TRAF2
-
Official Full Name
TNF receptor-associated factor 2 -
Overview
TNF receptor associated factor 2 (TRAF2) is thought to be a common signal transducer that associates with the cytoplasmic domains of the tumor necrosis factor receptor (TNFR) superfamily such as TNFR2, CD40 and CD30. TRAF2 indirectly associates with TNFR1 -
Synonyms
TRAF2;TNF receptor-associated factor 2;TRAP3;E3 ubiquitin-protein ligase TRAF2;tumor necrosis factor type 2 receptor associated protein 3;tumor necrosis factor type 2 receptor-associated protein 3;TRAP;MGC:45012
Recombinant Proteins
- Human
- Mouse
- Rhesus macaque
- E.coli
- Insect Cells
- Mammalian Cells
- HEK293
- His
- GST
- Non
- Flag
- Avi
- Fc
- DDK
- Myc
Background
What is TRAF2 protein?
TRAF2 (TNF receptor associated factor 2) gene is a protein coding gene which situated on the long arm of chromosome 9 at locus 9q34. The protein encoded by this gene is a member of the TNF receptor associated factor (TRAF) protein family. TRAF proteins associate with, and mediate the signal transduction from members of the TNF receptor superfamily. This protein directly interacts with TNF receptors, and forms a heterodimeric complex with TRAF1. This protein is required for TNF-alpha-mediated activation of MAPK8/JNK and NF-kappaB. The protein complex formed by this protein and TRAF1 interacts with the inhibitor-of-apoptosis proteins (IAPs), and functions as a mediator of the anti-apoptotic signals from TNF receptors. The interaction of this protein with TRADD, a TNF receptor associated apoptotic signal transducer, ensures the recruitment of IAPs for the direct inhibition of caspase activation. The TRAF2 protein is consisted of 501 amino acids and its molecular mass is approximately 55.9 kDa.
What is the function of TRAF2 protein?
TRAF2 is an intracellular signaling protein that is mainly involved in the signaling process of a variety of cell surface receptors, especially in the signaling of members of the tumor necrosis factor receptor (TNFR) family. By binding to these receptors, TRAF2 is involved in the regulation of a variety of cellular responses, including cell survival, proliferation, differentiation, inflammatory response, and immune response. The TRAF2 protein's function is not limited to signaling, it is also involved in regulating the stability and activity of other signaling molecules in the cell, Such as NF-κB (nuclear factor kappa-light-chain-enhancer of activated B cells) and JNK (c-Jun N-terminal kinases), It affects how cells respond to various physiological and pathological stimuli.
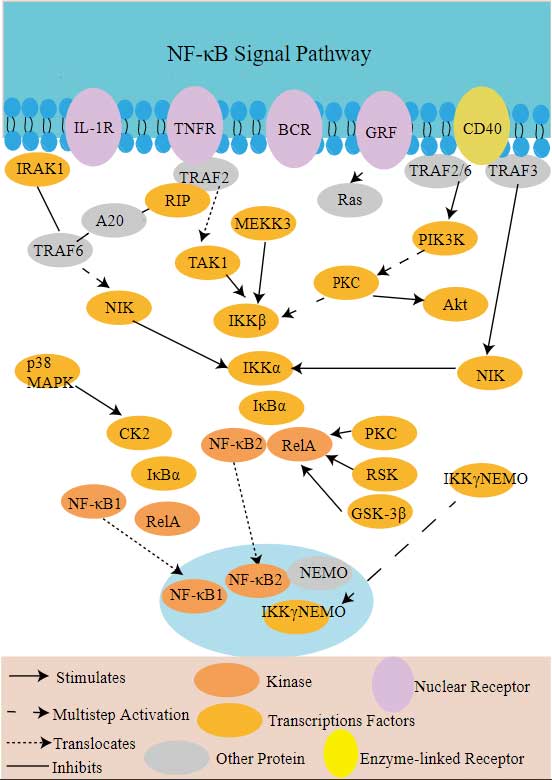
TRAF2 Related Signaling Pathway
TRAF2 proteins are involved in a variety of signaling pathways, the most important of which are the tumor necrosis factor (TNF) receptor superfamily and the nuclear factor κB (NF-κB) signaling pathway. As a member of the tumor necrosis factor receptor-related factor family, TRAF2 is involved in regulating biological processes such as inflammation, immune response, and apoptosis by binding to TNF receptors. In addition, TRAF2 interacts with other signaling pathways, such as Toll-like receptors (TLR), NOd-like receptors (NLR), and RIP1/RIP3 complexes, which further affect cell proliferation, differentiation, and survival.
TRAF2 Related Diseases
TRAF2 protein is associated with a variety of diseases, including autoimmune diseases, tumors, and infectious diseases. In autoimmune diseases, abnormal expression or functional mutation of TRAF2 may lead to overactivation of the immune system, triggering diseases such as rheumatoid arthritis, systemic lupus erythematosus, scleroderma, etc. In addition, TRAF2 is also involved in cell proliferation, differentiation and apoptosis, and is closely related to the occurrence and development of tumors. Studies have shown that TRAF2 expression levels are abnormally elevated in various tumors such as lung cancer, breast cancer, and colon cancer. At the same time, TRAF2 is also involved in the antiviral immune response, and its abnormal function may lead to the persistence and chronicity of viral infection.
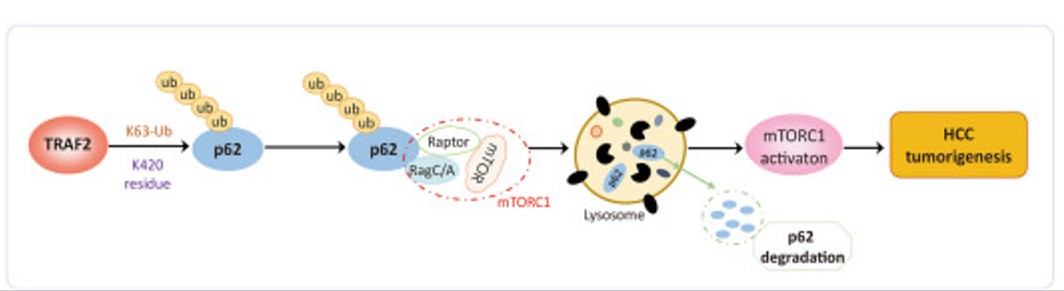
Fig1. A model for TRAF2 in liver tumorigenesis. (Xue Liang, 2023)
Bioapplications of TRAF2
In the field of drug discovery, TRAF2 has become an important drug target due to its key role in a variety of diseases. By inhibiting or activating the TRAF2 signaling pathway, researchers and pharmaceutical companies are developing new treatments to regulate the inflammatory response and tumor development. In terms of clinical diagnosis, TRAF2 expression levels are significantly elevated in some inflammatory diseases as well as certain tumors, making it a potential biomarker for these diseases.
Case Study
Case Study 1: Yawei Xu, 2023
The management of advanced clear cell renal cell carcinoma (ccRCC) remains a major challenge in clinical practice, and the construction of more reliable prognostic prediction models and the further elucidation of key molecular mechanisms of tumor progression are topics in urgent need of in-depth investigation. Expression patterns and clinical significance of TRAF2 were determined through bioinformatics analysis, real-time qPCR, Western Blot, immunohistochemistry. GSEA analysis, transmission electron microscopy, 2D/3D colony formation assay, cell migration and invasion assay, and tube-formation assay were used to investigate the underlying function and mechanism of the TRAF2/M2 macrophage/autophagy axis. As one of the constituent genes of the risk model, TRAF2 was determined to be upregulated in ccRCC and associated with poor clinical prognosis. TRAF2 promotes malignant progression of ccRCC by regulating macrophage polarization, migration and angiogenesis. Mechanistically, TRAF2 promotes the polarization of M2 macrophages, and this chemotaxis is achieved in an autophagy-dependent pathway.
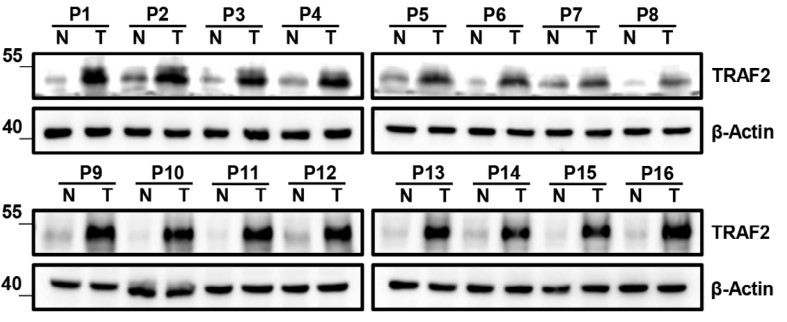
Fig1. Western Blot analysis of TRAF2 expression in 16 paired ccRCC and adjacent noncancerous tissues.
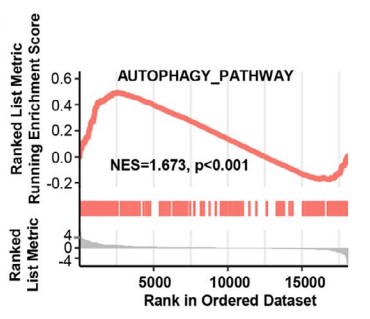
Fig2. GSEA analysis was performed in TCGA-KIRC cohort to reveal the association between TRAF2 and the activation of autophagy pathway.
Case Study 2: Xue Liang, 2023
Dysregulated expression of TRAF2 has been reported in a variety of human cancers. Whether and how TRAF2 regulates the growth of liver cancer cells remains elusive. The goal of this study is to investigate potential dysregulation of TRAF2 and its biological function in liver cancer. Here TRAF2 is up-regulated in human liver cancer cell lines and tissues, and high TRAF2 expression is associated with a poor prognosis of HCC patients. Proteomics profiling along with Co-immunoprecipitation analysis revealed that p62 is a new substrate of TRAF2, which is subjected to TRAF2-induced polyubiquitination via the K63 linkage at the K420 residue. TRAF2 depletion inhibited growth and survival of liver cancer cells both in vitro and in vivo by causing p62 accumulation, which is partially rescued by simultaneous p62 knockdown. Mechanistically, TRAF2-mediated p62 polyubiquitylation activates the mTORC1 by forming the p62-mTORC1-Rag complex, which facilitates the lysosome localization of mTORC1. TRAF2 depletion inhibited mTORC1 activity through the disruption of interaction between p62 and the mTORC1 complex.
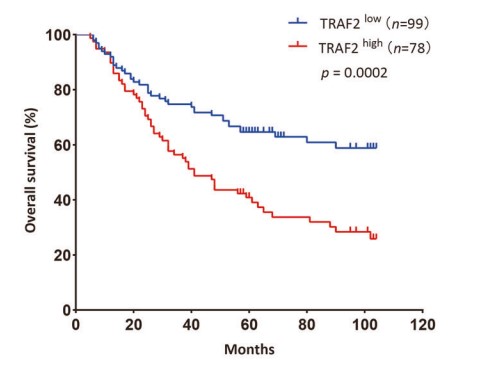
Fig3. The correlation between TRAF2 expression and overall survival in HCC patients.
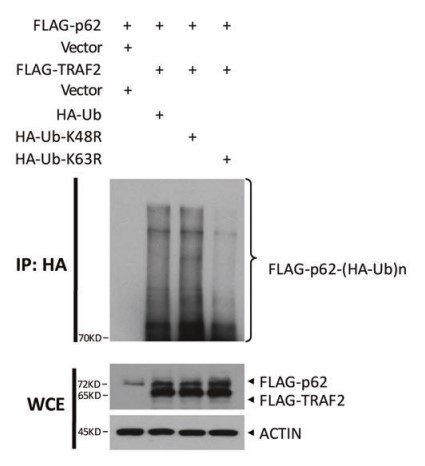
Fig4. TRAF2 promotes K63 polyubiquitination of p62 at K420site.
Quality Guarantee
High Purity
.jpg)
Fig1. SDS-PAGE (TRAF2-1764HFL)
Involved Pathway
TRAF2 involved in several pathways and played different roles in them. We selected most pathways TRAF2 participated on our site, such as MAPK signaling pathway,NF-kappa B signaling pathway,Sphingolipid signaling pathway, which may be useful for your reference. Also, other proteins which involved in the same pathway with TRAF2 were listed below. Creative BioMart supplied nearly all the proteins listed, you can search them on our site.
| Pathway Name | Pathway Related Protein |
|---|---|
| NF-kappa B signaling pathway | CD14,IL-8,GM10591,VCAM1,GM1987,BIRC3,TICAM2,BCL2A1A,ATM,LTBR |
| Sphingolipid signaling pathway | MAPK10,SMPD1,PPP2R5A,CERS2,SPTLC2,AKT1,NFKB1,SGPP1,PRKCG,PPP2CA |
| Herpes simplex infection | HNRNPK,CD74,IFNA14,CSNK2A2,DDX58,EIF2AK3,TLR2,NFKBIA,POLR2A,IRF9 |
| Epstein-Barr virus infection | TRAF3,EIF2AK1,PSMC5,PSMD2,EP300,POLR2C,TAB2,PIK3CG,GSK3B,LYN |
| Non-alcoholic fatty liver disease (NAFLD) | NDUFA8,UQCRH,Casp3,SDHB,SOCS3,TGFB1,AKT2,COX7B,IL6,MAPK9 |
| Viral carcinogenesis | HIST1H4M,HDAC4,KAT2A,CCNA2,HDAC8,PIK3R1,GTF2A1,MAPKAPK2,HLA-F,IRF3 |
| Pathways in cancer | TRP53,WNT7A,PTGER2,FGF19,GNG2,Ar,TCEB1,BMP2,RXRG,WNT2 |
| Osteoclast differentiation | CYBB,PPP3CB,STAT1,MAP2K1,TGFBR1,IFNGR2,IFNAR1,IKBKG,PPARG,TGFBR2 |
| TNF signaling pathway | MAP2K3,IL6,MAPK10,MAP3K5,IKBKG,MAP3K7IP3,IKBKB,AKT2,SELE,RELA |
Protein Function
TRAF2 has several biochemical functions, for example, CD40 receptor binding,enzyme binding,identical protein binding. Some of the functions are cooperated with other proteins, some of the functions could acted by TRAF2 itself. We selected most functions TRAF2 had, and list some proteins which have the same functions with TRAF2. You can find most of the proteins on our site.
| Function | Related Protein |
|---|---|
| ligase activity | TRIM13,SHRPRBCK1R,TRIM68,RNF14,HERC5,RNF170,TRIM38,UBR2,PELI1,GLULA |
| zinc ion binding | ZMAT3,NR5A2,MT1,BMP1A,LIMS1,TNKS,BRF1B,ADA,MYLIP,ADH8B |
| tumor necrosis factor receptor binding | TNFSF10L4,TNFSF9,TNFSF10L3,TNFSF12,TRAF4,TRIM37,TRAF3,FASLG,TNFSF15,LTA |
| ubiquitin protein ligase binding | PIAS2,CUL4A,SMAD2,TRAF5,UBE2KA,AMBRA1,GPI1,TCEB2,BRCA1,TRIB3 |
| mitogen-activated protein kinase kinase kinase binding | MAPK9,MARVELD3,MAP2K1,MAPK8IP3,PPEF2,TCF3,STK38,CDC42,TRAF6,MAP3K11 |
| ubiquitin-protein transferase activity | UHRF2,TRIM23,CDC23,MARCH8,PEX2,MARCH2,UBE2N,CMTM2A,MARCH5L,MUL1B |
| sphingolipid binding | S1PR1 |
| signal transducer activity | HTR5AL,GNG4,TAAR7D,DRD4B,STAT4,PRMT2,DKK1,GNRHR1,GNAO1A,GPR152 |
| identical protein binding | AGXT2L1,NME1,RAD52,SLC2A1,CLDN14,ALDOB,CBLL1,DAPK2,CLDN7,TMEM115 |
Interacting Protein
TRAF2 has direct interactions with proteins and molecules. Those interactions were detected by several methods such as yeast two hybrid, co-IP, pull-down and so on. We selected proteins and molecules interacted with TRAF2 here. Most of them are supplied by our site. Hope this information will be useful for your research of TRAF2.
BIRC2;BIRC3
TRAF2 Related Signal Pathway
Resources
Related Services
Related Products
References