CC Chemokine Receptors
Related Symbol Search List
Immunology Background
Available Resources for CC Chemokine Receptors Research
Creative BioMart excels as the premier destination for all your research requirements regarding CC chemokine receptors. Our meticulously curated array of products and tailored services is designed to aid you in exploring the intricate domain of CC chemokine receptors and their significant role in various physiological processes.
- Our product range features high-quality recombinant proteins, protein pre-coupled magnetic beads, cell and tissue lysates, and more, all intricately crafted to meet your research needs with precision and excellence.
- Furthermore, we provide a plethora of resources on CC chemokine receptors, including in-depth insights on associated pathways, protein functions, interacting proteins, relevant literature, and the latest research areas. Trust Creative BioMart to be your ultimate resource hub for everything related to CC chemokine receptors.
Our Featured Products
| Cat.# | Product name | Species | Source (Host) | Tag |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| CCNH-10868H | Recombinant Human CCNH, GST-tagged | Human | E.coli | GST |
| CCR3-10884H | Recombinant Human CCR3, GST-tagged | Human | E.coli | GST |
| CCR5-10886H | Recombinant Human CCR5, GST-tagged | Human | E.coli | GST |
| CCR9-3960H | Recombinant Human CCR9 Protein, His tagged, Biotinylated | Human | E.coli | His |
About CC Chemokine Receptors
CC chemokine receptors (CCR) are a subgroup of chemokine receptors that specifically bind to CC chemokines. The CC chemokine receptor family is a part of the larger chemokine receptor superfamily, which includes other subgroups such as CXC chemokine receptors.
There are several CC chemokine receptors identified to date, including CCR1, CCR2, CCR3, CCR4, CCR5, CCR6, CCR7, CCR8, CCR9, and CCR10. Each receptor has a specific pattern of chemokine ligand binding and distinct roles in immune cell trafficking and function.
CC chemokine receptors belong to the G-protein coupled receptor (GPCR) family, characterized by their seven transmembrane helical domains. They possess an extracellular N-terminal region, which is involved in ligand binding, and an intracellular C-terminal region, which interacts with intracellular signaling molecules. The conserved regions within the receptor structure allow for specific binding and activation upon chemokine binding. The name "CC" refers to the presence of adjacent cysteine residues near the N-terminus of the chemokines, which is a characteristic feature of CC chemokines.
CC chemokine receptors play crucial roles in immune cell migration, immune system regulation, and inflammatory responses. They are expressed on various immune cells, including monocytes, macrophages, lymphocytes, dendritic cells, and eosinophils. The binding of CC chemokines to their respective receptors initiates intracellular signaling, leading to cellular responses such as cell migration, adhesion, activation, and survival.
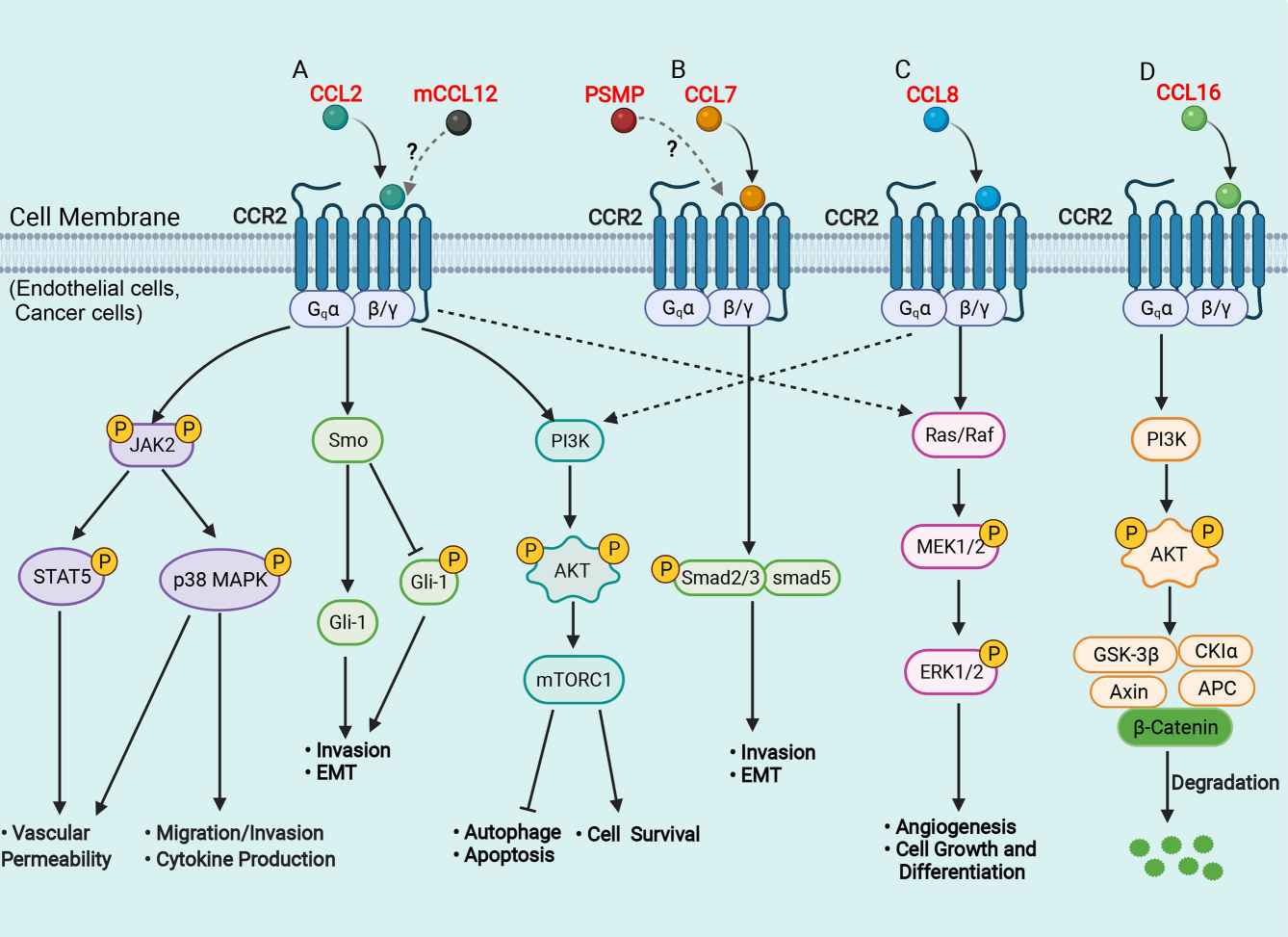 Fig.1 Schematic representation of signaling pathways in the liver of CCR2 and its ligands. (She S, et al., 2022)
Fig.1 Schematic representation of signaling pathways in the liver of CCR2 and its ligands. (She S, et al., 2022)
Role of CC Chemokine Receptors in Immunomodulation and Cell Signaling
CCRs) play a crucial role in immunomodulation and cell signaling, contributing to the regulation of immune responses. Here are some key roles of CCRs in immunomodulation and cell signaling:
- Immune Cell Migration and Homing: CCRs enable immune cells, such as monocytes, lymphocytes, dendritic cells, and eosinophils, to migrate towards sites of inflammation, infection, or tissue damage. CCRs recognize and bind specific CC chemokines, guiding immune cells to the appropriate locations within the body.
- Immune Cell Activation and Function: CCR signaling can activate immune cells and modulate their functions. Activation of CCRs can lead to the release of cytokines, chemokines, and other immune mediators, promoting inflammation and immune responses. CCRs can also regulate immune cell adhesion, proliferation, survival, and differentiation, thus influencing the overall immune cell function.
- Inflammatory Responses: Upon activation, CCRs recruit immune cells to inflammatory sites, amplifying the immune response against pathogens or tissue injury. CCR-mediated signaling also contributes to the production of pro-inflammatory cytokines and chemokines, promoting inflammation and orchestrating immune cell recruitment and activation.
- Immune Cell Communication and Crosstalk: CCRs facilitate immune cell communication and crosstalk. By interacting with their specific chemokine ligands, CCRs enable immune cells to navigate through tissues, interact with other immune cells, and form immune cell clusters for coordinated immune responses. This communication is essential for the proper functioning of the immune system.
- Regulation of Immune Cell Trafficking and Compartmentalization: CCRs are involved in the regulation of immune cell trafficking and compartmentalization within lymphoid tissues and organs. They guide immune cells to specific lymphoid compartments, such as lymph nodes and spleen, where immune responses are coordinated. CCRs also regulate the movement of immune cells within these compartments, ensuring effective immune surveillance and response.
- Modulation of Autoimmunity and Allergic Responses: Dysregulation of CCRs can contribute to autoimmune disorders and allergic responses. Aberrant expression or signaling of CCRs can lead to the accumulation of immune cells in tissues, causing chronic inflammation and tissue damage. Modulating CCR signaling has been explored as a therapeutic approach to regulate immune responses in these conditions.
- Disease Pathogenesis: CCRs have been implicated in various diseases, including infectious diseases, chronic inflammatory conditions, and cancer. For example, CCR5 is known for its role as a co-receptor for HIV entry into target cells. In cancer, CCRs can be involved in tumor cell migration, metastasis, and immune evasion, making them potential targets for cancer therapy
Understanding the role of CCRs in immunomodulation and cell signaling is crucial for deciphering immune responses, developing therapeutic interventions, and targeting specific immune cell populations in various diseases. Manipulating CCR signaling pathways holds promise for modulating immune responses, controlling inflammation, and treating immune-related disorders.
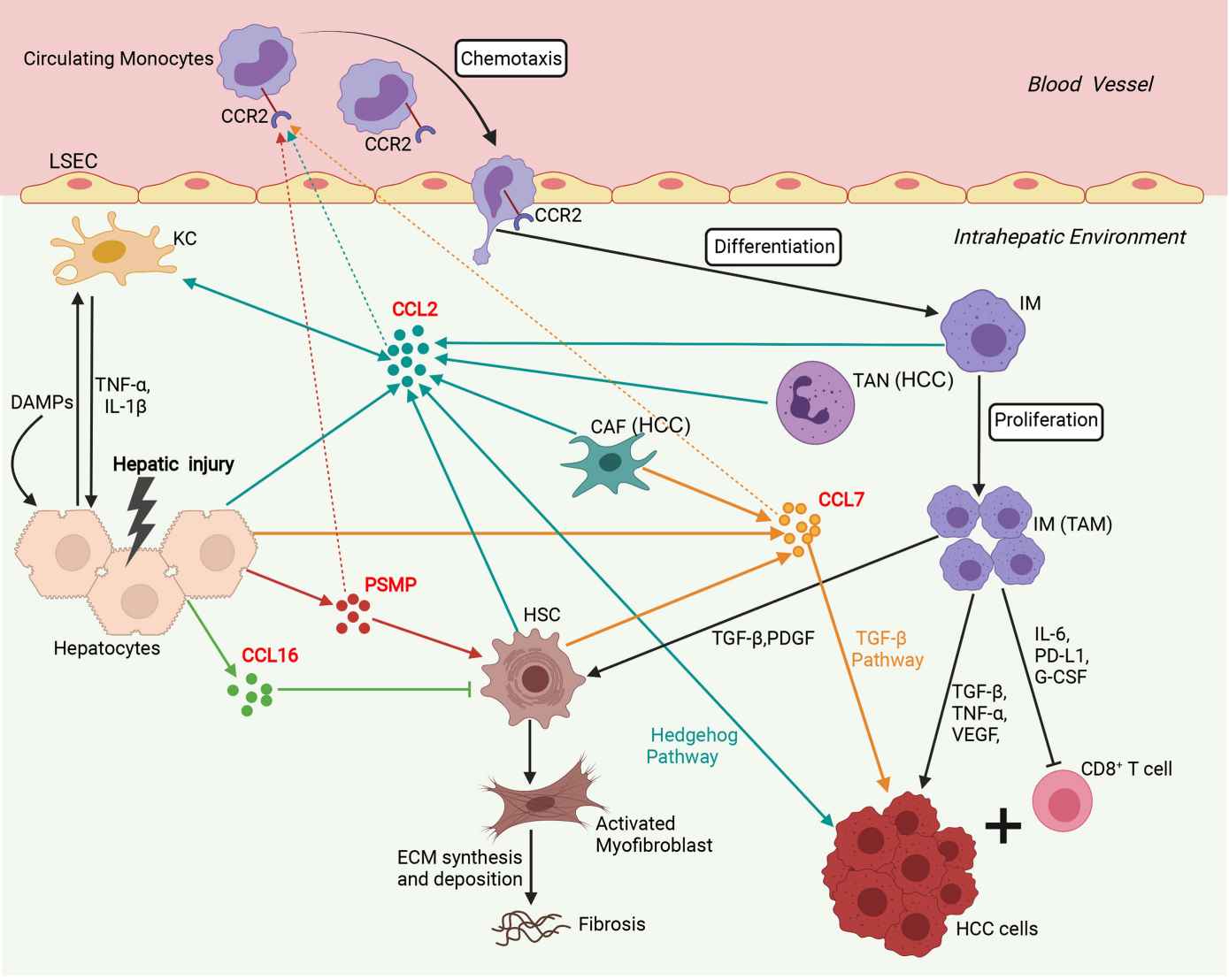 Fig.2 Involvement of the network of CCR2 and its ligands in regulation of immune mechanisms during liver injury, fibrosis and hepatocarcinogenesis. (She S, et al., 2022)
Fig.2 Involvement of the network of CCR2 and its ligands in regulation of immune mechanisms during liver injury, fibrosis and hepatocarcinogenesis. (She S, et al., 2022)
If you have any questions, requirements, or cooperation intentions, please feel free to contact us. We very much look forward to working with you and helping you achieve research and commercial success.
Related References
- She S, Ren L, Chen P, et al. Functional Roles of Chemokine Receptor CCR2 and Its Ligands in Liver Disease. Front Immunol. 2022;13:812431.
- Korbecki J, Grochans S, Gutowska I, Barczak K, Baranowska-Bosiacka I. CC Chemokines in a Tumor: A Review of Pro-Cancer and Anti-Cancer Properties of Receptors CCR5, CCR6, CCR7, CCR8, CCR9, and CCR10 Ligands. International Journal of Molecular Sciences. 2020; 21(20):7619.
- Bill CA, Allen CM, Vines CM. C-C Chemokine Receptor 7 in Cancer. Cells. 2022; 11(4):656.
