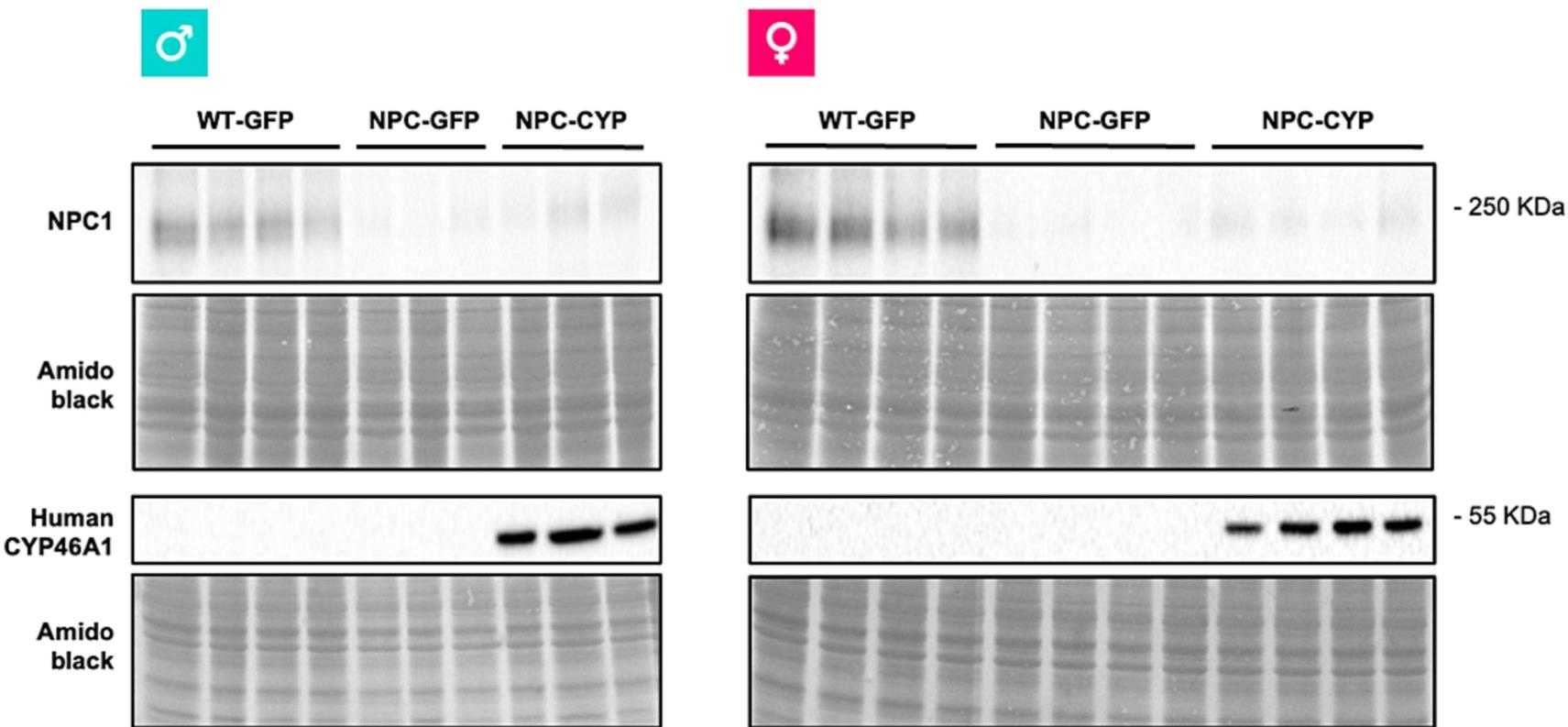
Fig3. Western blot analysis of NPC1 and CYP46A1 in total extracts.

Fig4. Effect of CYP46A1 ectopic expression on neuroinflammation in NPC mouse cerebellum.
Quality Guarantee
High Purity
.jpg)
Fig1. SDS-PAGE (CYP46A1-221HFL)
Involved Pathway
CYP46A1 involved in several pathways and played different roles in them. We selected most pathways CYP46A1 participated on our site, such as Bile acid and bile salt metabolism,Biological oxidations,Cytochrome P450 - arranged by substrate type, which may be useful for your reference. Also, other proteins which involved in the same pathway with CYP46A1 were listed below. Creative BioMart supplied nearly all the proteins listed, you can search them on our site.
| Pathway Name | Pathway Related Protein |
|---|---|
| Endogenous sterols | CYP17A1,FDX1,CYP1B1,POMCB,FDXR,CYP27A1,CYP7A1,CYP11B1,CYP11A1,CYP21A2 |
| Bile acid and bile salt metabolism | ACOT8,SLC27A5,SCP2B,AKR1C6,AKR1C4,CYP27A1,SLCO1B1,BRSK2,SLC27A2A,AKR1C2 |
| Biological oxidations | GLYATL1,CYP2K6,CYP27B1,UGT1B5,DPEP2,ACY3,PAOX,CYP3A7-CYP3AP1,CYP2K19,SULT2ST2 |
| Metabolism | OAZ3,NUDT4,CYP2F1,AK8,COX5B,SACM1LA,PMVK,CYGB,MMS19,GSTK1 |
| Cytochrome P450 - arranged by substrate type | CYP17A1,CYP2AD3,CYP2R1,CYP3A5,CYP2J2,CYP8B2,CYP2Y3,CYP3A7-CYP3AP1,CYP4T8,CYP1B1 |
| Phase 1 - Functionalization of compounds | CYP2K22,CYP2C18,CYP2K8,CYP2V1,CYP4F12,CES1,ADH8A,CYP2Y3,CYP26A1,CYP3A7-CYP3AP1 |
| Primary bile acid biosynthesis | CYP46A1.4,AMACR,SLC27A5,CYP46A1.2,BAAT,CYP8B1,SCP2,BRSK2,SCP2A,ACOX2 |
| Metabolism of lipids and lipoproteins | MED25,ALOX5AP,YAP1,CERS5,CYP2V1,APOEB,CYP27A1,SLC25A1A,ACER1,Agmo |
Protein Function
CYP46A1 has several biochemical functions, for example, cholesterol 24-hydroxylase activity,heme binding,iron ion binding. Some of the functions are cooperated with other proteins, some of the functions could acted by CYP46A1 itself. We selected most functions CYP46A1 had, and list some proteins which have the same functions with CYP46A1. You can find most of the proteins on our site.
| Function | Related Protein |
|---|---|
| iron ion binding | HIF1AN,LCN2,HBB,CYP19A1,CYP2X8,CYP2AA9,CYP19A1A,P4HA1,C14orf169,CYP3C4 |
| cholesterol 24-hydroxylase activity | CYP46A1.2,CYP46A1.3,CYP46A1.4 |
| steroid hydroxylase activity | CYP2C55,CYP2K16,CYP2E1,CYP2C19,CYP2D6,CYP2AD2,CYP2A4,CYP2C70,CYP2A12,CYP3A4 |
| heme binding | CYP4F12,CYP2C55,HBZ,CYP26C1,CBS,CYP8B2,NOS1,CYP2X9,FECH,MPO |
Interacting Protein
CYP46A1 has direct interactions with proteins and molecules. Those interactions were detected by several methods such as yeast two hybrid, co-IP, pull-down and so on. We selected proteins and molecules interacted with CYP46A1 here. Most of them are supplied by our site. Hope this information will be useful for your research of CYP46A1.
RIN3
Resources
Related Services
Related Products
References


