Recombinant Proteins
Recombinant Protein Search
Browse Recombinant Proteins by Gene
Featured Products:
-
Cytokines
-
PROTAC targets
-
GPCRs
-
Avi-labeled proteins
-

full-length proteins
-
SARS-CoV-2-related proteins
-
CAR-T cell targets
-

Biomarkers
-
CD antigens
-
Cytokines for Organoid Culture
-
Immune Checkpoint Proteins
-
Labeled Protein for Car-T Therapy
-
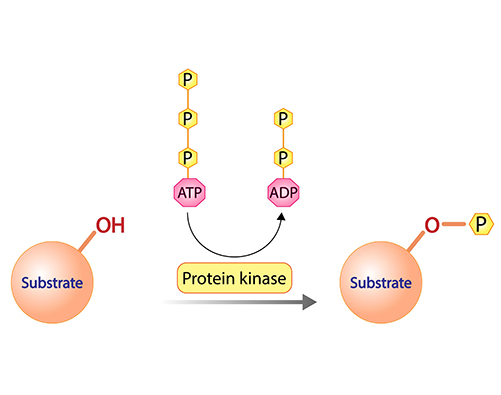
Protein Kinases
-
Heavy-labeled Full-length Proteins
-
Fluorescent-labeled Proteins
-
Site-specific Labeled Recombinant Proteins
-
Monkeypox Virus-related Proteins
-
Full Length Protein
-
Membrane Protein
-

Animal-free Proteins
What is Recombinant Protein?
Recombinant proteins refer to proteins produced using recombinant DNA or RNA technology. Recombinant protein engineering first involves obtaining the gene of interest (GOI) through gene cloning or chemical synthesis. The GOI is then connected to a suitable expression vector and introduced into a specific host cell. By exploiting the genetic system of the host cell, functionally active protein molecules are expressed. Recombinant proteins are widely used for researching protein structure and function as well as developing therapeutics. This technology allows mass production of proteins that can be purified for various applications in biomedicine and biotechnology.
Recombinant protein is a manipulated form of protein encoded by recombinant DNA, which has been cloned in a foreign expression system to support the expression of the exogenous gene. This recombinant DNA construct can be used to manufacture large quantities of useful protein products. The recombinant DNA, usually the cDNA sequence of the target protein, is designed to be under the control of a well-characterized promoter to express the target protein within the chosen host cell to achieve high-level protein expression.
Different protein expression systems have different features and applications. Creative BioMart provides multiple sources of recombinant proteins to meet your specific requirements.

How to choose the appropriate recombinant protein?
- Having a clear research purpose can eliminate many confounding factors when selecting a suitable recombinant protein.
Selection of recombinant protein expression system Research objective
Protein requirements
Optimal expression system
Used as an antigen to obtain specific antibodies for detection
Purity>80%, no protein modification or natural activity required, can be labeled
Prokaryotic expression system
Research on protein crystallization and crystal structure
Purity>95%, concentration typically at 10 mg/mL
2/3 are prokaryotic expression systems, 1/3 are insect cell expression systems and mammalian cell expression systems
Functional research on proteins
Need to preserve the natural activity of proteins
Prokaryotic expression system and eukaryotic expression system
Proteins used for drug research
Required to preserve natural sequences as much as possible and have natural activity
Eukaryotic expression system
Comparison of recombinant protein expression systems Expression system
Advantages
Disadvantages

Prokaryotic system
Fast reproduction, low cost, high yield
Cannot undergo glycosylation modification, often containing bodies

Mammalian cells
The structure is closest to natural proteins, with complete post-translational processing and better activity
Expression level is low, the cycle is long, and the technical requirements are high

Yeast cell
Easy to operate, with weak protein background, suitable for large-scale production and easy purification
Low yield and inadequate glycosylation requirements

Insect cell
Functionally similar to natural proteins, it has advantages over some toxic or difficult to express proteins
Low degree of glycosylation, a relatively simple form, and less activity than mammalian cell expression systems
- Understand the product characteristics and select based on the biological activity data (ED50) of the product.
ED50 in quantitative reactions refers to the amount of medication that can cause 50% of the maximum reaction intensity, and in qualitative reactions refers to the amount of medication that causes 50% of the experimental subjects to show a positive reaction. - At present, recombinant protein drugs mainly include multiple sub fields such as peptide hormones, cytokines, and recombinant enzymes.
|
Segmented fields |
Main varieties |
Therapy area |
|
 |
Polydermal hormones |
Recombinant human insulin and insulin analogues (Cat. No. INS-315H ) |
Diabetes |
|
Recombinant human growth hormone (Cat. No. GH1-76H ) |
Childhood dwarfism |
||
|
Recombinant human follicle stimulating hormone (Cat. No. FSHB-4519H ) |
Promoting female ovulation in the field of assisted reproductive therapy |
||
 |
Cytokine |
Recombinant human interferon α、β、γ(Cat. No. IFN-a-62B ) |
Hepatitis B, Hepatitis C and Multiple Sclerosis |
|
Recombinant human granulocyte colony-stimulating factor (Cat. No. CSF3-4407C ) |
Symptoms of various blood cell reductions caused by tumor radiotherapy and chemotherapy, enhancing the patient's own immunity |
||
|
Recombinant human granulocyte macrophage stimulating factor |
|||
|
Recombinant human erythropoietin (Cat. No. EPO-01H ) |
|||
|
Recombinant human interleukin-2, 11 (Cat. No. IL2-341H ) |
|||
|
Recombinant human epidermal growth factor (Cat. No. EGF-12320H ) |
Wound healing and recovery |
||
|
Recombinant human fibroblast growth factor (Cat. No. FGF2-11H ) |
|||
 |
Recombinase |
Recombinant human prourokinase |
Acute myocardial infarction |
|
Recombinant human glucose enzyme preparation (Cat. No. Kit-0372 ) |
Pompeii's disease |
||
 |
Other |
Recombinant human bone morphogenetic protein (Cat. No. BMP4-06H ) |
Promote bone healing |
|
Recombinant hirudin (Cat. No. Hirudin-02 ) |
Thrombotic diseases |
||
Recombinant protein CRO services and related products
Creative BioMart provides a wide range of off-the-shelf recombinant protein products. We also can custom-produce according to your exact request if your target is not in our catalog. Please do not hesitate to contact us . Creative BioMart provides a Protein Expression and Purification Platform that includes more than 20 expression systems to meet your requirements:
- For bulk protein order , please inquire for detail.
- For GMP-grade protein , please see our specific GMP-grade Protein Products and services.
- For custom membrane protein production , especially for drug discovery, please see our Membrane Protein Service .
- To obtain a stable cell line for target protein expression, please see our stable cell line development service .
- For protein modification and engineering , we provide Protein PEGylation , Protein Biotinylation , Fluorescence Labeling , Isotope Labeling , Site-specific and Custom Labeling services.
- For protein purification , besides various chromatography and filtration techniques, we also provide Endotoxin Removal Service and Inclusion Body Renaturation Service .
Our Advantages
Wide Coverage
- 100,000+ recombinant proteins covering most genes;
- Multiple species (human, mouse, rat, rabbit, chicken, zebrafish, dog, monkey, pig…);
- Multiple sources (CHO, HEK293, NS0, Sf 9 Insect cells, Sf21, E. coli , Yeast, Wheat Germ…);
- Various tags (His, GST, Flag, T7, HA, MYC, Fc, Strep…) on N-terminus or C-terminus;
- Different fragments/full-length protein/proteins with various mutations.
High Quality
- Close to natural status;
- Validated bio-activity using functional ELISA and/or other activity assays;
- Lower endotoxin level: less than 0.1 EU per μg protein by LAL assay;
- High purity: most of the products are over 90% pure by SDS-PAGE;
Case Study
Case 1 : Catlin, D. S., Reidl, C. T., Trzupek, T. R., et al. (2020). (S)-4-Amino-5-phenoxypentanoate designed as a potential selective agonist of the bacterial transcription factor GabR. Protein Science, 29(8), 1816-1828. https://doi.org/10.1002/pro.3905
Disruption of transcriptional regulation through targeting transcription factors that regulate the expression of key enzymes in bacterial metabolism may provide a promising method for controlling the bacterial metabolic pathways. To this end, researchers have selectively targeted a bacterial transcription regulator through the design and synthesis of a series of γ-aminobutyric acid (GABA) derivatives, including (S)-4-amino-5-phenoxypentanoate (4-phenoxymethyl-GABA), which are based on docking insights gained from a previously-solved crystal structure of GabR from Bacillus subtilis.

Fig1. Screening for potential off-target aminotransferase activity of hOAT, Asp-AT, GABA-AT, and Ala-AT.

Fig2. smFRET distribution curves. Observed smFRET distribution for (a) DNA only, (b) DNA + GabR, (c) DNA + GabR + GABA, and (d) DNA + GabR + 13. Curves were fit by multimodal using Gaussian distributions.
Case 2: Chan, S., Belmar, N., Ho, S., et al. (2022). An anti-PD-1–GITR-L bispecific agonist induces GITR clustering-mediated T cell activation for cancer immunotherapy. Nature Cancer, 3(3), 337-354. https://doi.org/10.1038/s43018-022-00334-9
In human clinical trials, GITR agonist antibodies have shown limited therapeutic effect, which may be due to suboptimal receptor clustering-mediated signaling. To overcome this potential limitation, a rational protein engineering approach is needed to optimize GITR agonist-based immunotherapies. In this article, researchers show a bispecific molecule consisting of an anti-PD-1 antibody fused with a multimeric GITR ligand (GITR-L) that induces PD-1-dependent and FcγR-independent GITR clustering, resulting in enhanced activation, proliferation and memory differentiation of primed antigen-specific GITR+PD-1+ T cells.

Fig1. h, GITR and PD-1 expression on transfected and activated Jurkat-NFκB-huGITR+ reporter cells (representative data of n = 2 independent experiments with similar results). i, NFκB signaling in an anti-CD3-activated Jurkat-NFκB-huGITR+ reporter assay following threefold titration with the anti-huPD-1-huGITR-L bispecific.

Fig2. Representative CD8, PD-1, GITR and FoxP3 multiplex immunofluorescence imaging (excluding PanCK, CD3 and DAPI) and spatial distribution cell density heatmaps (cells mm–2) (CD8, PD-1 and GITR) of FFPE sections of primary HNSCC (excluded compartment) and matching lymph node metastases (LN mets) (20×).
Resources
Contact us or send an email at for project quotations and more detailed information.
Quick Links
-

Papers’ PMID to Obtain Coupon
Submit Now -

Refer Friends & New Lab Start-up Promotions