CUL1
-
Official Full Name
cullin 1 -
Overview
Cullin 1, also known as CUL1, is a human protein and gene from cullin family. This protein plays an important role in protein degradation and protein ubiquitination. This is an essential component of the SCF (SKP1-CUL1-F-box protein) E3 ubiquitin ligase complex, which mediates the ubiquitination of proteins involved in cell cycle progression, signal transduction and transcription. In the SCF complex, it serves as a rigid scaffold that organizes the SKP1-F-box protein and RBX1 subunits. May contribute to catalysis through positioning of the substrate and the ubiquitin-conjugating enzyme. -
Synonyms
CUL1;cullin 1;MGC149834;MGC149835;cullin-1;CUL-1;OTTHUMP00000202347
Recombinant Proteins
- Human
- Mouse
- Insect Cell
- E.coli
- Mammalian Cell
- HEK293
- HEK293T
- Mammalian cells
- E. coli
- In Vitro Cell Free System
- Non
- GST
- His
- Myc&DDK
- Flag
- His&Fc&Avi
Background
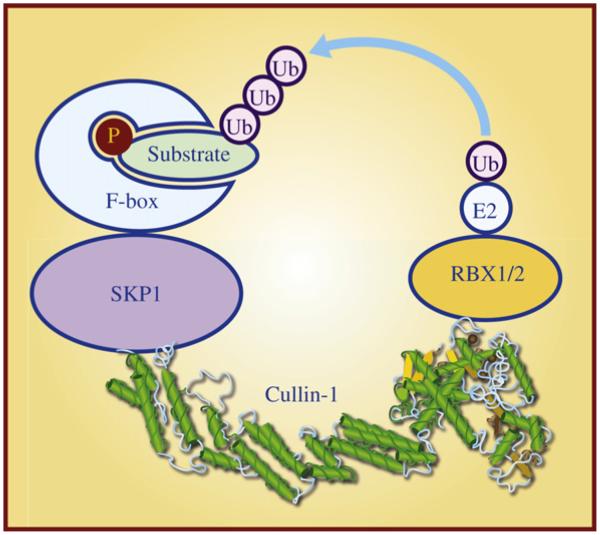
Fig1. SCF E3 ubiquitin ligase and its four components. (Chuan-Ming Xie, 2013)
What is CUL1 Protein?
CUL1 gene (cullin 1) is a protein coding gene which situated on the long arm of chromosome 7 at locus 7q36. CUL1 protein is a multifunctional protein that functions as a core component of multiple cullin-RING-based SCF (SKP1-CUL1-F-box protein) E3 ubiquitin protein ligase complexes. These complexes are responsible for regulating ubiquitination of proteins during the cell cycle, signal transduction, and transcription. The CUL1 protein interacts with the Skp1 protein and the F-box protein through its n-terminal domain, while its C-terminal domain interacts with Rbx1 (also known as ROC1), a RING protein that links the E2 ubiquitin-binding enzyme and facilitates the ubiquitination process. The CUL1 protein is consisted of 776 amino acids and CUL1 molecular weight is approximately 89.7 kDa.
What is the Function of CUL1 Protein?
CUL1 plays a role in regulating the cell cycle, particularly through its involvement in the SCF complexes that target specific proteins for degradation, allowing the cell to transition through different phases of the cycle. CUL1 is implicated in the regulation of gene expression by mediating the degradation of transcription factors or other regulatory proteins. By targeting proteins for ubiquitination, CUL1 helps maintain a balance of protein levels within the cell, ensuring that damaged or unnecessary proteins are degraded. CUL1 has been found to associate with chromatin and regulate the transcription of specific genes, including those involved in mitochondrial function and splicing. The modification of CUL1 by Nedd8, a process called neddylation, activates the E3 ligase activity of the SCF complex, which is crucial for its function in protein ubiquitination.
CUL1 Related Signaling Pathway
CUL1 protein, as a core component of the E3 ubiquitin ligase complex SCF (Skp1-CUL1-F-box), is involved in regulating a variety of signal transduction pathways. It is involved in cell cycle, signal transduction, transcriptional regulation and other important biological processes by labeling target proteins through ubiquitination. For example, the SCF complex is involved in the regulation of the NF-κB signaling pathway by ubiquitinating IκBα, influencing immune response and cell survival. In addition, CUL1 is involved in the Wnt signaling pathway, which is regulated by ubiquitinating beta-catenin. In plants, CUL1 is also involved in regulating the biological clock, affecting the circadian rhythm. In addition, CUL1 binding to chromatin, especially to gene promoter regions controlled by c-MYC transcription factors, is involved in transcriptional regulation of specific genes. This effect of CUL1 may have important implications for the metabolic status and stress response of cells, such as mitochondrial stress observed in CUL1-deficient cells.
CUL1 Related Diseases
Abnormal function of the CUL1 protein has been associated with a variety of diseases, especially certain types of cancer, for example by affecting cell cycle progression and signaling pathways, which may lead to the proliferation and survival of tumor cells. In addition, the role of CUL1 in the immune response may also be relevant to autoimmune diseases. Because CUL1 plays a key role in important physiological processes of cells, dysregulation of its expression or function may affect a variety of cellular processes and thus be associated with the occurrence and development of diseases.
Bioapplications of CUL1
CUL1 protein has emerged as a potential target for some cancer therapies due to its key role in regulating cell cycle, signal transduction, and transcription processes, and its related applications have focused on the development of small molecule inhibitors targeting CUL1 or its interacting partners with a view to treating cancer by interfering with the function of CUL1. In addition, CUL1's role in the immune response has also made it a focus of research in immune-related diseases, which may help in the development of new therapies to modulate the immune response. However, CUL1 protein-related drugs or therapies have not yet been widely used in the clinic and are still in the research and development stage.
Case Study
Case Study 1: Zhou Yu, 2016
Protein ubiquitination regulated by ubiquitin ligases plays important roles in innate immunity. However, key regulators of ubiquitination during innate response and roles of new types of ubiquitination (apart from Lys48- and Lys63-linkage) in control of innate signaling have not been clearly understood. Here with rhCUL1 protein, the in vitro analysis of ubiquitination of ASK1 was performed. F-box only protein Fbxo21, a functionally unknown component of SCF (Skp1-Cul1-F-box protein) complex, facilitates Lys29-linkage and activation of ASK1 (apoptosis signal-regulating kinase 1), and promotes type I interferon production upon viral infection. Fbxo21 deficiency in mice cells impairs virus-induced Lys29-linkage and activation of ASK1, attenuates c-Jun N-terminal kinase (JNK) and p38 signaling pathway, and decreases the production of proinflammatory cytokines and type I interferon, resulting in reduced antiviral innate response and enhanced virus replication.
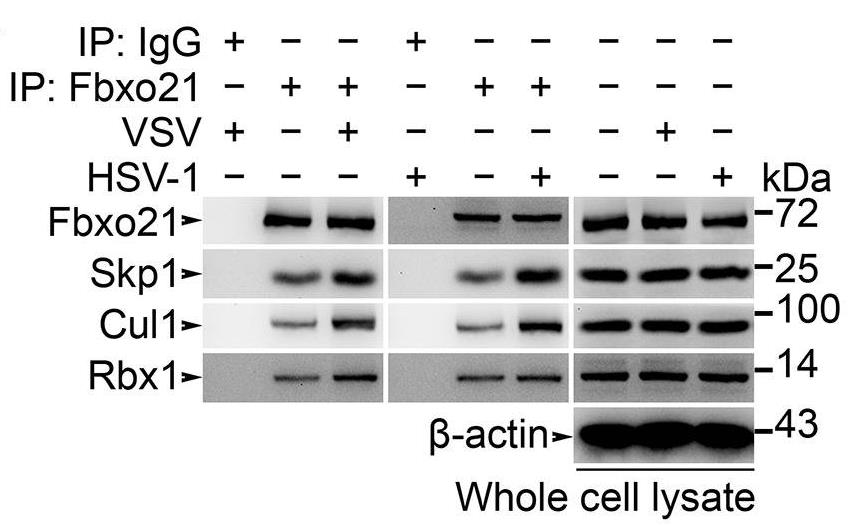
Fig1. Wild type RAW264.7 cells were treated with or without VSV (MOI = 1) or HSV-1 (MOI = 5) as indicated for 2 hr.

Fig2. Polyubiquitination of ASK1 was examined by immunoblot (IB) after immunoprecipitations (IP).
Case Study 2: Melanie A Sweeney, 2020
The ubiquitin-proteasome system is responsible for site- and target-specific ubiquitination and protein degradation. Specificity of ubiquitination is conferred by ubiquitin ligases. Cullin-RING complexes, the largest family of ligases, require multi-unit assembly around one of seven cullin proteins. To investigate the direct role of cullins in ubiquitination of DNA-bound proteins and in gene regulation, researchers analyzed their subcellular locations and DNA-affinities. CUL4A and CUL7 to be largely excluded from the nucleus, whereas CUL4B was primarily nuclear. CUL1,2,3, and 5 showed mixed cytosolic and nuclear expression. When analyzing chromatin affinity of individual cullins, CUL1 preferentially associated with active promoter sequences and co-localized with 23% of all DNA-associated protein degradation sites. CUL1 co-distributed with c-MYC and specifically repressed nuclear-encoded mitochondrial and splicing-associated genes.
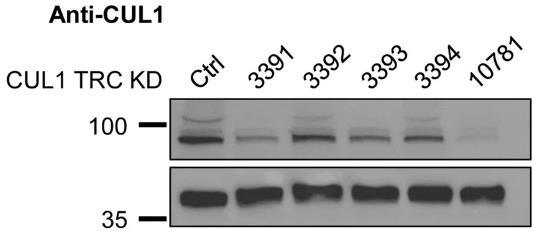
Fig3. HeLa cells stably transduced with shRNA against CUL1 show a stable reduction in CUL1 expression based on immunoblot against endogenous CUL1.

Fig4. Genome browser tracks of CUL1, H3K27ac, degradative ubiquitin, and c-MYC at select splicing-associated CUL1 and c-MYC target genes.
Quality Guarantee
High Purity
.jpg)
Fig1. SDS-PAGE (CUL1-26258TH)
.
.jpg)
Fig2. SDS-PAGE (CUL1-1937HFL)
Involved Pathway
CUL1 involved in several pathways and played different roles in them. We selected most pathways CUL1 participated on our site, such as Cell cycle,Oocyte meiosis,Ubiquitin mediated proteolysis, which may be useful for your reference. Also, other proteins which involved in the same pathway with CUL1 were listed below. Creative BioMart supplied nearly all the proteins listed, you can search them on our site.
| Pathway Name | Pathway Related Protein |
|---|---|
| Cell cycle | PLK1,CENPE,GINS4,ORC6,DULLARD,SKA1,YWHAG,VRK1,GORASP1,CLASP1 |
| Herpes simplex infection | TBP,TNFRSF14,OAS2,IFIT1,CSNK2A2,FADD,IRF9,CCL5,IFNA6,UBE2R2 |
| TGF-beta signaling pathway | SPAW,SKP1,ZFYVE16,PITX2,GDF7,BMPR1B,ACVR2AA,BMP2,PPP2R1B,INHBAB |
| Circadian rhythm | PRKAG1,PRKAB2,PER1,SKP1,CSNK1E,RORB,CRY1,RBX1,BTRC,CRY2 |
| Oocyte meiosis | PPP3CCA,ANAPC5,ANAPC13,YWHAQA,SKP1,MAD2L2,SMC1A,CAMK2B1,CAMK2B,YWHAQB |
| Wnt signaling pathway | WNT5A,NKD2,WNT4,FBXW11B,FZD7A,RHOAD,FBXW2,FZD3A,DVL1B,CAMK2B1 |
| Ubiquitin mediated proteolysis | UBE2IA,ANAPC5,UBE2N,UBE2IB,UBA3,RCHY1,WWP2,NEDD4L,UBE2S,CUL4B |
| Protein processing in endoplasmic reticulum | SELS,UBQLN2,UBQLN3,SEC63,DNAJC1,CAPN2A,PARK2,ATF6,UBE2G1,EIF2S1B |
Protein Function
CUL1 has several biochemical functions, for example, protein binding,contributes_to ubiquitin protein ligase activity,ubiquitin protein ligase binding. Some of the functions are cooperated with other proteins, some of the functions could acted by CUL1 itself. We selected most functions CUL1 had, and list some proteins which have the same functions with CUL1. You can find most of the proteins on our site.
| Function | Related Protein |
|---|---|
| ubiquitin protein ligase binding | TMEM189,YOD1,TRIM28,BAG6,USP13,PACRG,GPR19,MOAP1,SUMO1,TOLLIP |
| contributes_to ubiquitin protein ligase activity | FBXL5,FBXL3,MED12,CUL5,FBXL6,FBXL18,CUL1B,FBXL4,FBXL7,CUL1A |
| protein binding | PAICS,RAN,HMG20A,STK38,UTP14A,ALG2,TACC1,PPP3R2,HDHD2,CAPN1 |
Interacting Protein
CUL1 has direct interactions with proteins and molecules. Those interactions were detected by several methods such as yeast two hybrid, co-IP, pull-down and so on. We selected proteins and molecules interacted with CUL1 here. Most of them are supplied by our site. Hope this information will be useful for your research of CUL1.
RBX1;SKP1
Resources
Related Services
Related Products
References
- Ramakrishnan, R; Liu, HB; et al. Identification of novel CDK9 and Cyclin T1-associated protein complexes (CCAPs) whose siRNA depletion enhances HIV-1 Tat function. RETROVIROLOGY 9:-(2012).
- Surjit, M; Varshney, B; et al. The ORF2 glycoprotein of hepatitis E virus inhibits cellular NF-kappa B activity by blocking ubiquitination mediated proteasomal degradation of I kappa B alpha in human hepatoma cells. BMC BIOCHEMISTRY 13:-(2012).



