TXN2
-
Official Full Name
thioredoxin 2 -
Overview
This nuclear gene encodes a mitochondrial member of the thioredoxin family, a group of small multifunctional redox-active proteins. The encoded protein may play important roles in the regulation of the mitochondrial membrane potential and in protection against oxidant-induced apoptosis. -
Synonyms
TXN2;thioredoxin 2;thioredoxin, mitochondrial;MT TRX;thioredoxin-2;mitochondrial thioredoxin;MTRX;TRX2;MT-TRX
Recombinant Proteins
- Zebrafish
- Human
- Mouse
- Chicken
- Rat
- Cattle
- Mammalian Cells
- E.coli
- HEK293
- His
- Non
- T7
- DDK
- Myc
- GST
- Avi
- Fc
Background
What is TXN2 protein?
TXN2 gene (thioredoxin 2) is a protein coding gene which situated on the long arm of chromosome 22 at locus 22q12. TXN2 also known as Trx2, is a mitochondrial protein that plays a significant role in maintaining the redox balance within cells. As a member of the thioredoxin family, it is involved in various biological processes including electron transport and response to oxidative stress. TXN2 possesses dithiol-reducing activity, which is crucial for controlling mitochondrial reactive oxygen species homeostasis, apoptosis regulation, and cell viability. It is implicated in human diseases related to metabolism and mitochondrial function. The TXN2 protein is consisted of 166 amino acids and TXN2 molecular weight is approximately 18.4 kDa.
What is the function of TXN2 protein?
TXN2 is involved in the decomposition of hydrogen peroxide (H2O2) into water through its sulfhydryl (-SH) group, reducing the accumulation of reactive oxygen species (ROS) and protecting cells from oxidative damage. TXN2 inhibits age-related muscle loss by inhibiting mitochondrial oxidative stress and apoptosis. Overexpression of TXN2 can partially normalize age-related gene expression changes, help maintain cell REDOX activity, and inhibit gene expression of apoptosis and ubiquitin-like binding pathways associated with protein degradation. TXN2 maintains mitochondrial permeability transition and protects mitochondrial function by resisting peroxy-induced necrosis and apoptotic changes. TXN2 is essential for cell survival, and in cell culture and animal models, TXN2 reduction leads to ROS accumulation, cytochrome C release, and apoptosis.
TXN2 related signaling pathway
In the antioxidant signaling pathway, TXN2 is involved in reducing hydrogen peroxide (H2O2) to water through its sulfhydryl (-SH) group, reducing the accumulation of reactive oxygen species (ROS), and protecting cells from oxidative damage. TXN2 promotes the breakdown of H2O2, removes peroxides by reducing mitochondrial catalase (Prx3), and is the primary mitochondrial H2O2 scavenging enzyme. TXN2 interacted with TXNIP (Thioredoxin interacting protein), a central physiological inhibitor of the TRX system that acted in cellular stress responses by modulating REDOX equilibria. TXNIP promotes the inflammatory response through its formation with the NLRP3 inflammatory body and is a key factor in connecting ER stress and inflammation. TXN2 plays an important role in maintaining mitochondrial function by resisting peroxysis-induced necrosis and apoptosis, maintaining mitochondrial permeability transition and protecting mitochondrial function.
TXN2 related diseases
The abnormal expression of TXN2 is closely related to the occurrence and development of tumor. Studies have shown that TXN2 is highly expressed in a variety of tumor cells and is involved in the proliferation, invasion and metastasis of tumor cells. In addition, TXN2 is also associated with resistance of tumor cells to chemotherapy drugs. Secondly, the abnormal expression of TXN2 is also closely related to the occurrence and development of cardiovascular diseases. It is highly expressed in cardiomyocytes and is involved in the oxidative stress reaction and apoptosis of cardiomyocytes. In addition, TXN2 is also associated with the occurrence and development of neurological diseases such as Parkinson's disease and Alzheimer's disease.
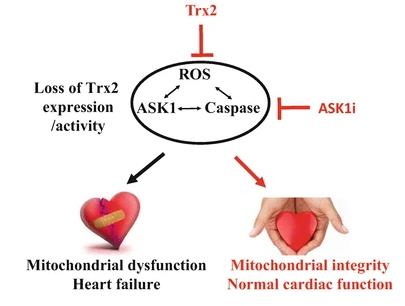
Fig1. Trx2-cKO Model and therapeutics for the treatment of heart failure. (Chaofei Chen, 2017)
Bioapplications of TXN2
As a potential target for tumor therapy, the expression level of TXN2 is significantly different in various tumor types, which provides a possibility for tumor individualized therapy. At the same time, the drug action of TXN2 can significantly reduce the risk of cardiac degeneration and metastasis of tumors, improve the immunogenicity and enhance the intensity of immunotherapy of tumors. TXN2 is also of high value in the field of drug development, and by studying its biological characteristics, it can optimize the therapeutic effect of existing drugs and provide an important theoretical basis for drug clinical trials. In addition, TXN2 can also be used as a biological monitor in the process of tumor treatment to monitor the effect of tumor treatment in real time and guide the adjustment of individual treatment plans.
Case Study
Case Study 1: Kun-Yi Li, 2021
Thioredoxin-2 (TXN2), a mitochondrial antioxidant enzyme, is implicated in Alzheimer's disease (AD) pathogenesis. This study shows that in cells expressing human amyloid-β precursor protein (APP), TXN2 affects the transcription of BACE1, impacting β-amyloid protein (Aβ) levels. TXN2's role in reactive oxygen species (ROS) clearance is highlighted by its silencing in 3-nitropropionic acid (3-NP) treated cells, which increases BACE1 levels. TXN2 also modulates NFκB signaling, reducing p65 and IκBα phosphorylation, and its regulation of BACE1 is attenuated by p65 knockdown. Cellular ROS, apoptosis, and viability are influenced by TXN2's expression levels. In an AD mouse model, TXN2 protein levels decline with age, particularly at 12 months.
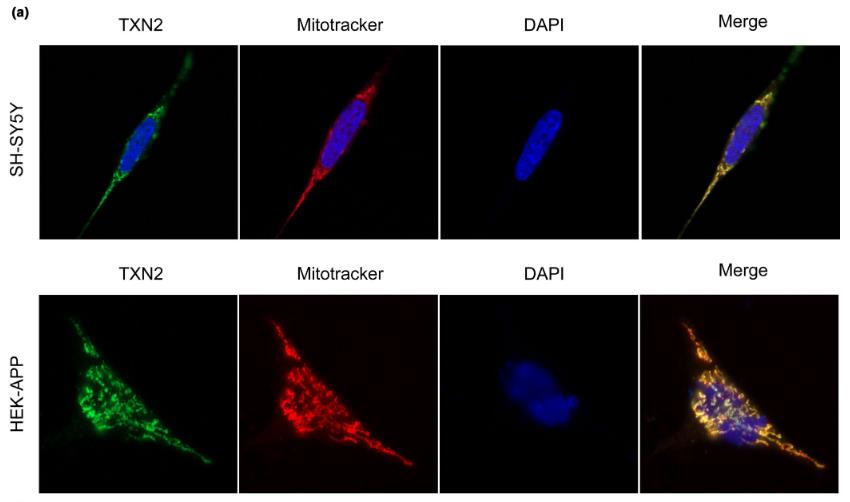
Fig1. Immunofluorescent images show that TXN2 colocalizes with mitotracker in SH-SY5Y and HEK-APP cells.
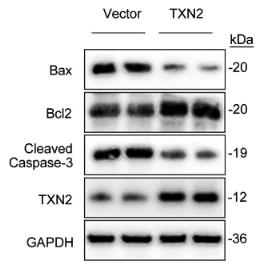
Fig2. Representative western blots and quantification of Bax, Bcl2, and Cleaved Caspase-3 in HEK-APP cells transfected with TXN2 or vector.
Case Study 2: Sherry E Adesina, 2017
Mitochondrial antioxidants' impact on hypoxia-induced pulmonary hypertension (PH) is unclear. Researchers studied thioredoxin 2 (Trx2), a key mitochondrial redox regulator, in human pulmonary cells under hypoxia. Hypoxia reduced Trx2 expression. Overexpressing Trx2 in vitro decreased H2O2 production caused by hypoxia. Transgenic mice with elevated Trx2 exposed to hypoxia showed increased PH symptoms and lung ROS. Trx2 overexpression did not reduce Trx2 oxidation or Nox4 expression. A Trx2 mutant mimicking oxidation worsened hypoxia-induced H2O2 levels and cell proliferation in smooth muscle cells. Overall, Trx2 overexpression did not mitigate hypoxia-induced PH or cell proliferation.
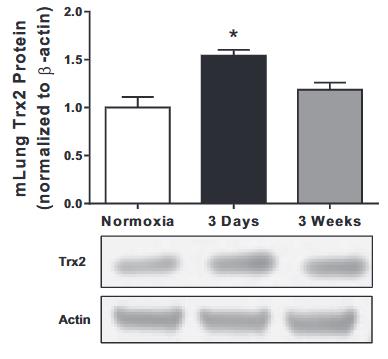
Fig3. Trx2 expression is sensitive to fluctuations in oxygen levels.
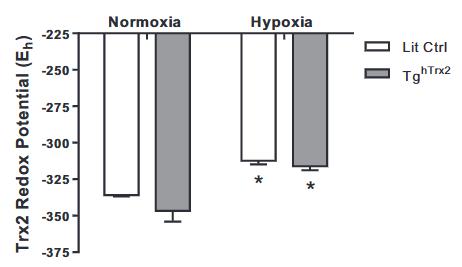
Fig4. Hypoxia decreases Trx2 redox potential in vivo.
Quality Guarantee
High Purity
.jpg)
Fig1. SDS-PAGE (TXN2-1700H)
.
.jpg)
Fig2. SDS-PAGE (TXN2-8002C)
Involved Pathway
TXN2 involved in several pathways and played different roles in them. We selected most pathways TXN2 participated on our site, such as Cellular responses to stress,Detoxification of Reactive Oxygen Species,Oxidative Stress, which may be useful for your reference. Also, other proteins which involved in the same pathway with TXN2 were listed below. Creative BioMart supplied nearly all the proteins listed, you can search them on our site.
| Pathway Name | Pathway Related Protein |
|---|---|
| Oxidative Stress | NOX4,JUNBA,NFIX,TXNRD2,NQO1 |
| Cellular responses to stress | ERF,HMGA1B,SUZ12B,HMGA1,MAP1LC3C,TINF2,GABARAP,CDKN2C,EEF1A1,SCMH1 |
| Detoxification of Reactive Oxygen Species | PRDX2,Txn1,PRDX3,TXN,TXNRD2 |
Protein Function
TXN2 has several biochemical functions, for example, oxidoreductase activity, acting on a sulfur group of donors, disulfide as acceptor,peptide-methionine (R)-S-oxide reductase activity,peptide-methionine (S)-S-oxide reductase activity. Some of the functions are cooperated with other proteins, some of the functions could acted by TXN2 itself. We selected most functions TXN2 had, and list some proteins which have the same functions with TXN2. You can find most of the proteins on our site.
| Function | Related Protein |
|---|---|
| peptide-methionine (R)-S-oxide reductase activity | MSRB3,MSRB1,MSRB2,MSRB1B,MSRB1A |
| protein binding | SLIT2,C21orf119,TIPRL,TLX1,CDKN2B,TRAM1,GSTK1,RADIL,AMDHD2,RAB14 |
| protein complex binding | PPFIA2,NFKBIA,TG,IST1,FGFR1,ARRB2,GNB4,RAD18,KAT2B,NDUFA9 |
| oxidoreductase activity, acting on a sulfur group of donors, disulfide as acceptor | DNAJC10,MSRB1A,ERO1LB,TXN,TXNDC8,TXNL1,ERO1L,MSRB1B |
| peptide-methionine (S)-S-oxide reductase activity | MSRB1A,MSRA |
| protein disulfide oxidoreductase activity | GLRX5,GRX2,SH3BGRL3,PTGESL,PTGES2,CHCHD4,TXNL1,ERO1LB,DNAJC10,TXN |
Interacting Protein
TXN2 has direct interactions with proteins and molecules. Those interactions were detected by several methods such as yeast two hybrid, co-IP, pull-down and so on. We selected proteins and molecules interacted with TXN2 here. Most of them are supplied by our site. Hope this information will be useful for your research of TXN2.
SSNA1;ZBTB14;TRIM21;DCTD;MAGEA11;RPIA;PSME3
Resources
Related Services
Related Products
References
- Lim, J; Luderer, U; et al. Oxidative Damage Increases and Antioxidant Gene Expression Decreases with Aging in the Mouse Ovary. BIOLOGY OF REPRODUCTION 84:775-782(2011).


