BARD1
-
Official Full Name
BRCA1 associated RING domain 1 -
Overview
This gene encodes a protein which interacts with the N-terminal region of BRCA1. In addition to its ability to bind BRCA1 in vivo and in vitro, it shares homology with the 2 most conserved regions of BRCA1: the N-terminal RING motif and the C-terminal BRCT domain. The RING motif is a cysteine-rich sequence found in a variety of proteins that regulate cell growth, including the products of tumor suppressor genes and dominant protooncogenes. This protein also contains 3 tandem ankyrin repeats. The BARD1/BRCA1 interaction is disrupted by tumorigenic amino acid substitutions in BRCA1, implying that the formation of a stable complex between these proteins may be an essential aspect of BRCA1 tumor suppression. This protein may be the target of oncogenic mutations in breast or ovarian cancer. Multiple alternatively spliced transcript variants encoding different isoforms have been found for this gene. [provided by RefSeq, Sep 2013] -
Synonyms
BARD1;BRCA1 associated RING domain 1;BRCA1-associated RING domain protein 1;BRCA1-associated RING domain gene 1
Recombinant Proteins
- Human
- Mouse
- Chicken
- Rat
- Wheat Germ
- Mammalian Cell
- E.coli
- In Vitro Cell Free System
- HEK293
- GST
- His
- Non
- Fc
- His&Fc&Avi
| Cat.# | Product name | Source (Host) | Species | Tag | Protein Length | Price |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| BARD1-074H | Recombinant Human BARD1 protein, GST-tagged | Wheat Germ | Human | GST |
|
|
| BARD1-2291M | Recombinant Mouse BARD1 Protein | Mammalian Cell | Mouse | His |
|
|
| BARD1-26645TH | Recombinant Human BARD1 | Wheat Germ | Human | Non | 100 amino acids |
|
| BARD1-2905C | Recombinant Chicken BARD1 | Mammalian Cell | Chicken | His |
|
|
| BARD1-940R | Recombinant Rat BARD1 Protein | Mammalian Cell | Rat | His |
|
|
| BARD1-03HF | Recombinant Full Length Human BARD1 Protein, Fc tagged | E.coli | Human | Fc | Full L. |
|
| BARD1-1816HF | Recombinant Full Length Human BARD1 Protein, GST-tagged | In Vitro Cell Free System | Human | GST | Full L. 777 amino acids |
|
| BARD1-228H | Recombinant Human BARD1 protein, His-tagged | E.coli | Human | His | 428-777 aa |
|
| BARD1-598R | Recombinant Rat BARD1 Protein, His (Fc)-Avi-tagged | HEK293 | Rat | His&Fc&Avi |
|
|
| BARD1-598R-B | Recombinant Rat BARD1 Protein Pre-coupled Magnetic Beads | HEK293 | Rat |
|
||
| BARD1-963M | Recombinant Mouse BARD1 Protein, His (Fc)-Avi-tagged | HEK293 | Mouse | His&Fc&Avi |
|
|
| BARD1-963M-B | Recombinant Mouse BARD1 Protein Pre-coupled Magnetic Beads | HEK293 | Mouse |
|
Background
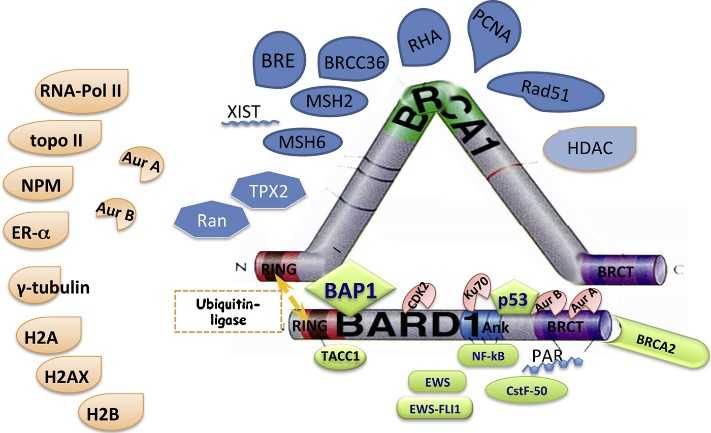
Fig1. Proteins interacting with the BARD1-BRCA1 complex or BARD1. (Irmgard Irminger-Finger, 2016)
What is BARD1 protein?
BARD1 (BRCA1 associated RING domain 1) gene is a protein coding gene which situated on the chromosome 2 at locus 2q35. This gene encodes a protein which interacts with the N-terminal region of BRCA1. In addition to its ability to bind BRCA1 in vivo and in vitro, it shares homology with the 2 most conserved regions of BRCA1: the N-terminal RING motif and the C-terminal BRCT domain. The RING motif is a cysteine-rich sequence found in a variety of proteins that regulate cell growth, including the products of tumor suppressor genes and dominant protooncogenes. This protein also contains 3 tandem ankyrin repeats. The BARD1/BRCA1 interaction is disrupted by tumorigenic amino acid substitutions in BRCA1, implying that the formation of a stable complex between these proteins may be an essential aspect of BRCA1 tumor suppression. The BARD1 protein is consisted of 777 amino acids and its molecular mass is approximately 86.6 kDa.
What is the function of BARD1 protein?
BARD1 forms a heterodimer with BRCA1 and acts as an E3 ubiquitin-protein ligase, which is involved in the formation of 'Lys-6'-linked polyubiquitin chains. BARD1 is involved in the initial nucleolytic resection of DNA double-strand breaks (DSBs), a process that is essential for the repair of DNA damage through the homologous recombination (HR) pathway. BARD1 interacts with many protein factors that are involved in cellular processes such as DNA repair, cell cycle regulation, and apoptosis. BARD1 has been shown to induce apoptosis by catalyzing the phosphorylation of p53 by DNA-damage response kinase. BARD1 is involved in the transcriptional regulation of estrogen metabolism genes through its interaction with histone proteins.
BARD1 Related Signaling Pathway
BARD1 has been reported to interact with components of the Wnt signaling pathway, which is involved in cell fate determination and carcinogenesis. BARD1 can stabilize and activate the p53 protein in response to DNA damage, which then triggers downstream effects such as cell cycle arrest, DNA repair, or apoptosis. BARD1 may also be involved in the TGF-beta signaling pathway, which is important for cell proliferation and differentiation. BARD1 is a critical component of the BRCA1 pathway, which is involved in various aspects of DNA repair and maintenance of genomic stability. BARD1 may interact with components of the Fanconi anemia pathway, which is associated with DNA repair and genomic stability.
BARD1 Related Diseases
A germline heterozygous deletion of BARD1 exons has been reported in a family diagnosed with familial colorectal cancer type X syndrome. BARD1 germline variants have been associated with neuroblastoma, a type of cancer commonly imaged as lethal in more than 50% of patients despite treatment. These variants induce haploinsufficiency and DNA repair defects. The combination of olaparib, a PARP inhibitor, with abiraterone (Zytiga) has shown significant improvement in the progression-free survival (PFS) and overall survival (OS) of patients with HRR (homologous recombination repair) mutated metastatic castration-resistant prostate cancer (mCRPC). Other cancers are also related with BARD1 including breast cancer, ovarian cancer, pancreatic cancer and so on.
Bioapplications of BARD1
The BRCA1-BARD1 complex is a target for PARP inhibitors, which are used in the treatment of certain types of cancer. Understanding the structural and functional aspects of BARD1 can lead to the development of new drugs and therapies. BARD1's involvement in the recruitment and retention of the BRCA1-BARD1 complex at sites of DNA damage makes it a potential therapeutic target for enhancing the effectiveness of DNA-damaging agents in cancer treatment.
Case Study
Case Study 1: Qi Hu, 2021
The BRCA1-BARD1 tumour suppressor is an E3 ubiquitin ligase necessary for the repair of DNA double-strand breaks by homologous recombination. The BRCA1-BARD1 complex localizes to damaged chromatin after DNA replication and catalyses the ubiquitylation of histone H2A and other cellular targets. The molecular bases for the recruitment to double-strand breaks and target recognition of BRCA1-BARD1 remain unknown. Here the researchers use cryo-electron microscopy to show that the ankyrin repeat and tandem BRCT domains in BARD1 adopt a compact fold and bind to nucleosomal histones, DNA and monoubiquitin attached to H2A amino-terminal K13 or K15, two signals known to be specific for double-strand breaks. They further show that RING domains in BRCA1-BARD1 orient an E2 ubiquitin-conjugating enzyme atop the nucleosome in a dynamic conformation, primed for ubiquitin transfer to the flexible carboxy-terminal tails of H2A and variant H2AX. This work reveals a regulatory crosstalk in which recognition of monoubiquitin by BRCA1-BARD1 at the N terminus of H2A blocks the formation of polyubiquitin chains and cooperatively promotes ubiquitylation at the C terminus of H2A.
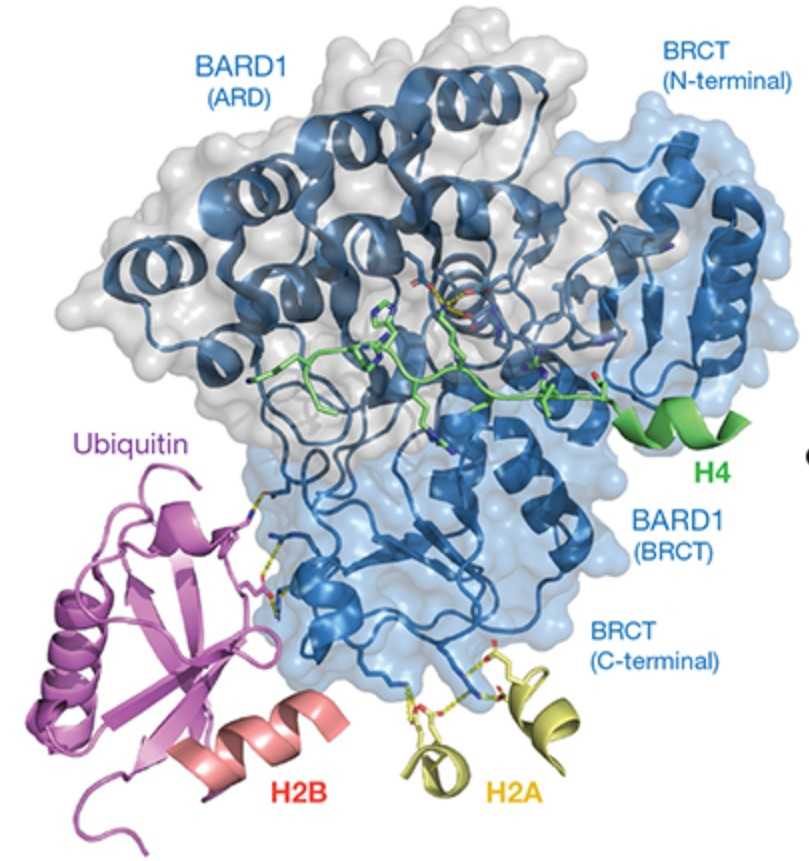
Fig1. Overview of the interactions of BARD1 with histone proteins and ubiquitin in the NCP context.
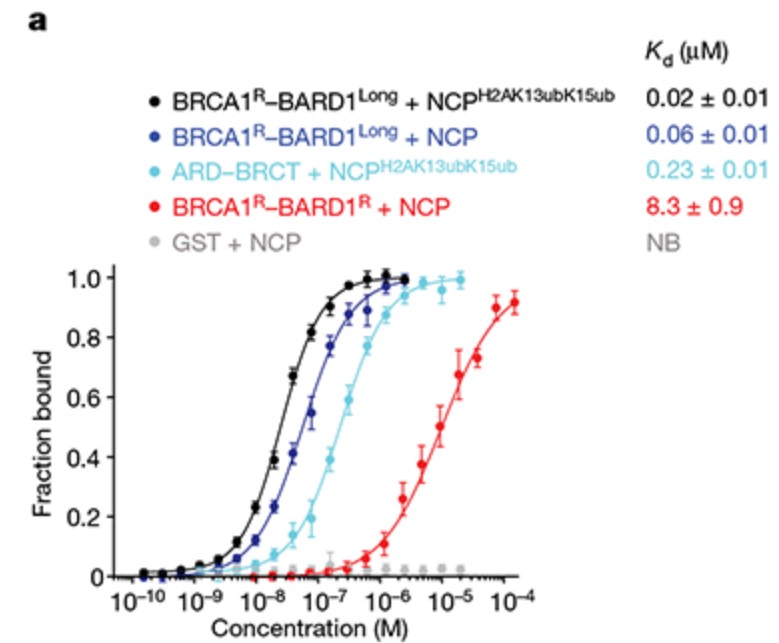
Fig2. Affinities of the indicated BRCA1–BARD1 constructs.
Case Study 2: Duo Wu, 2023
The BRCA1/BARD1 complex plays a key role in the repair of DNA double-strand breaks (DSBs) in both somatic cells and germ cells. However, the underlying molecular mechanism by which this complex mediates DSB repair is not fully understood. Here, the researchers examined the XY body of male germ cells, where DSBs are accumulated. They show that the recruitment of the BRCA1/BARD1 complex to the unsynapsed axis of the XY body is mediated by pre-ribosomal RNA (pre-rRNA). Similarly, the BRCA1/BARD1 complex associates with pre-rRNA in somatic cells, which not only forms nuclear foci in response to DSBs, but also targets the BRCA1/BARD1 complex to DSBs. The interactions between the BRCT domains of the BRCA1/BARD1 complex and pre-rRNA induce liquid-liquid phase separations, which may be the molecular basis of DSB-induced nuclear foci formation of the BRCA1/BARD1 complex. Moreover, cancer-associated mutations in the BRCT domains of BRCA1 and BARD1 abolish their interactions with pre-rRNA.

Fig3. The BRCT domains of BRCA1 and BARD1 directly interact with rRNA.
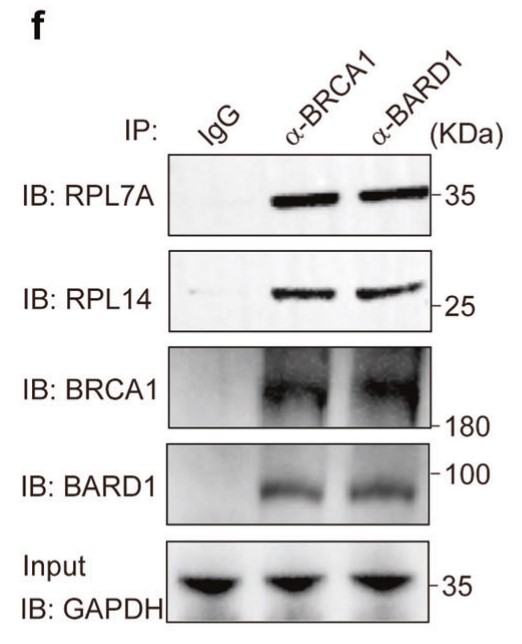
Fig4. Associations between the endogenous BRCA1/BARD1 complex and ribosomal proteins were examined.
Quality Guarantee
High Purity
.jpg)
Fig1. SDS-PAGE (BARD1-03HF)
Involved Pathway
BARD1 involved in several pathways and played different roles in them. We selected most pathways BARD1 participated on our site, such as BARD1 signaling events,Cell Cycle,Cell Cycle Checkpoints, which may be useful for your reference. Also, other proteins which involved in the same pathway with BARD1 were listed below. Creative BioMart supplied nearly all the proteins listed, you can search them on our site.
| Pathway Name | Pathway Related Protein |
|---|---|
| DNA Double Strand Break Response | BRCC3,CHEK2,FAM175A,KDM4A,THRSP,RNF168,RAD50,EYA3,HTATIP,BABAM1 |
| DNA Double-Strand Break Repair | CHEK2,RAD9B,WRN,EYA4,EME1,TDP2,RTEL1,BRCC3,PPP4CB,EME2 |
| G2/M DNA damage checkpoint | THRSP,UIMC1,BRCC3,TP53BP1,RNF168,BRE,BABAM1,FAM175A |
| BARD1 signaling events | CDK2,NPM1,CSTF1,RBBP8,RAD50 |
| DNA Repair | TDP2,ZNF830,NFRKB,TFPT,APITD1,PARP1,ZFP830,DTL,UBE2V2,POLI |
| G2/M Checkpoints | BRE,RAD9,UIMC1,THRSP,BRCC3,RAD9A,RAD17,HUS1,RNF168,RAD1 |
| Cell Cycle Checkpoints | RNF168,CDK2,TP53BP1,HIST4H4,BABAM1,CDK5RAP2,HUS1,DBF4,MCM8,CDKN1B |
| Cell cycle | CCNB3,CENPW,RBL2,RNF168,LMNB1,CEP72,ARF1,STAG1,CNEP1R1,NEK9 |
Protein Function
BARD1 has several biochemical functions, for example, RNA binding,kinase binding,ligase activity. Some of the functions are cooperated with other proteins, some of the functions could acted by BARD1 itself. We selected most functions BARD1 had, and list some proteins which have the same functions with BARD1. You can find most of the proteins on our site.
| Function | Related Protein |
|---|---|
| contributes_to ubiquitin-protein transferase activity | KLHL2,PHOSPHO2-KLHL23,KLHL10,KLHL15,KBTBD8,CCIN,KLHL40A,KLHL4,FBXW8,UBE2C |
| protein binding | SNRPB,ATL2,TAF13,IKZF3,EIF4G2,PIP5K1B,DRG2,OS9,MRC1,SPI1 |
| protein heterodimerization activity | GRIN2A,TENM2,GABPA,TCF4,H3F3A,USF2,JAM2A,TERF1,PIK3R2,HIST2H2L |
| protein homodimerization activity | TESC,SRGAP2A,DAXX,ADH5,KCNK3,ERP29,CEBPA,BMPR1A,ADAM10,DNTTIP1 |
| ligase activity | PELI3,RNF135,RNF125,BIRC7,DTX1,RNF138,MARCH2,HERC6,RNF168,RNF139 |
| zinc ion binding | TCEA1,ZZZ3,PEX10,ZNRF1,TRIM71,RNF19B,ZFPL1,TRIM37,RNF34A,RAPSN |
| ubiquitin-protein transferase activity | RAG1,RNF4,UBE2R2,BRAP,TRAF6,RNF130,RBBP6,BIRC5A,RBCK1,UBE2E1 |
| kinase binding | TENC1,PER3,SIT1,DLG1,PARP16,WWC1,BTG1,WWC3,CAB39,STRADA |
| RNA binding | QKI2,MRPL23,PATL2,RPS25,PABPC1L,RNASET2,PUS10,SRP9,RCAN3,SARNP |
Interacting Protein
BARD1 has direct interactions with proteins and molecules. Those interactions were detected by several methods such as yeast two hybrid, co-IP, pull-down and so on. We selected proteins and molecules interacted with BARD1 here. Most of them are supplied by our site. Hope this information will be useful for your research of BARD1.
BRCA1;CSTF2;par
Resources
Related Services
Related Products
References
- Zhang, YQ; Pilyugin, M; et al. Expression of oncogenic BARD1 isoforms affects colon cancer progression and correlates with clinical outcome. BRITISH JOURNAL OF CANCER 107:675-683(2012).
- Cosandey, V; Debrot, F; et al. Construction of a Peptide Microarray for Auto-antibody Detection. CHIMIA 66:803-806(2012).


