UCHL5
-
Official Full Name
ubiquitin carboxyl-terminal hydrolase L5 -
Overview
Ubiquitin carboxyl-terminal hydrolase isozyme L5 (UCHL5) belongs to the peptidase C12 family. This protein is protease that specifically cleaves Lys-48-linked polyubiquitin chains, and deubiquitinating enzyme associated with the 19S regulatory subunit -
Synonyms
UCHL5;ubiquitin carboxyl-terminal hydrolase L5;ubiquitin carboxyl-terminal hydrolase isozyme L5;CGI 70;INO80 complex subunit R;INO80R;UCH37;ubiquitin thioesterase L5;ubiquitin C-terminal hydrolase UCH37;ubiquitin carboxyl-terminal esterase L5;CG
Recombinant Proteins
- Bovine
- Mouse
- Human
- Zebrafish
- Chicken
- E.coli
- Mammalian Cells
- Human
- HEK293
- His
- GST
- SUMO
- Non
- Flag
- Avi
- Fc
- DDK
- Myc
Background
What is UCHL5 Protein?
UCHL5 is quite the multitasker in the cell. As a deubiquitinase, it snips ubiquitin off proteins, which is crucial for maintaining protein balance in the cell. Think of it as proofreading proteins to decide their fate—whether they get recycled or continue doing their job. When it latches onto the proteasome’s 19S subunit, it dives into action. Beyond just protein clean-up, UCHL5 influences how cells communicate and react to signals, especially in the Wnt pathway. By keeping Axin1 in check, it keeps the Wnt signals from going haywire, which is important for cell growth and development.What is the Function of UCHL5 Protein?
UCHL5, short for Ubiquitin C-terminal hydrolase like 5, is an enzyme that removes ubiquitin from proteins and partners up with the 19S subunit of the proteasome to help manage how proteins are broken down. It plays roles in various cellular activities, like keeping the Wnt signaling pathway under control. By interacting with Axin1, UCHL5 helps stabilize this protein, which in turn suppresses Wnt signaling. Interestingly, UCHL5 is also crucial in the context of cancer. The levels at which it is expressed have been linked with the progression and outcome of several cancers, suggesting it might be a useful marker for prognosis and even a target for cancer treatment. This makes UCHL5 a key player not just in normal cell operations but also in cancer research and therapy development.UCHL5 Related Signaling Pathway
UCHL5 is involved in several important signaling pathways, with the Wnt/β-catenin pathway being especially noteworthy. It interacts with Axin1 to manage the β-catenin destruction complex, which helps dial down Wnt signals. On another front, UCHL5 boosts the growth and spread of bladder cancer cells by switching on the AKT/mTOR pathway. These roles make UCHL5 a key player in how cells grow, change, and even turn cancerous. Its influence on these pathways underscores its significance in both everyday cell activity and the development of diseases, making it an interesting target for research and potential therapies.UCHL5 Related Diseases
UCHL5 is connected to numerous health conditions, with a significant emphasis on cancer. High concentrations of UCHL5 are observed in various types of cancer, including those affecting the cervix, breast, esophagus, liver, colon, bladder, lungs, and endometrium. In these scenarios, it supports the development and progression of tumors by engaging the Wnt/β-catenin signaling route. It also plays a part in how some tumors resist drugs; in bladder cancer, for example, UCHL5 inhibitors can help make cisplatin more effective. On the neurological front, UCHL5 is connected to Machado-Joseph disease, a type of spinocerebellar ataxia. This makes UCHL5 a key player in disease progression and a potential target for new therapies.Bioapplications of UCHL5
UCHL5 protein has a bunch of uses in research, industry, and clinical studies. In science, it's a deubiquitinating enzyme that's key for looking into protein degradation and signaling, especially in the Wnt/β-catenin pathway. Researchers often study its expression in various cancers to understand its role in tumor progression and patient outcomes. On the industrial side, UCHL5 can be produced as a recombinant protein for experimental reagents and research purposes. In clinical settings, it's viewed as a potential biomarker for different cancers, with high levels linked to poorer outcomes, making it valuable for cancer diagnosis and treatment strategies.Case Study
Case Study 1: Wan B. et al. BMC Cancer. 2024
Hepatocellular carcinoma (HCC) is a tough-to-treat cancer with a poor outlook, and current therapies fall short. UCHL5, a type of ubiquitinase, has caught interest but isn't yet a main target for treatment. Using data from the Cancer Genome Atlas (TCGA) and techniques like RT-qPCR, Western blot, and immunohistochemistry, researchers found that UCHL5 is highly expressed in HCC tumors, which correlates with worse patient survival. Lab tests showed knocking down UCHL5 reduced HCC growth, highlighting its role in promoting cell proliferation and metastasis. UCHL5 affects HCC by boosting glycolysis and working with the Wnt/β-catenin pathway, where it binds β-catenin and lowers its ubiquitination, further fueling tumor growth. This makes UCHL5 a promising target for future HCC therapies.-
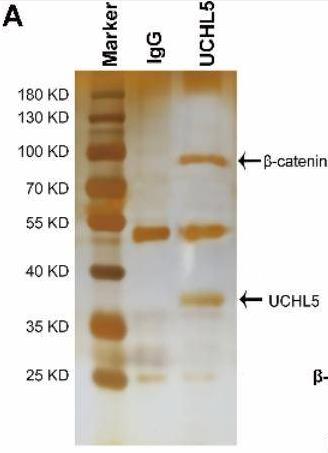 Fig1. Immunoprecipitation of UCHL5 or IgG was carried out in HCC cells.
Fig1. Immunoprecipitation of UCHL5 or IgG was carried out in HCC cells. -
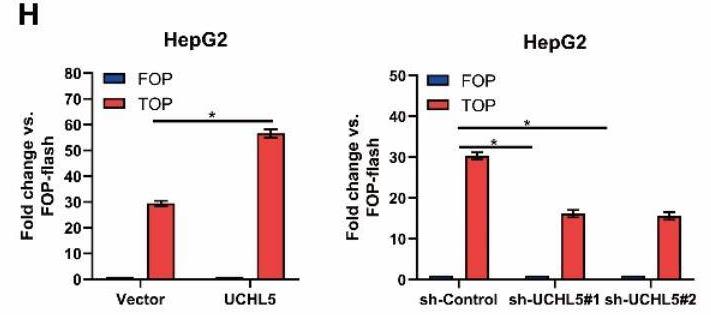 Fig2. The TOP/FOP fold change after knockdown or overexpression of UCHL5.
Fig2. The TOP/FOP fold change after knockdown or overexpression of UCHL5.
Case Study 2: Deol KK. et al. Mol Cell. 2020
Researchers have found that the linkage, length, and structure of ubiquitin (Ub) chains are crucial for controlling various biological processes. Though branched chain architectures play roles in regulating protein breakdown by the proteasome, the specific proteins that recognize and handle these chains remain unknown. By combining synthetic and enzyme-derived Ub chains with mass spectrometry, researchers discovered that the deubiquitinase UCH37/UCHL5, which is linked to the proteasome, specifically cleaves K48 branched chains. The selectivity and activity of this cleaving are greatly boosted by the proteasomal Ub receptor RPN13/ADRM1. When using reconstituted proteasome complexes, they observed that debranching these chains speeds up the degradation of substrates tagged with branched chains in conditions requiring multiple processing cycles. This finding is reinforced by proteome-wide pulse-chase experiments showing that loss of UCH37 activity disrupts overall protein turnover.-
 Fig3. SDS-PAGE analysis of K6/K48 branch tri-Ub (10 μM) cleavage with varying concentrations of UCH37.
Fig3. SDS-PAGE analysis of K6/K48 branch tri-Ub (10 μM) cleavage with varying concentrations of UCH37. -
 Fig4. SDS-PAGE analysis of debranching reactions with UCH37 (1 μM) or UCH37•RPN13 (1 μM).
Fig4. SDS-PAGE analysis of debranching reactions with UCH37 (1 μM) or UCH37•RPN13 (1 μM).
Quality Guarantee
High Purity
-
.jpg) Fig1. SDS-PAGE (UCHL5-5898H)
Fig1. SDS-PAGE (UCHL5-5898H) -
.jpg) Fig2. SDS-PAGE (UCHL5-2070HFL)
Fig2. SDS-PAGE (UCHL5-2070HFL)
Involved Pathway
UCHL5 involved in several pathways and played different roles in them. We selected most pathways UCHL5 participated on our site, such as Downregulation of TGF-beta receptor signaling,Signal Transduction,Signaling by TGF-beta Receptor Complex, which may be useful for your reference. Also, other proteins which involved in the same pathway with UCHL5 were listed below. Creative BioMart supplied nearly all the proteins listed, you can search them on our site.
| Pathway Name | Pathway Related Protein |
|---|---|
| Downregulation of TGF-beta receptor signaling | STRAP,USP15,SMAD3B,PMEPA1,STUB1 |
| TGF-beta receptor signaling activates SMADs | STRAP,NEDD8,NEDD8L,USP15,PMEPA1 |
| Signaling by TGF-beta Receptor Complex | SKIA,NEDD8,NEDD8L,CGNB,PMEPA1,TRIM33,SKIB,USP9,USP15,STRAP |
| Signal Transduction | ARHGAP29,GPR177,CCBP2,PTPRU,GPR77,GPR37L1,AKR1C6,NOTUM,CSN2,RGS18 |
-
 Fig1. A model for how UCH37 promotes substrate processing and recycling of the proteasome through debranching of polyUb chains. (Aixin Song, 2021)
Fig1. A model for how UCH37 promotes substrate processing and recycling of the proteasome through debranching of polyUb chains. (Aixin Song, 2021) -
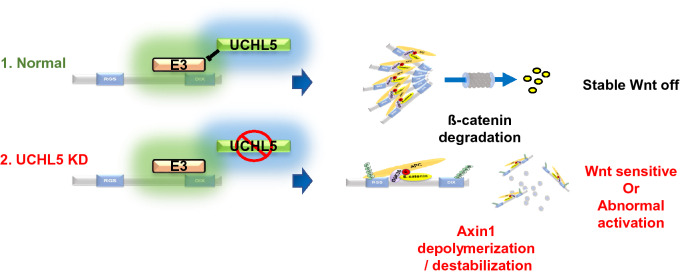 Fig2. UCHL5 is required for the functional activity of Axin1. (Wonhee Han, 2022)
Fig2. UCHL5 is required for the functional activity of Axin1. (Wonhee Han, 2022)
Protein Function
UCHL5 has several biochemical functions, for example, endopeptidase inhibitor activity,omega peptidase activity,poly(A) RNA binding. Some of the functions are cooperated with other proteins, some of the functions could acted by UCHL5 itself. We selected most functions UCHL5 had, and list some proteins which have the same functions with UCHL5. You can find most of the proteins on our site.
| Function | Related Protein |
|---|---|
| protein binding | CREB5,GOLPH3L,POC5,CIB2,PAGE2,SLC6A12,TIMM8A,CCL28,ZP3,LRP6 |
| proteasome binding | ID1,USP13,UBD,PSMF1,PSMD14,DNAJB2,BAG6,USP14,ADRM1,PSMG1 |
| endopeptidase inhibitor activity | TFPI,WFDC2,RENBP,C3A.3,Serpina1c,STFA1,C3B.2,A2ML,SERPINA1A,PROS1 |
| poly(A) RNA binding | NOM1,FBL,GRWD1,NOL12,RPS26,MTO1,MRPL45,UTP14A,METAP2,TBCA |
| ubiquitin-specific protease activity | COPS5,OTUD3,USP18,USP38,IWS1,USP13,USP17L2,USP50,USP14,USP46 |
| omega peptidase activity | UCHL1,USP13,USP5,GGH,JOSD1,APEH,ATXN3L,ATXN3,JOSD2 |
Interacting Protein
UCHL5 has direct interactions with proteins and molecules. Those interactions were detected by several methods such as yeast two hybrid, co-IP, pull-down and so on. We selected proteins and molecules interacted with UCHL5 here. Most of them are supplied by our site. Hope this information will be useful for your research of UCHL5.
ADRM1
Resources
Related Services
Related Products
References
- Wang, X; Stafford, W; et al. The 19S Deubiquitinase Inhibitor b-AP15 Is Enriched in Cells and Elicits Rapid Commitment to Cell Death. MOLECULAR PHARMACOLOGY 85:932-945(2014).
- Ouh, IO; Seo, MG; et al. Proteomic Analysis of Testicular Ischemia-Reperfusion Injury in Rats. JOURNAL OF VETERINARY MEDICAL SCIENCE 76:313-321(2014).


