UBA2
-
Official Full Name
ubiquitin-like modifier activating enzyme 2 -
Overview
Posttranslational modification of proteins by the addition of the small protein SUMO (see SUMO1; MIM 601912), or sumoylation, regulates protein structure and intracellular localization. SAE1 (MIM 613294) and UBA2 form a heterodimer that functions as a SUMO-activating enzyme for the sumoylation of proteins (Okuma et al., 1999 [PubMed 9920803]).[supplied by OMIM, Mar 2010] -
Synonyms
UBA2;ubiquitin-like modifier activating enzyme 2;ARX;SAE2;HRIHFB2115;SUMO-activating enzyme subunit 2;SUMO1 activating enzyme subunit 2;SUMO-1 activating enzyme subunit 2;ubiquitin-like 1-activating enzyme E1B;anthracycline-associated resistance ARX;ubiquitin-like modifier-activating enzyme 2;UBA2, ubiquitin-activating enzyme E1 homolog
Recombinant Proteins
- Human
- Zebrafish
- Chicken
- Mouse
- E.coli
- Mammalian Cells
- Sf9 Cells
- HEK293
- GST
- His
- Non
- Flag
- Avi
- Fc
- SUMO
- DDK
- Myc
Background
What is UBA2 Protein?
UBA2 is a protein that acts as a key player in the SUMOylation process, which attaches small ubiquitin-like modifiers (SUMO) to various proteins. This modification impacts how proteins behave, where they go, and how stable they are, playing a critical role in regulating cell function and gene expression. UBA2 is essentially part of the machinery that starts this modification process. Though its full significance in different cancers isn't completely known, higher levels of UBA2 have been noted in some cancer types, hinting at its potential role in tumor development or progression.What is the Function of UBA2 Protein?
UBA2 is crucial for the SUMOylation pathway, which is a process that modifies proteins in your cells by adding a SUMO (Small Ubiquitin-like Modifier) group. This modification can change how proteins interact with each other, affect their stability, and determine where they are located within the cell. Through these changes, UBA2 influences various cellular activities like DNA repair, gene expression, and cell cycle progression. By regulating these pathways, UBA2 helps maintain normal cellular function and can play a role in responding to stress or damage. Its activity is especially significant in contexts like cancer, where these pathways often go awry.UBA2 Related Signaling Pathway
UBA2 is involved in the SUMOylation signaling pathway, which is crucial for modifying proteins with SUMO groups. This pathway affects a variety of cellular processes such as DNA repair, transcription regulation, and maintaining the stability and location of proteins within cells. Through SUMOylation, UBA2 indirectly influences other pathways by modifying key regulatory proteins, impacting how cells respond to stress, control the cell cycle, and regulate gene expression. This makes UBA2 a vital component in maintaining cellular balance and responding to environmental changes, with particular importance in cancer and stress responses.
Fig1. Proposed pathway of recovery of R28 cells, induced by hPMSC-derived exosomes, after hypoxic damage. (Kyungmin Koh, 2020)
UBA2 Related Diseases
UBA2 is linked to various diseases, mainly through its role in the SUMOylation process. Abnormalities in this pathway can contribute to cancer development, as seen in some lung and breast cancers, where UBA2 expression is often higher. This elevated activity might lead to uncontrolled cell growth and survival. Disorders in SUMOylation can also impact neurological diseases and developmental problems because of its widespread role in regulating protein function. By understanding UBA2's role, researchers are looking into targeted therapies that might correct these irregularities in diseases where UBA2 plays a crucial part.Bioapplications of UBA2
UBA2 has potential bioapplications due to its role in the SUMOylation process. In cancer research, UBA2 could be a target for therapies aimed at modulating how proteins interact and function in cancer cells, given its involvement in cell cycle regulation and stress responses. It's also relevant in developing treatments for diseases where protein misregulation plays a part, like neurodegenerative disorders. Additionally, studying UBA2 can provide insights into cellular stress responses and gene expression control, which could lead to advances in regenerative medicine and novel drug development. Understanding UBA2's function might help design therapeutic interventions that restore balance in disease-affected pathways.Case Study
Case Study 1: Du X. et al. Ir J Med Sci. 2022
Renal cell carcinoma (RCC), a common kidney cancer in adults, involves a web of complex signaling paths, and we still don't fully understand the detailed molecular workings. This study looked into UBA2's role in RCC progression and its impact on downstream molecules. Researchers used RT-qPCR and western blotting to check UBA2 levels alongside related molecules. Cell growth was studied with CCK-8 assays and Ki-67 staining, while flow cytometry helped analyze cell distribution and apoptosis. They found UBA2 was overexpressed in RCC tissues, linking it to larger tumors, advanced stages, and lower survival rates. Knocking down UBA2 cut RCC cell growth and caused cell cycle arrest in the G0/G1 phase. Additionally, UBA2 appears to influence RCC biology through the p53 signaling pathway.-
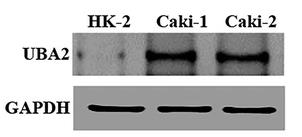 Fig1. Protein levels of UBA2 were enhanced in Caki-1 and Caki-2 cells compared to the control.
Fig1. Protein levels of UBA2 were enhanced in Caki-1 and Caki-2 cells compared to the control. -
 Fig2. The expression of the p53-associated molecules was examined in RCC cells treated with si-UBA2.
Fig2. The expression of the p53-associated molecules was examined in RCC cells treated with si-UBA2.
Case Study 2: Jiang B. et al. J Cell Biochem. 2019
Ubiquitin activating enzyme 2 (UBA2) plays a role in the SUMOylation process, but its cancer links aren't well understood. This study explored UBA2 in non-small-cell lung cancer. Immunochemistry showed UBA2 was higher in cancer tissues (53.3%, 40 of 75) versus normal lung tissues (14.3%, 4 of 28) with a focus in the nucleus. High UBA2 levels connected to poor differentiation, bigger tumors, advanced stages, and more spread. Lab tests found UBA2 in various cell lines like A549, 95D, H1975, and H1299. Reducing UBA2 in A549 cells slowed growth and boosted apoptosis. It also led to more cells in the G1 and G2/M phases and fewer in the S phase. Gene analysis post-UBA2 knockdown linked it to cell growth, death, and proliferation. Western blotting revealed lower levels of poly(ADP-ribose) polymerase 1 and some mini-chromosome maintenance proteins with less UBA2.-
 Fig3. UBA2 was effectively knocked down through transfection of shUBA2 in A549 cells.
Fig3. UBA2 was effectively knocked down through transfection of shUBA2 in A549 cells. -
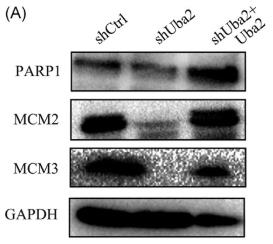 Fig4. Knockdown of Uba2 expression in cancer cells significantly downregulated the expression of PRAP1, MCM2, and MCM3.
Fig4. Knockdown of Uba2 expression in cancer cells significantly downregulated the expression of PRAP1, MCM2, and MCM3.
Quality Guarantee
High Purity
-
.jpg) Fig1. SDS-PAGE (UBA2-1373HFL)
Fig1. SDS-PAGE (UBA2-1373HFL)
Involved Pathway
UBA2 involved in several pathways and played different roles in them. We selected most pathways UBA2 participated on our site, such as Metabolism of proteins,Post-translational protein modification,Processing and activation of SUMO, which may be useful for your reference. Also, other proteins which involved in the same pathway with UBA2 were listed below. Creative BioMart supplied nearly all the proteins listed, you can search them on our site.
| Pathway Name | Pathway Related Protein |
|---|---|
| Ubiquitin mediated proteolysis | PARK2,SMURF1,HUWE1,FBXW11A,RFWD2,DET1,FBXW11,CDH1-A,WWP2,CBL |
| Post-translational protein modification | DHPS,PHC3,ST6GALNAC2,ADAMTS18,ST6GAL2B,TRAPPC6B,SAE1,MPDU1,ADAMTS5,MPDU1B |
| SUMO is conjugated to E1 (UBA2:SAE1) | SAE1 |
| Metabolism of proteins | IGFBP6A,ST6GAL2B,SAE1,F9B,SLC30A6,SPON1A,YKT6,SEC16B,ARSJ,MPDU1 |
| Processing and activation of SUMO | SENP5,SAE1,SENP1 |
| SUMOylation | SAE1,NSMCE2,RNF2,SENP1,PHC3,PHC1,SMC6,RING1,CBX8,SMC5 |
| SUMO is transferred from E1 to E2 (UBE2I, UBC9) | SAE1 |
-
 Fig1. Schematic diagram of UBA2 SUMOylation of NQO1 and its role in promoting hepatocellular carcinoma proliferation via modulation of the MAPK pathway. (Hailong Chen, 2024)
Fig1. Schematic diagram of UBA2 SUMOylation of NQO1 and its role in promoting hepatocellular carcinoma proliferation via modulation of the MAPK pathway. (Hailong Chen, 2024) -
 Fig2. The schematic cartoon of the mechanism of UBA2 promoted SUMOylation of RALY to regulate vasculogenic mimicry of glioma cells. (Shuo Cao, 2023)
Fig2. The schematic cartoon of the mechanism of UBA2 promoted SUMOylation of RALY to regulate vasculogenic mimicry of glioma cells. (Shuo Cao, 2023)
Protein Function
UBA2 has several biochemical functions, for example, ATP binding,SUMO activating enzyme activity,enzyme activator activity. Some of the functions are cooperated with other proteins, some of the functions could acted by UBA2 itself. We selected most functions UBA2 had, and list some proteins which have the same functions with UBA2. You can find most of the proteins on our site.
| Function | Related Protein |
|---|---|
| enzyme activator activity | TRIM23,GTF3C4,GM1679,MMP16,PSAPL1,PPP1R12B,APOA5,PRKCE,ASAP2,GM749 |
| transcription factor binding | MYOCD,H2-AB1,FOS,TLE1,MDFIC,PPARG,NLK,POU1F1,TFDP2,JUN |
| ATP binding | ERCC3,PANK4,TK2,STK33,PHKG1,ULK1,ATP1A1B,UCK1,ERCC6,ATAD1B |
| protein binding | EZR,TICAM2,SH3PXD2B,OAZ2,TRIM10,PUM1,TFR2,GORAB,CCNY,RBM39 |
| metal ion binding | HBB-Y,FCNA,ZC3H3,TTC4,CACNA2D1,AMDHD1,ZNF384L,SUMF1,ZFP42,HBBE3 |
| protein heterodimerization activity | HIST1H4B,ADRa1A,ATF1,EGFR,SOX5,HIST1H2BM,SCUBE1,GTF2A1,ALG2,PKNOX1 |
Interacting Protein
UBA2 has direct interactions with proteins and molecules. Those interactions were detected by several methods such as yeast two hybrid, co-IP, pull-down and so on. We selected proteins and molecules interacted with UBA2 here. Most of them are supplied by our site. Hope this information will be useful for your research of UBA2.
SAE1;g2xkq0_human;SUMO1;UBE2I;MCC;HLA-B;PCBD1;IKBKE;TRAF6;SETX
Resources
Related Services
Related Products
References


