TUBG1
-
Official Full Name
tubulin, gamma 1 -
Synonyms
TUBG1;tubulin, gamma 1;TUBG, tubulin, gamma polypeptide;tubulin gamma-1 chain;TUBGCP1;gamma-1-tubulin;tubulin, gamma polypeptide;gamma-tubulin complex component 1;TUBG;GCP-1
Recombinant Proteins
- Human
- Zebrafish
- Mouse
- Rhesus macaque
- Insect Cells
- Mammalian Cells
- E.coli
- Wheat Germ
- Human
- HEK293
- HeLa
- In Vitro Cell Free System
- His
- Non
- Avi
- Fc
- DDK
- Myc
- Flag
Background
What is TUBG1 protein?
TUBG1 gene (tubulin gamma 1) is a protein coding gene which situated on the long arm of chromosome 17 at locus 17q21. This gene encodes a member of the tubulin superfamily. The encoded protein localizes to the centrosome where it binds to microtubules as part of a complex referred to as the gamma-tubulin ring complex. The protein mediates microtubule nucleation and is required for microtubule formation and progression of the cell cycle. The TUBG1 protein is consisted of 451 amino acids and TUBG1 molecular weight is approximately 51.2 kDa.
What is the function of TUBG1 protein?
TUBG1 is a highly conserved component of the centrosome and plays a crucial role in the organization of the microtubule cytoskeleton and the process of cell division, particularly mitosis. TUBG1 is involved in the formation and function of the spindle apparatus during cell division, ensuring the proper segregation of chromosomes into the resulting daughter cells. It is also a part of the γ-Tubulin ring complex (γ-TuRC), which is necessary for microtubule nucleation. TUBG1's expression levels and function are closely related to abnormalities in cell mitosis and chromosomal instability, making it a potential biomarker or therapeutic target for certain tumors.
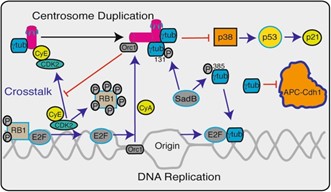
Fig1. Schematic representation of the different ways in which γ-tubulin (γtub) and the centrosomes control the G1-to-S transition and S phase progression. (Maria Alvarado-Kristensson, 2018)
TUBG1 Related Signaling Pathway
Although TUBG1's direct association with TNF signaling was not explicitly mentioned in the search results, given TUBG1's role in the cytoskeleton and cell division, it may indirectly affect signaling pathways activated by TNF-α, which are involved in inflammatory responses and cell survival. Studies have shown that TUBG1 promotes the development of hepatocellular carcinoma (HCC) through ATR/P53 apoptosis and cell cycle pathways. When TUBG1 is silenced in HCC cell lines, G1 phase cell cycle arrest, inhibition of cell proliferation and invasion, and promotion of apoptosis are observed.
TUBG1 Related Diseases
Mutations in the TUBG1 gene can lead to cortical dysplasias, which are brain malformations often linked to intellectual disabilities, developmental delays, and epilepsy. Furthermore, TUBG1 has been implicated in hepatocellular carcinoma (HCC), where its upregulation is associated with poor patient prognosis and is involved in the promotion of tumor growth and apoptosis pathways. Additionally, TUBG1 is connected to acute lymphoblastic leukemia, where it may play a role in the disease's progression.
Bioapplications of TUBG1
TUBG1 has a variety of applications in the biomedical field, mainly focused on research as a potential target and biomarker for disease treatment. In addition, functional studies of TUBG1 contribute to the understanding of its role in cell division and microtubule organization, which provides a basis for the development of therapies targeting neurodevelopmental disorders and tumogenesis caused by its mutations. In HCC immunization, association analysis of TUBG1 with immune-related prognostic genes and its role in HCC immunotherapy have also been explored.
Case Study
Case Study 1: Darina Malycheva, 2023
The centrosome of mammalian cells is in constant movement and its motion plays a part in cell differentiation and cell division. The purpose of this study was to establish the involvement of the TUBG meshwork in centrosomal motility. In live cells, researchers used a monomeric red-fluorescence-protein-tagged centrin 2 gene and a green-fluorescence-protein-tagged TUBG1 gene for labeling the centrosome and the TUBG1 meshwork, respectively. They found that centrosome movements occurred in cellular sites rich in GTPase TUBG1 and single-guide RNA mediated a reduction in the expression of TUBG1, altering the motility pattern of centrosomes. They propose that the TUBG1 meshwork enables the centrosomes to move by providing them with an interacting platform that mediates positional changes.
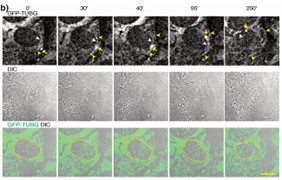
Fig1. U2OS and U2OS cells stably co-expressing TUBG shRNA (shTUBG) and a TUBG1 green fluorescence protein shRNA-resistant gene.
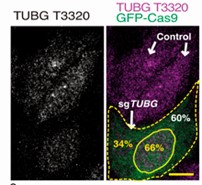
Fig2. Quantification of TUBG was performed comparing immunofluorescently labeled TUBG1 in cells expressing GFP-Cas9 with non-expressing cells.
Case Study 2: Yan Zhang, 2024
As reported, γ-tubulin (TuBG1) is related to the occurrence and development of various types of malignant tumors. However, its role in hepatocellular cancer (HCC) is not clear. The present study was to investigate the relationship between TuBG1 and clinical parameters and survival in HCC patients. The molecular function of TuBG1 was measured using colony formation, scratch assay, trans-well assay and flow cytometry. The tumor-immune system interactions and drug bank database (TISIDB) was used to evaluate TuBG1 and immunity. Based on the TuBG1-related immune genes, a prognostic model was constructed and was further validated internally and externally. The correlation analysis of immunohistochemistry and clinical parameters and survival data revealed that TuBG1 was negatively correlated with the overall survival. The constructed immune prognosis model could effectively evaluate the prognosis.
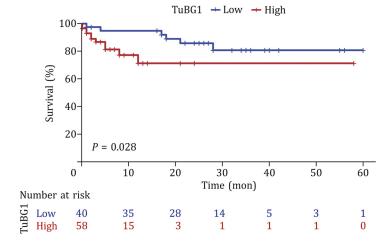
Fig3. The TuBG1expression is negatively correlated to the survival probability in the survival analysis.
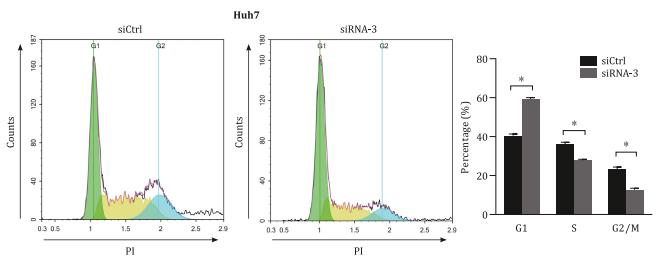
Fig4. More G1 arrested phases observed in TuBG1 silenced Huh7 cells.
Quality Guarantee
High Purity
.jpg)
Fig1. SDS-PAGE (TUBG1-4815H)
.
.jpg)
Fig2. SDS-PAGE (TUBG1-12H)
Involved Pathway
TUBG1 involved in several pathways and played different roles in them. We selected most pathways TUBG1 participated on our site, such as Anchoring of the basal body to the plasma membrane,Assembly of the primary cilium,Cell Cycle, which may be useful for your reference. Also, other proteins which involved in the same pathway with TUBG1 were listed below. Creative BioMart supplied nearly all the proteins listed, you can search them on our site.
| Pathway Name | Pathway Related Protein |
|---|---|
| Cell Cycle, Mitotic | ODF2B,TMPO,GOLGA2,CSNK1E,PHF8,CETN2,KIF2A,WAPAL,PMF1,GMNN |
| Anchoring of the basal body to the plasma membrane | CENPJ,CLASP1A,SCLT1,CEP63,TTBK2,CEP89,DYNC1I2,OFD1,CEP78,TSGA14 |
| G2/M Transition | ODF2B,CDK11B,CEP63,TUBGCP5,MAPRE1B,NDE1,ODF2,FOXM1,NUMA1,SDCCAG8 |
| Cell cycle | ANAPC4,BARD1,FAM175A,DSN1,CDC25C,RAD21B,GADD45G,CDC26,WRAP53,HIST2H3C |
| Assembly of the primary cilium | CEP57,IFT-20,TMEM216,CEP152,NEK2,CSNK1E,CCT5,TUBB4A,CP110,FLR |
| Loss of Nlp from mitotic centrosomes | CEP76,CEP135,HAUS2,PLK4,SDCCAG8,CEP78,CCP110,CEP152,MAPRE1A,CEP70 |
| Centrosome maturation | CEP164,CEP57,CEP72,TSGA14,CSNK1E,HAUS2,SSNA1,MAPRE1B,NEDD1,CCP110 |
| Loss of proteins required for interphase microtubule organizationfrom the centrosome | MAPRE1,TSGA14,CEP63,CEP72,PCM1,MAPRE1A,CLASP1A,MAPRE1B,CEP152,CEP76 |
Protein Function
TUBG1 has several biochemical functions, for example, GTP binding,GTPase activity,protein binding. Some of the functions are cooperated with other proteins, some of the functions could acted by TUBG1 itself. We selected most functions TUBG1 had, and list some proteins which have the same functions with TUBG1. You can find most of the proteins on our site.
| Function | Related Protein |
|---|---|
| structural constituent of cytoskeleton | TUBA8,NEFM,MSN,VIM,TUBGCP5,ANK1,ACTR2,TUBD1,TUBGCP4,VILL |
| protein binding | PTK2B,CEACAM1,TCEB3,OSBPL1A,RP2,MYC,GBAS,KHDRBS2,AMIGO2,LDHA |
| GTPase activity | EEF1A1,GTPBP1,RAB14L,ARL4D,RAB8A,RAB1B,TUBB5,EEFSEC,GNA14,GNB5 |
| GTP binding | RHOBTB1,GNAI3,GNA13,RAB13,MFN1B,SEPT3,RAB10,RABL6,EIF2S3Y,RHOT1B |
Interacting Protein
TUBG1 has direct interactions with proteins and molecules. Those interactions were detected by several methods such as yeast two hybrid, co-IP, pull-down and so on. We selected proteins and molecules interacted with TUBG1 here. Most of them are supplied by our site. Hope this information will be useful for your research of TUBG1.
MZT1;MARK4;Mzt2;TUBGCP3;AXIN1;MZT2B;DISC1;Tubgcp3
Resources
Related Services
Related Products
References



