C Chemokine Receptors
Related Symbol Search List
Immunology Background
Available Resources for C Chemokine Receptors Research
Creative BioMart stands out as the ultimate destination catering to all your research needs concerning C chemokine receptors. Our carefully curated selection of meticulously crafted products and customized services is tailored to assist you in delving into the intricate realm of C chemokine receptors and their vital involvement in numerous physiological processes.
- Our product line showcases top-tier recombinant proteins, protein pre-coupled magnetic beads, cell and tissue lysates, and more, each meticulously designed to fulfill your research demands with unparalleled quality and precision.
- Moreover, we offer a wealth of resources on C chemokine receptors, comprising detailed insights into associated pathways, protein functionalities, interacting proteins, relevant literature, and current research domains. Count on Creative BioMart to be your ultimate go-to hub for all things related to C chemokine receptors.
Our Featured Products
| Cat.# | Product name | Species | Source (Host) | Tag |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Xcr1-585M | Recombinant Mouse Xcr1 protein, His-tagged | Human | E.coli | His |
| XCR1-3497C | Recombinant Chicken XCR1 | Chicken | Mammalian Cell | His |
About C Chemokine Receptors
C chemokine receptors belong to a subfamily of chemokine receptors that interact specifically with C chemokines. Chemokines are small signaling proteins that play crucial roles in immune cell migration, immune system regulation, inflammation, and various disease processes. C chemokine receptors are expressed on the surface of immune cells and mediate their responses to C chemokines.
XCR1 is a G protein-coupled receptor (GPCR) predominantly expressed on dendritic cells (DCs), specifically the cross-presenting subset of DCs known as CD8α+ DCs or XCR1+ DCs. XCR1 has been identified as the specific receptor for XCL1 (lymphotactin), a C chemokine secreted by activated T cells and natural killer (NK) cells.
The XCR1 receptor is involved in regulating immune responses by mediating the attraction and activation of DCs. XCL1 binding to XCR1 triggers intracellular signaling pathways, leading to DC migration to lymphoid organs and the induction of antigen-specific T cell responses. XCR1 signaling is particularly important in cross-presentation, a process in which DCs present exogenous antigens on major histocompatibility complex class I (MHC-I) molecules to activate CD8+ cytotoxic T cells.
The XCR1+ DC subset plays a crucial role in antiviral immune responses and the initiation of effective cellular immunity against tumors. XCR1 expression on DCs is often used as a marker to identify this specialized subset. Targeting XCR1 has been explored as a potential strategy to enhance antitumor immune responses and vaccine development.
In summary, XCR1 is a C chemokine receptor predominantly expressed on XCR1+ dendritic cells. Its specific ligand, XCL1, regulates the attraction and activation of DCs, particularly in the context of cross-presentation and CD8+ T cell responses. Understanding the role of XCR1 in immune cell interactions and its potential as a therapeutic target contributes to our knowledge of immune regulation and the development of immunotherapies.
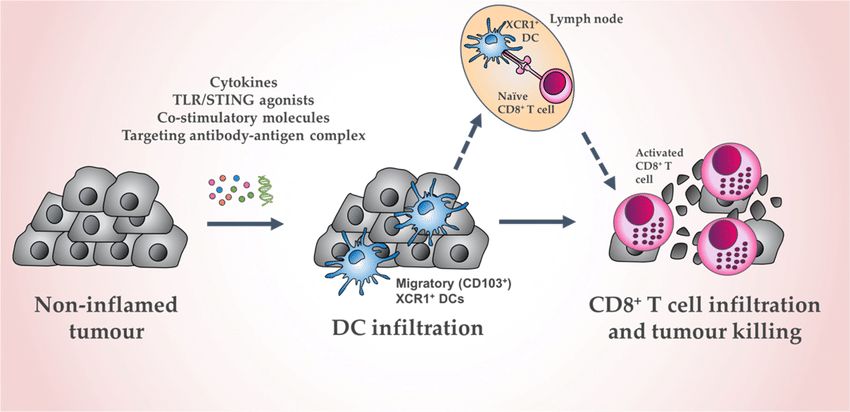 Fig.1 Schematic of in vivo XCR1 + DC activation to induce tumor cell death. (Audsley KM, et al., 2020)
Fig.1 Schematic of in vivo XCR1 + DC activation to induce tumor cell death. (Audsley KM, et al., 2020)
Role of C Chemokine Receptors in Immunomodulation and Inflammatory Processes
C chemokine receptors play crucial roles in immunomodulation and inflammatory processes by regulating immune cell migration, activation, and recruitment to inflammatory sites. Here are some key roles of C chemokine receptors in these processes:
- Immune cell recruitment: C chemokine receptors are involved in guiding immune cells to specific tissues during immune responses. They regulate the migration and homing of various immune cell populations, including neutrophils, monocytes, T cells, and dendritic cells, to sites of inflammation or infection. By interacting with their ligands, C chemokine receptors promote the directional movement of immune cells, enabling them to reach the sites where their effector functions are required.
- Inflammatory cell activation: C chemokine receptors contribute to the activation and functional responses of inflammatory cells. Activation of C chemokine receptors on immune cells leads to intracellular signaling events that trigger cellular activation, cytokine production, and effector functions. For example, binding of CXC chemokines to CXCR2 on neutrophils induces their activation, leading to the release of antimicrobial substances and tissue-damaging molecules.
- Regulation of leukocyte trafficking: C chemokine receptors play a role in regulating leukocyte trafficking within lymphoid tissues and between lymphoid and non-lymphoid tissues. They are involved in the positioning and migration of immune cells within lymph nodes, spleen, and other lymphoid organs, thereby facilitating immune cell interactions and the initiation of immune responses.
- Immunomodulation in diseases: C chemokine receptors contribute to the pathogenesis of various inflammatory and immune-mediated diseases. Dysregulated expression or function of C chemokine receptors can lead to aberrant immune cell recruitment, chronic inflammation, and tissue damage. For example, in diseases like rheumatoid arthritis, multiple sclerosis, and inflammatory bowel disease, C chemokine receptors and their ligands play a role in the recruitment and activation of immune cells, perpetuating the inflammatory processes.
- Tumor immunity: C chemokine receptors and their ligands are involved in the recruitment and activation of immune cells within the tumor microenvironment. They affect the infiltration of immune cells, such as cytotoxic T cells and natural killer cells, into tumors, influencing antitumor immune responses. Modulating C chemokine receptor signaling has been explored as a strategy to enhance immune surveillance and antitumor immunity.
Understanding the roles of C chemokine receptors in immunomodulation and inflammatory processes provides insights into the regulation of immune cell trafficking, immune responses, and the development of immune-related diseases. Targeting C chemokine receptors and their ligands offers potential therapeutic opportunities for modulating immune cell behavior and controlling inflammatory disorders.
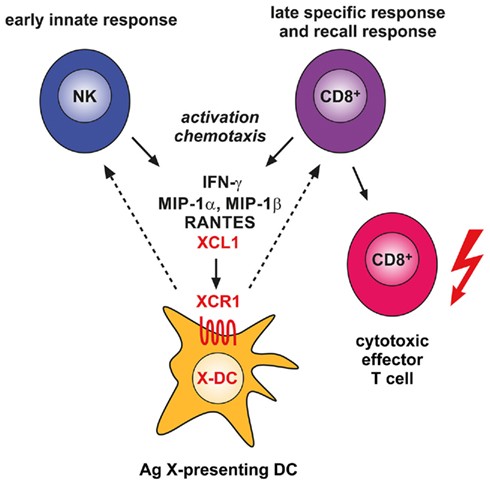 Fig.2 Involvement of the XCL1–XCR1 communication axis in the innate and adaptive cytotoxic responses to cross-presented microbial and tumor antigens. (Kroczek RA, et al., 2012)
Fig.2 Involvement of the XCL1–XCR1 communication axis in the innate and adaptive cytotoxic responses to cross-presented microbial and tumor antigens. (Kroczek RA, et al., 2012)
If you have any questions, requirements, or cooperation intentions, please feel free to contact us. We very much look forward to working with you and helping you achieve research and commercial success.
Related References
- Kroczek RA, Henn V. The Role of XCR1 and its Ligand XCL1 in Antigen Cross-Presentation by Murine and Human Dendritic Cells. Front Immunol. 2012;3:14. Published 2012 Feb 10.
- Wylie B, Read J, Buzzai AC, et al. CD8+XCR1neg Dendritic Cells Express High Levels of Toll-Like Receptor 5 and a Unique Complement of Endocytic Receptors. Front Immunol. 2019;9:2990.
- Audsley KM, McDonnell AM, Waithman J. Cross-Presenting XCR1+ Dendritic Cells as Targets for Cancer Immunotherapy. Cells. 2020;9(3):565.
