CD209
-
Official Full Name
CD209 molecule -
Overview
This gene encodes a transmembrane receptor and is often referred to as DC-SIGN because of its expression on the surface of dendritic cells and macrophages. The encoded protein is involved in the innate immune system and recognizes numerous evolutionarily divergent pathogens ranging from parasites to viruses with a large impact on public health. The protein is organized into three distinct domains: an N-terminal transmembrane domain, a tandem-repeat neck domain and C-type lectin carbohydrate recognition domain. The extracellular region consisting of the C-type lectin and neck domains has a dual function as a pathogen recognition receptor and a cell adhesion receptor by binding carbohydrate ligands on the surface of microbes and endogenous cells. The neck region is important for homo-oligomerization which allows the receptor to bind multivalent ligands with high avidity. Variations in the number of 23 amino acid repeats in the neck domain of this protein are rare but have a significant impact on ligand binding ability. This gene is closely related in terms of both sequence and function to a neighboring gene (GeneID 10332; often referred to as L-SIGN). DC-SIGN and L-SIGN differ in their ligand-binding properties and distribution. Alternative splicing results in multiple variants.[provided by RefSeq, Feb 2009] -
Synonyms
CD209;CD209 molecule;CDSIGN;CLEC4L;DC-SIGN;DC-SIGN1;CD209 antigen;HIV gpl20-binding protein;C-type lectin domain family 4 member L;C-type lectin domain family 4, member L;dendritic cell-specific ICAM-3-grabbing non-integrin 1;dendritic cell-specific intracellular adhesion molecules (ICAM)-3 grabbing non-integrin
Recombinant Proteins
- Human
- Rhesus macaque
- Zebrafish
- Chlorocebus Aethiops
- HEK293
- CHO
- Mammalian cells
- Wheat Germ
- E.coli
- Mammalian Cell
- Human Cell
- In Vitro Cell Free System
- E.coli expression system
- Fc
- Non
- GST
- His&T7
- His
- Flag
- His&Flag&Strep
- His&Fc&Avi
| Cat.# | Product name | Source (Host) | Species | Tag | Protein Length | Price |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| CD209-633H | Recombinant Human CD209 protein, hFc-tagged | HEK293 | Human | Fc | 62-404 a.a. | |
| CD209-635H |
Active Recombinant Human CD209 protein
|
CHO | Human | Non | Gln59-Ala404 |
|
| CD209-636H |
Active Recombinant Human CD209 protein, Fc-tagged
|
Mammalian cells | Human | Fc | Lys62-Ala404 |
|
| CD209-0747H | Recombinant Human CD209 Protein | Wheat Germ | Human | Non |
|
|
| CD209-0748H | Recombinant Human CD209 Protein, GST-Tagged | Wheat Germ | Human | GST |
|
|
| CD209-634H | Recombinant Human CD209 protein, Fc-tagged | HEK293 | Human | Fc | Lys62-Ala404 |
|
| CD209-7173H | Recombinant Human CD209 protein, His & T7-tagged | E.coli | Human | His&T7 | Glu70~Ala404 |
|
| CD209-727R | Recombinant Rhesus CD209 protein, His-tagged | HEK293 | Rhesus macaque | His | Lys62-Glu381 |
|
| CD209-728R | Recombinant Rhesus CD209 protein, Fc-tagged | HEK293 | Rhesus macaque | Fc | Lys62-Glu381 |
|
| CD209-7858Z | Recombinant Zebrafish CD209 | Mammalian Cell | Zebrafish | His |
|
|
| CD209-2986HCL | Recombinant Human CD209 cell lysate | Human Cell | Human | Non |
|
|
| CD209-057H | Recombinant Human CD209 Protein, C-His-tagged | E.coli | Human | His |
|
|
| CD209-0810H | Recombinant Human CD209 Protein (M1-A404), Flag tagged | E.coli | Human | Flag | M1-A404 |
|
| CD209-0811H | Recombinant Human CD209 Protein (M1-A404), His/Strep, Flag tagged | E.coli | Human | His&Flag&Strep | M1-A404 |
|
| CD209-0919H | Recombinant Human CD209 Protein (Glu70-Ala404), N-His tagged | E.coli | Human | His | Glu70-Ala404 |
|
| CD209-14H | Recombinant Human CD209 Protein, His (Fc)-Avi-tagged | HEK293 | Human | His&Fc&Avi |
|
|
| CD209-14H-B | Recombinant Human CD209 Protein Pre-coupled Magnetic Beads | HEK293 | Human |
|
||
| CD209-3033HF | Recombinant Full Length Human CD209 Protein | In Vitro Cell Free System | Human | Full L. 359 amino acids |
|
|
| CD209-3034HF | Recombinant Full Length Human CD209 Protein, GST-tagged | In Vitro Cell Free System | Human | GST | Full L. 404 amino acids |
|
| CD209-4236H | Recombinant Human CD209 Protein (Gln59-Ala404), N-Fc tagged | Mammalian cells | Human | Fc | Gln59-Ala404 |
|
| CD209-643H | Recombinant Human CD209 protein, His-tagged | HEK293 | Human | His | Gln59-Ala404 |
|
| CD209-726R | Recombinant Rhesus CD209 protein (Lys62-Glu381), His-tagged | HEK293 | Rhesus macaque | His | 62-381 a.a. |
|
| RFL7980CF | Recombinant Full Length Chlorocebus Aethiops Cd209 Antigen(Cd209) Protein, His-Tagged | E.coli expression system | Chlorocebus Aethiops | His | Full L. Full Length (1-381) |
|
Background
What is CD209 Protein?
CD209, or DC-SIGN, hangs out on immune cell surfaces like those of dendritic cells and macrophages. Imagine it as a lookout, catching intruders by grabbing onto specific sugars that decorate viruses or bacteria. The cool thing is, it helps the immune system decide when to attack by recognizing these foreign patterns. However, it's not all good news; some viruses like HIV, ebola, and even the pesky COVID-19 virus actually exploit CD209 to sneak into cells. With its role in both defense and sneak attacks by pathogens, CD209 is a hot topic in research, especially for designing therapies that block bad guys without messing with the essential functions of your immune system.
What is the Function of CD209 Protein?
CD209, often called DC-SIGN, is pretty much a lookout on immune cells such as dendritic cells and macrophages. It acts like a sensor, spotting intruders by hooking onto specific sugar molecules found on the surface of many viruses and bacteria. Once it's latched onto these sugars, it doesn't just sit around; it kicks off a series of immune responses. This protein is also involved in helping the immune cells communicate and can even assist viruses like HIV and SARS-CoV-2 in entering host cells, which isn't great but shows its wide range of interactions. Blocking this protein's action is being looked at as a way to slow down some infections or overly aggressive immune responses, especially in the case of severe cases of illnesses like COVID-19.
CD209 Related Signaling Pathway
CD209, or DC-SIGN, plays a key role in the immune system as it helps spot and respond to pathogens. It sits on the surface of certain immune cells like dendritic cells and macrophages. This protein acts as a kind of lookout, recognizing nasty invaders by binding to specific sugar molecules commonly found on viruses and bacteria. By doing so, it kicks off a series of immune responses. It's like a first alert that triggers further actions to tackle infections, playing into the larger web of immune signaling that battles pathogens.
CD209 Related Diseases
CD209, or DC-SIGN, plays a role in how our body deals with certain diseases, acting like a gateway for some nasty viruses to sneak into immune cells. This protein is like a handle virus particles use to get a grip on the host's cells. Notably, it's been linked to illnesses like COVID-19, Ebola, and HIV, where the viruses exploit CD209 to infect cells more efficiently. The way it aids these viruses suggests it's a key player in how some infections spread and worsen, potentially affecting the severity of diseases by influencing how the body's immune response gets triggered or dampened. Understanding its interactions could be critical for developing treatments that block these entry points, offering a way to fend off these infections.
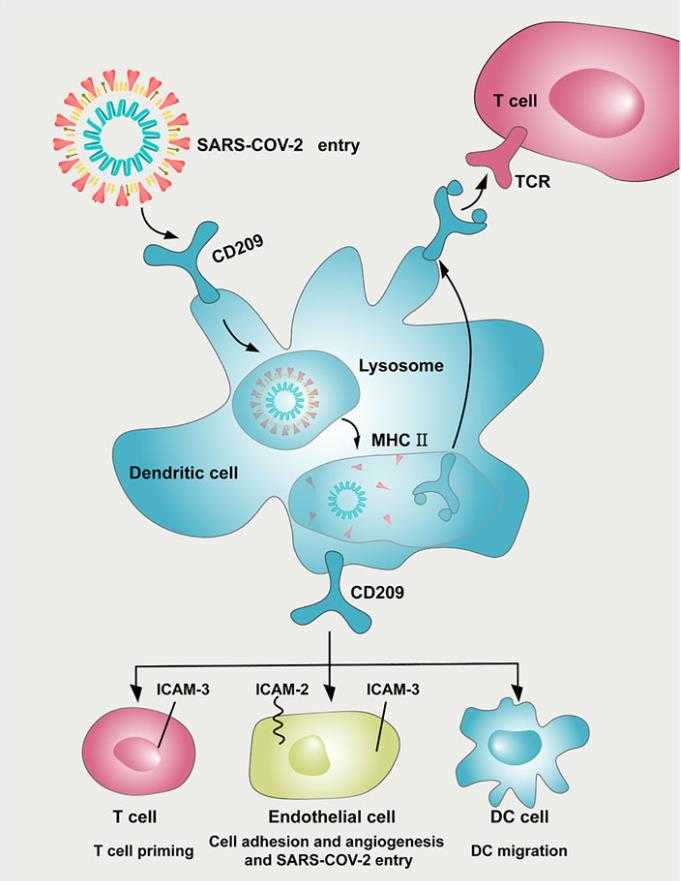
Fig1. Potential implication of CD209 inhibitor in preventing SARS-CoV-2 damage in tumor patients. (Jinyuan Li, 2022)
Bioapplications of CD209
Recombinant CD209 protein, often known for its role as DC-SIGN, is used a lot in research and industry, mainly because it's a key player in immune system studies. Scientists use it to dive into how our bodies recognize and fight off pathogens, like viruses and bacteria. It's also a tool for developing new vaccines or treatments by figuring out how to block harmful interactions with viruses such as HIV or even something like COVID-19. Plus, in industrial settings, it's helping in the creation of diagnostic tests, giving us better ways to catch infections early. So, whether it's in labs for basic research or in industry for creating new tech, recombinant CD209 is pretty versatile.
Case Study
Case Study 1: Vanessa Porkolab, 2018
On the surface of dendritic cells, C-type lectin receptors (CLRs) are key in spotting sugar-based signatures from harmful invaders and help regulate immune responses. But sometimes, these receptors get tricked by nasty viruses and bacteria. That's why making molecules that can precisely target one specific CLR—either to tweak the immune response or stop an infection—is super valuable in medicine. One example is trying to block DC-SIGN, which helps HIV latch onto T cells, without disrupting langerin, which clears the virus away. This is tricky since both receptors recognize similar sugars. In our research, we compared how well DC-SIGN and langerin stick to natural sugars, discovering that while both latch onto GlcNAc, adding sulfate groups can tilt preference towards langerin. We used special mutagenesis and X-ray analysis, finding that adding a 6-sulfate group to the sugar made it more specific to langerin. A particular part of langerin, the K313 residue, was key in its binding. With this info, we crafted a new sugar-like compound that specifically targets DC-SIGN over langerin. Tests showed our compound kept the natural binding feel but had a better grip and was exclusively for DC-SIGN.
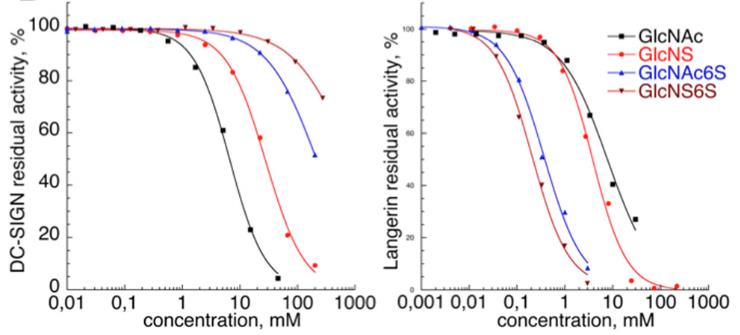
Fig1. Inhibition curves for DC-SIGN (left) and langerin (right).
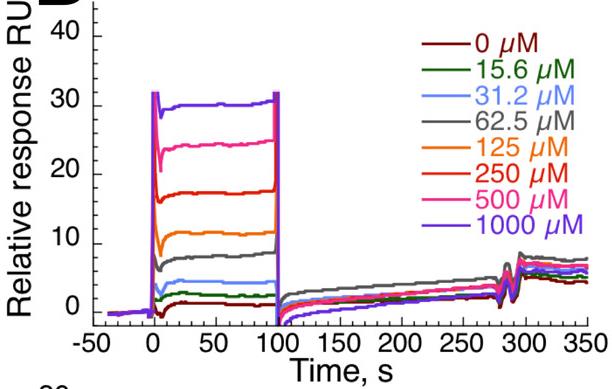
Fig2. Titration of glycomimetic 7 onto DC-SIGN ECD functionalized surface.
Case Study 2: Jonathan Cramer, 2021
DC-SIGN is a type of pattern recognition receptor found on macrophages and dendritic cells, playing a key role in how our bodies recognize invading pathogens. It's kind of a catch-all gateway for many nasty viruses like SARS-CoV-2, Ebola, and HIV-1. With the whole COVID-19 crisis, scientists have been eyeing DC-SIGN because it might be behind some of those severe cases by sparking intense immune responses. Blocking the virus from latching onto DC-SIGN could be a smart move to tone down these responses and stop the disease from getting worse. Researchers recently stumbled upon a new group of molecules that act as DC-SIGN blockers. These molecules, built from triazole-based mannose lookalikes, can stop SARS-CoV-2 from attaching to cells that have DC-SIGN, and even prevent the virus from using this receptor to hop onto other cells. This breakthrough offers a promising avenue for crafting super-targeted therapies against a range of viral threats by focusing on DC-SIGN.
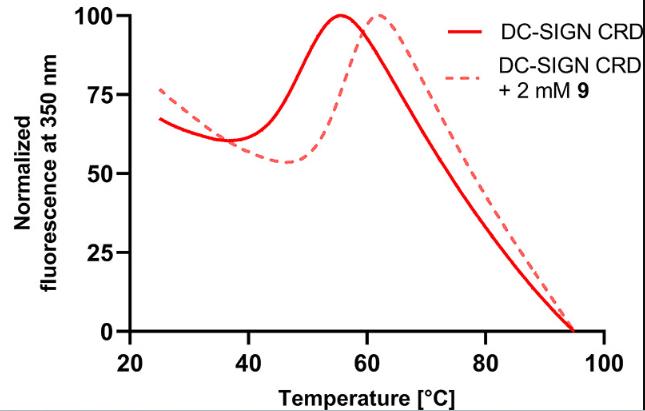
Fig3. Thermal denaturation curve of DC-SIGN CRD in the absence and presence of 2 mM 9.
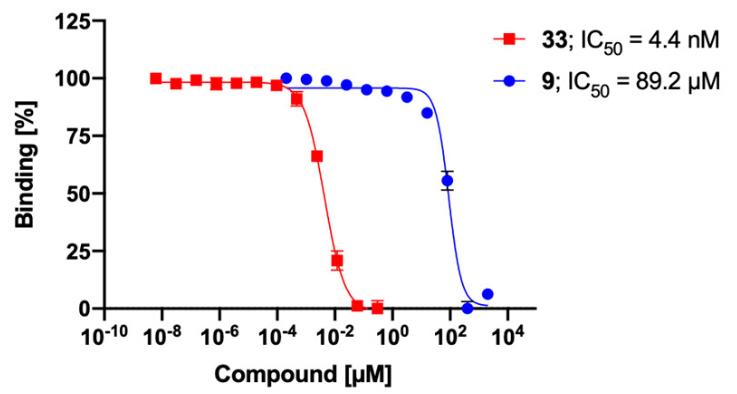
Fig4. Glycoprotein binding assay: DC-SIGN+ B-THP-1 cells were incubated with 10 nM Cy5-labeled SARS-CoV-2 spike glycoprotein S1 subunit.
Quality Guarantee
High Purity
.jpg)
Fig1. SDS-PAGE (CD209-7173H)
.
.jpg)
Fig2. SDS-PAGE (CD209-0748H)
Involved Pathway
CD209 involved in several pathways and played different roles in them. We selected most pathways CD209 participated on our site, such as Phagosome,Tuberculosis,Measles, which may be useful for your reference. Also, other proteins which involved in the same pathway with CD209 were listed below. Creative BioMart supplied nearly all the proteins listed, you can search them on our site.
| Pathway Name | Pathway Related Protein |
|---|---|
| Phagosome | CLEC4M,BF2,ITGB1,HLA-DQA2,ATP6V1E1B,HLA-F,cgr2b,LAMP1,CALR,TUBA1B |
| Tuberculosis | cgr2b,IFNA21,HLA-DQA2,TLR9,RAB7,TNFRSF1A,IFNA14,CORO1A,IL1A,ARHGEF12 |
| Measles | BBC3,IFNA5,Cd209g,PIK3R1,IFNAR1,IFNGR2,TACR1,AKT1,IFNA12,FASLG |
Protein Function
CD209 has several biochemical functions, for example, carbohydrate binding,mannose binding,metal ion binding. Some of the functions are cooperated with other proteins, some of the functions could acted by CD209 itself. We selected most functions CD209 had, and list some proteins which have the same functions with CD209. You can find most of the proteins on our site.
| Function | Related Protein |
|---|---|
| protein binding | MAF,TNPO3,MED30,BCL2L2,C2orf50,FHL3,MTOR,ITM2A,UNKL,METTL17 |
| mannose binding | LMAN2L,CD209C,CD209B,MBL1,MANBA,LMAN2,LMAN1,Acr,BSG,CLEC4M |
| carbohydrate binding | PYGB,MAN2B2,LGALSLB,GALNTL4,PKD1L2,CLEC19A,GALNT4,PRG2,GALNT10,CHODL |
| metal ion binding | ZHX1,PGM2L1,COX5B,CHN1,OSR1,GCM2,ZNF556,SALL2,CYP27C1,PLA2G4AA |
| peptide antigen binding | H2-AB1,HLA-DRB5,BF2,MHC1UJA,MHC1UIA,HLA-E,MHC1UHA,MHC1ZDA,TRGV3,MR1 |
| virion binding | PTX3,HSP90B1,CLEC4M,PVRL1,PPIA,HIPK2,TSG101,APCS |
| virus receptor activity | CD86,CD80,SELPLG,HAVCR1,SLAMF1,SLC1A5,LAMP1,SERPINB4,ITGB5,PVR |
Interacting Protein
CD209 has direct interactions with proteins and molecules. Those interactions were detected by several methods such as yeast two hybrid, co-IP, pull-down and so on. We selected proteins and molecules interacted with CD209 here. Most of them are supplied by our site. Hope this information will be useful for your research of CD209.
VAC14;q03463-pro_0000278734
Resources
Research Area
Immune Regulatory Molecules on Endothelial CellsInflammatory/Monocyte-derived Dendritic Cells
CD Antigen (Dendritic Cell Pathogen Recognition Uptake)
Macrophage Marker CD Antigen
C-type Lectin Receptors
Dendritic Cell Adhesion and Migration
Dendritic Cell Pathogen Recognition/Uptake
C-type Lectin Family
Immune Checkpoints
Related Services
Related Products
References
- Park, KT; Burnett, S; et al. Development and characterization of a monoclonal antibody specific for bovine CD209. VETERINARY IMMUNOLOGY AND IMMUNOPATHOLOGY 163:216-220(2015).
- Paul, M; Reljic, R; et al. Characterization of a plant-produced recombinant human secretory IgA with broad neutralizing activity against HIV. MABS 6:1585-1597(2014).


