COMT
-
Official Full Name
catechol-O-methyltransferase -
Overview
Catechol-O-methyltransferase catalyzes the transfer of a methyl group from S-adenosylmethionine to catecholamines, including the neurotransmitters dopamine, epinephrine, and norepinephrine. This O-methylation results in one of the major degradative pathways of the catecholamine transmitters. In addition to its role in the metabolism of endogenous substances, COMT is important in the metabolism of catechol drugs used in the treatment of hypertension, asthma, and Parkinson disease. COMT is found in two forms in tissues, a soluble form (S-COMT) and a membrane-bound form (MB-COMT). The differences between S-COMT and MB-COMT reside within the N-termini. Several transcript variants are formed through the use of alternative translation initiation sites and promoters. -
Synonyms
COMT;catechol-O-methyltransferase;catechol O-methyltransferase;Catechol O methyltransferase;COMT_HUMAN;EC 2.1.1.6;OTTHUMP00000197748;OTTHUMP00000197749;OTTHUMP00000197750;OTTHUMP00000197751;OTTHUMP00000197846;OTTHUMP00000198331
Recombinant Proteins
- Human
- Mouse
- Rhesus macaque
- Rat
- Bovine
- Mus musculus
- E.coli
- Human
- Wheat Germ
- Mammalian Cells
- HEK293
- In Vitro Cell Free System
- Insect Cells
- His
- Non
- GST
- SUMO
- Avi
- Fc
- DDK
- Myc
Background
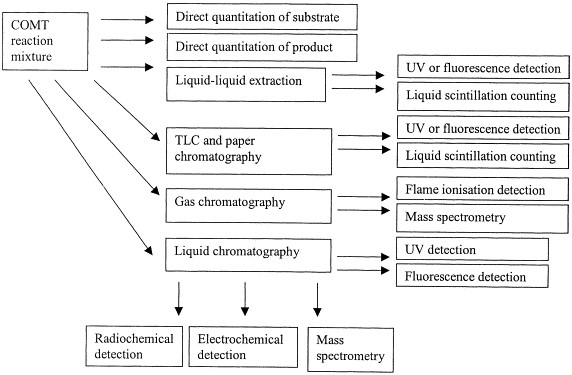
Fig1. Analytical methods applied to COMT activity analysis. (Pia Pihlavisto, 2002)
What is COMT protein?
COMT (catechol-O-methyltransferase) gene is a protein coding gene which situated on the long arm of chromosome 22 at locus 22q11. Catechol-O-methyltransferase catalyzes the transfer of a methyl group from S-adenosylmethionine to catecholamines, including the neurotransmitters dopamine, epinephrine, and norepinephrine. This O-methylation results in one of the major degradative pathways of the catecholamine transmitters. In addition to its role in the metabolism of endogenous substances, COMT is important in the metabolism of catechol drugs used in the treatment of hypertension, asthma, and Parkinson disease. COMT is found in two forms in tissues, a soluble form (S-COMT) and a membrane-bound form (MB-COMT). The differences between S-COMT and MB-COMT reside within the N-termini. COMT protein is consisted of 271 amino acids and its molecular mass is approximately 30.0 kDa.
What is the function of COMT protein?
COMT regulates levels of neurotransmitters such as dopamine and norepinephrine in the brain, which are involved in mood, cognitive function, and stress response, among other things. COMT is involved in the metabolic processes of certain drugs, including some used to treat Parkinson's disease and depression. Changes in COMT activity may affect pain perception because catecholamines play a role in pain signaling. COMT also plays a role in cell proliferation and differentiation and may be involved in the development of some cancers. Polymorphisms in the COMT gene may affect COMT enzyme activity, which in turn affects an individual's response to stress and neurotransmitter levels, which have been linked to the risk of multiple mental health disorders.
COMT Related Signaling Pathway
COMT regulates the activity and levels of catecholamine neurotransmitters such as dopamine, norepinephrine and epinephrine through O-methylation. COMT plays a role in pain signaling and may modulate pain perception by affecting levels of catecholamines. COMT is involved in estrogen metabolism, affecting estrogen activity and levels through methylation, and has been linked to the risk of hormone-related diseases such as breast cancer. Changes in COMT activity may affect homocysteine levels and are associated with hyperhomocysteinemia.
COMT Related Diseases
COMT is associated with a variety of neurological diseases, including Parkinson's disease, schizophrenia, major depression, anxiety disorders, etc. COMT is involved in breast Cancer by metabolizing estrogen, as well as Bladder Cancer, Cataract, Vitiligo, Prostate Cancer, and so on. COMT may be involved in the development of diabetes and is associated with insulin resistance. COMT activity is associated with pain perception and may affect pain sensitivity. COMT is related to restless leg syndrome, where symptoms include back pain, headaches and aches. In addition, Anorexia Nervosa, Diabetic Neuropathy, Fibromyalgia, Dystonia, these diseases are associated with COMT gene polymorphism.
Bioapplications of COMT
As a key metabolic enzyme of catecholamines, COMT plays an important role in the metabolism of the neurotransmitter dopamine. Therefore, recombinant COMT proteins have been widely used to study dopamine signaling pathways and the pathogenesis of related neuropsychiatric disorders. In the field of drug development, COMT inhibitors are new drugs for the treatment of Parkinson's disease (PD). By inhibiting COMT activity, dopamine levels in the brain can be increased, thereby improving symptoms in PD patients. In plants, COMT is a key enzyme in the phenylpropanoid pathway and plays an important role in regulating the biosynthesis of lignin and lignan. Genetic engineering can improve plant stress resistance and biomass energy conversion efficiency by changing the expression level of COMT in plants.
Case Study
Case Study 1: QiQi Zhou, 2023
Catechol-O-methyltransferase (COMT), an enzyme that inactivates and degrades biologically active catecholamines, plays an important role in numerous physiologic processes, including modulation of pain perception. This study's objective was to determine the mechanism(s) of how decreased colonic COMT in PI-IBS-D patients contributes to the chronic abdominal pain phenotype after enteric infections. Colon neurons, epithelial cells, and macrophages were procured with laser capture microdissection from PI-IBS-D patients to evaluate cell-specific colonic COMT, microRNA-155 (miR-155), and tumor necrosis factor (TNF) α expression levels compared to recovered patients (infection cleared: did not develop PI-IBS-D) and control individuals. COMT-/-, colon-specific COMT-/-, and miR-155-/- mice and human colonoids were used to model phenotypic expression of COMT in PI-IBS-D patients and to investigate signaling pathways linking abdominal pain. The results showed that Colonic COMT levels were significantly decreased and correlated with increased visual analog scale abdominal pain ratings in PI-IBS-D patients compared to recovered patients and control individuals. Colonic miR-155 and TNF-α were increased in PI-IBS-D patients with diminished colonic COMT. COMT-/- mice had significantly increased expression of miR-155 and TNF-α in both colon tissues and dorsal root ganglia.

Fig1. There was a significant inverse correlation between VAS pain scores and colonic COMT expression (ELISA assay).

Fig2. A significant decrease in COMT expression with increased TNF-α and miR-155.
Case Study 2: Yutaka Hashimoto, 2021
Catechol-estrogens can cause genetic mutations and to counteract their oncogenicity, the catechol-O-methyltransferase (COMT) gene is capable of neutralizing these reactive compounds. In this study, the researchers determined the functional effects and regulation of COMT in prostate cancer. Both the Cancer Genome Atlas (TCGA) and immunohistochemical analysis of clinical specimens demonstrated a reduction of COMT expression in prostate cancer. Also, western analyses of prostate cancer cell lines show COMT levels to be minimal in DuPro and DU145 and thus, these cells were used for further analyses. Re-expression of COMT led to suppressed migration ability (wound healing assay) and enhanced apoptosis (flow cytometric analyses), and when challenged with 4-hydroxyestradiol, a marked reduction of cell proliferation (MTT assay) was observed. Xenograft growth in athymic mice also resulted in inhibition due to COMT. As a mechanism, western analyses show cleaved CASP3 and BID were increased whereas XIAP and cIAP2 were reduced due to COMT. As COMT expression is low in prostate cancer, its regulation was determined. Databases identified several miRNAs capable of binding COMT and of these, miR-195 was observed to be increased in prostate cancer according to TCGA.

Fig3. COMT expression is downregulated in AR negative prostate cancer cell lines.
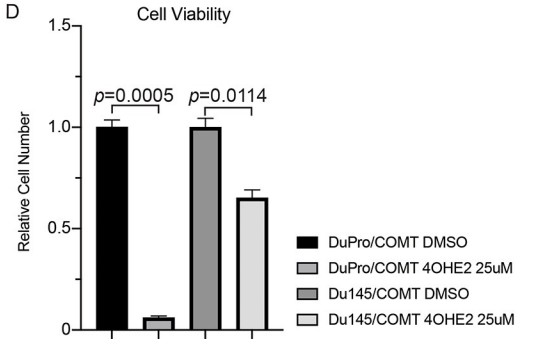
Fig4. COMT expression attenuates 4-hydroxyestradiol stimulated proliferation.
Quality Guarantee
High Purity
.jpg)
Fig1. SDS-PAGE (COMT-1688H)
.
.jpg)
Fig2. SDS-PAGE (COMT-3037H)
Involved Pathway
COMT involved in several pathways and played different roles in them. We selected most pathways COMT participated on our site, such as Biogenic Amine Synthesis,Biological oxidations,Dopamine clearance from the synaptic cleft, which may be useful for your reference. Also, other proteins which involved in the same pathway with COMT were listed below. Creative BioMart supplied nearly all the proteins listed, you can search them on our site.
| Pathway Name | Pathway Related Protein |
|---|---|
| Dopamine metabolism | DDC,NQO1 |
| Estrogen metabolism | CYP1A1,ARSE,CYP1B1,ARSD,NQO1 |
| Biogenic Amine Synthesis | DBH,CHAT,DDC |
| Biological oxidations | CYP2J2,AADAC,CYP2D6,CYP2Y3,UGT1B5,FDXR,CYP3C1,SULT4A1,SULT2ST2,CYP4F11 |
| Dopaminergic synapse | PPP2CB,PPP2R5C,GRIN2A,MAPK8,KIF5A,KCNJ5,SCN1A,GNG8,GNB4,DRD5 |
Protein Function
COMT has several biochemical functions, for example, O-methyltransferase activity,catechol O-methyltransferase activity,magnesium ion binding. Some of the functions are cooperated with other proteins, some of the functions could acted by COMT itself. We selected most functions COMT had, and list some proteins which have the same functions with COMT. You can find most of the proteins on our site.
| Function | Related Protein |
|---|---|
| protein binding | CAND2,MACF1,EMX2,AMBRA1,PACSIN3,BIRC7,MAP2K1,SULT1C2,RARG,ZBTB4 |
| catechol O-methyltransferase activity | TOMT,COMTB,COMTA |
| O-methyltransferase activity | TRMT10B,FAM86,RNMTL1A,METTL23,PRDM11,TRMT10C,PRDM13,COMTB,METTL8,METTL21A |
| magnesium ion binding | ATP4A,GTPBP10,ZAK,PPM1AA,HPRT1,FDXACB1,IRAK4,ICK,FIGNL1,TSSK2 |
Interacting Protein
COMT has direct interactions with proteins and molecules. Those interactions were detected by several methods such as yeast two hybrid, co-IP, pull-down and so on. We selected proteins and molecules interacted with COMT here. Most of them are supplied by our site. Hope this information will be useful for your research of COMT.
TRIP13;vpr;MCC;RGS2;LITAF;XRN2;c9jaw5_human;FN1;1C;COL1A2;FGF2;RIN1;USP6NL;PPA2;EXO1
Resources
Related Services
Related Products
References
- Hu, ZY; Lausted, C; et al. Quantitative Liver-Specific Protein Fingerprint in Blood: A Signature for Hepatotoxicity. THERANOSTICS 4:215-228(2014).
- Hartung, JE; Ciszek, BP; et al. beta(2)- and beta(3)-adrenergic receptors drive COMT-dependent pain by increasing production of nitric oxide and cytokines. PAIN 155:1346-1355(2014).


