TNKS
-
Official Full Name
tankyrase, TRF1-interacting ankyrin-related ADP-ribose polymerase -
Overview
Tankyrase-1 is an enzyme that in humans is encoded by the TNKS gene. -
Synonyms
TNKS;tankyrase, TRF1-interacting ankyrin-related ADP-ribose polymerase;tankyrase-1;PARP 5a;PARP5A;pART5;TIN1;TINF1;TNKS1;TANK1;TNKS-1;tankyrase I;poly [ADP-ribose] polymerase 5A;TRF1-interacting ankyrin-related ADP-ribose polymerase;PARPL;P
Recombinant Proteins
- Human
- Mouse
- Rhesus macaque
- Chicken
- E.coli
- Mammalian Cells
- Wheat Germ
- HEK293
- GST
- His
- Non
- Avi
- Fc
| Cat.# | Product name | Source (Host) | Species | Tag | Protein Length | Price |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| TNKS-3327H | Recombinant Human TNKS, GST-tagged | E.coli | Human | GST | 1-329aa | |
| TNKS-17187M | Recombinant Mouse TNKS Protein | Mammalian Cells | Mouse | His |
|
|
| TNKS-31498TH | Recombinant Human TNKS | Wheat Germ | Human | Non | 108 amino acids |
|
| TNKS-3328H | Recombinant Human TNKS protein, GST-tagged | Wheat Germ | Human | GST | 1017 a.a. - 1124 a.a. |
|
| TNKS-4878R | Recombinant Rhesus monkey TNKS Protein, His-tagged | Mammalian Cells | Rhesus macaque | His |
|
|
| TNKS-5912C | Recombinant Chicken TNKS | Mammalian Cells | Chicken | His |
|
|
| TNKS-0836H | Recombinant Human TNKS Protein (Q1091-Q1325), His tagged | E.coli | Human | His | Q1091-Q1325 |
|
| TNKS-0837H | Recombinant Human TNKS Protein (Q1091-Q1325), Tag Free | E.coli | Human | Non | Q1091-Q1325 |
|
| TNKS-459H | Recombinant Human TNKS Protein, His-tagged | E.coli | Human | His | Gly1105-Thr1327 |
|
| TNKS-4692R | Recombinant Rhesus Macaque TNKS Protein, His (Fc)-Avi-tagged | HEK293 | Rhesus macaque | Avi&Fc&His |
|
|
| TNKS-4692R-B | Recombinant Rhesus Macaque TNKS Protein Pre-coupled Magnetic Beads | HEK293 | Rhesus macaque |
|
||
| TNKS-9490M | Recombinant Mouse TNKS Protein, His (Fc)-Avi-tagged | HEK293 | Mouse | Avi&Fc&His |
|
|
| TNKS-9490M-B | Recombinant Mouse TNKS Protein Pre-coupled Magnetic Beads | HEK293 | Mouse |
|
Background
What is TNKS Protein?
TNKS gene (tankyrase) is a protein coding gene which situated on the short arm of chromosome 8 at locus 8p23. Enables histone binding activity; pentosyltransferase activity; and zinc ion binding activity. Involved in several processes, including negative regulation of maintenance of mitotic sister chromatid cohesion, telomeric; protein ADP-ribosylation; and regulation of nucleobase-containing compound metabolic process. Acts upstream of or within peptidyl-serine phosphorylation; peptidyl-threonine phosphorylation; and protein ADP-ribosylation. Located in several cellular components, including chromosome, telomeric region; mitotic spindle pole; and nucleus. The TNKS protein is consisted of 1327 amino acids and TNKS molecular weight is approximately 142.0 kDa.
What is the Function of TNKS Protein?
TNKS protein is a member of the polyadenosine diphosphate ribose polymerase (PARP) family. It has two unique domains: ankyloprotein repeat clusters and SAM domains, which mediate protein-protein interactions and form homologous or heterologous polymers. TNKS proteins play a role in a variety of cellular functions, including telomere homeostasis, Wnt signaling pathways, glucose metabolism, and spindle formation during mitosis. TNKS regulate the stability of target proteins mainly through polyADP-ribosylation (PARs), and its catalytic domain is a potential drug target. Drugs targeting TNKS are primarily inhibitors that inhibit the enzyme activity of TNKS by preventing it from catalyzing the transfer of ADP ribose from NAD+ to the target protein, thereby inhibiting its enzyme activity.
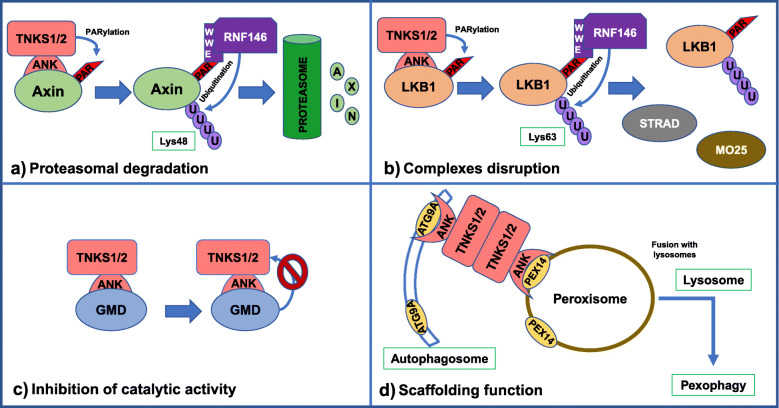
Fig1. Biological responses triggered after the recognition of TNKS1/2 substrates. (Esteban Zamudio-Martinez, 2021)
TNKS Related Signaling Pathway
The TNKS protein, end-anchor polymerase, is involved in several important cell signaling pathways, the most well-known of which is the Wnt/β-catenin signaling pathway. In the Wnt signaling pathway, TNKS regulate the stability of key proteins through their polyADP PARsylation activity. Specifically, TNKS were able to reduce the stability of degradation complexes containing the Axin protein, a negative regulator in the Wnt signaling pathway. By promoting Axin degradation, TNKS can increase the level of Wnt signaling, thereby affecting cell proliferation and tumorigenesis.
TNKS Related Diseases
Abnormal expression or dysfunction of TNKS protein is associated with a variety of diseases, especially cancer, such as colorectal cancer, ovarian cancer, breast cancer, etc., because of the regulatory role of TNKS in the Wnt/β-catenin signaling pathway, the abnormal activation of which is closely related to the proliferation, survival and migration of tumor cells. In addition, TNKS is also associated with the occurrence and development of neurodegenerative diseases and some genetic diseases, which indicates that TNKS plays an important role in cell cycle regulation, cell aging and genetic stability maintenance.
Bioapplications of TNKS
Due to its key role in the Wnt signaling pathway, the relevant off-the-shelf applications of TNKS are mainly concentrated in the field of drug development, especially inhibitors targeting TNKS, which can reduce the abnormal activation of Wnt signaling by blocking the polyADP ribosylylation activity of TNKS, thus in the treatment of certain types of cancer. Such as colorectal cancer, ovarian cancer and breast cancer have shown potential therapeutic effects. There are currently several PARP inhibitors, including olaparib and nilaparib, which inhibit TNKS and have been approved for the treatment of specific cancers. In addition, the research and development of TNKS inhibitors is still ongoing and aims to provide new therapeutic strategies for the treatment of diseases associated with the Wnt signaling pathway.
Case Study
Case Study 1: Xihua Yue, 2021
Altered glycosylation plays an important role during development and is also a hallmark of increased tumorigenicity and metastatic potentials of several cancers. In this study, Tankyrase-1 (TNKS1) controls protein glycosylation by Poly-ADP-ribosylation (PARylation) of a Golgi structural protein, Golgin45, at the Golgi. TNKS1 is a Golgi-localized peripheral membrane protein that plays various roles throughout the cell, ranging from telomere maintenance to Glut4 trafficking. This study indicates that TNKS1 localization to the Golgi apparatus is mediated by Golgin45. TNKS1-dependent control of Golgin45 protein stability influences protein glycosylation, as shown by Glycomic analysis. Further, FRAP experiments indicated that Golgin45 protein level modulates Golgi glycosyltransferease trafficking in Rab2-GTP-dependent manner.
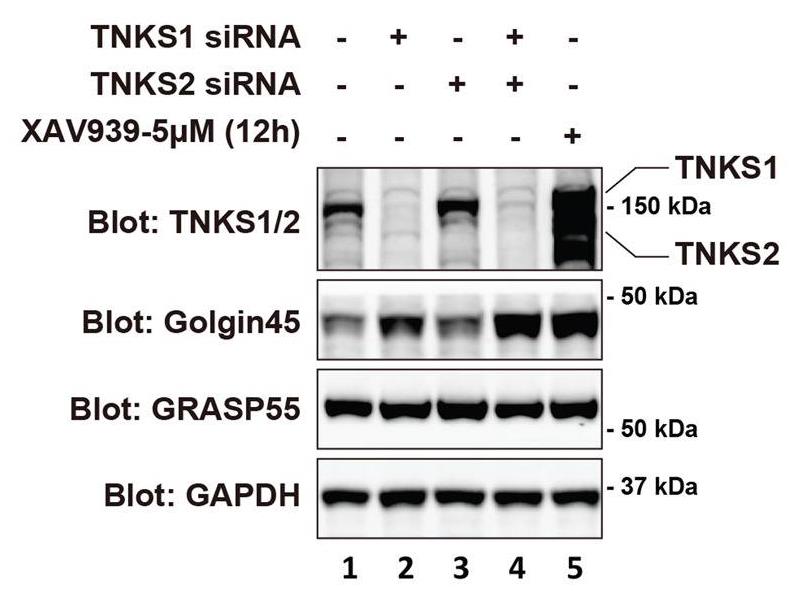
Fig1. Effects of knockdown of TNKS1 or/and TNKS2 on the protein level of Golgin45.
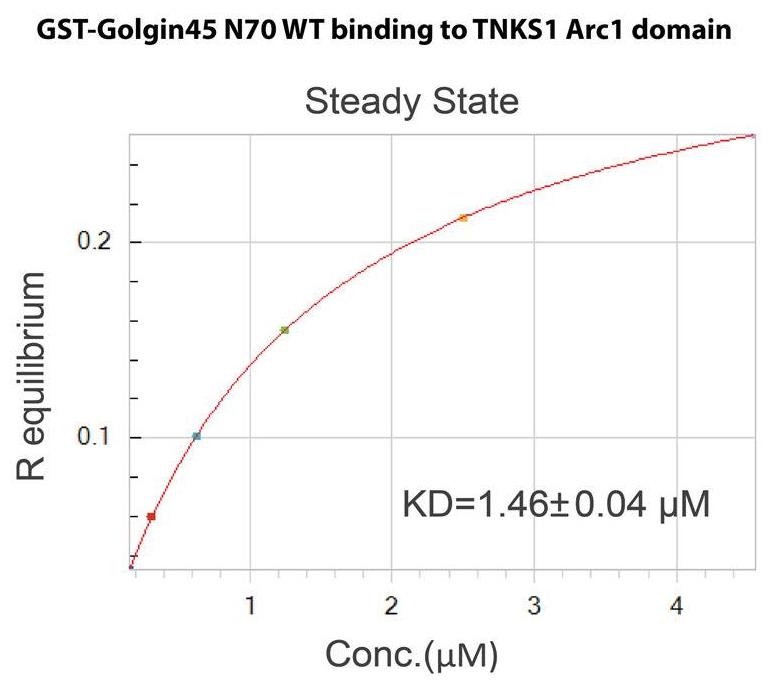
Fig2. Steady-state analysis of the interaction between Golgin45 N70 WT and TNKS1 Arc1 domain, using Biolayer interferometry assays.
Case Study 2: Yichi Zhou, 2019
Osteosarcoma is the most common malignant tumor of bone with a high potential for metastasis and poor prognosis. This study intends to explore the effect of tankyrase1 (TANK1) in the development of osteosarcoma cells and the underlying mechanism. The osteosarcoma cell line MG-63 cells were cultured and transfected with tankyrase1 antisense oligodeoxynucleotides (TANK1-ASODN). Cell proliferation was detected with CCK-8 and immunofluorescence. Cell migration and invasion were examined by wound healing assay and Transwell assay, respectively. Reverse transcription-quantitative polymerase chain reaction was performed to detect the mRNA level of TANK1 and western blot was conducted to detect relative protein expression during the research. As a result, TANK1 was upregulated in osteosarcoma. The TANK1-ASODN inhibited MG-63 cell proliferation, migration and invasion. The progress of epithelial-mesenchymal transition (EMT) was also suppressed in TANK1-ASODN transfected MG-63 cells compared to control group. Besides, the TANK1-ASODN activated and modulated the Hippo/YAP signaling which might be the pathway that TANK1 depended on.
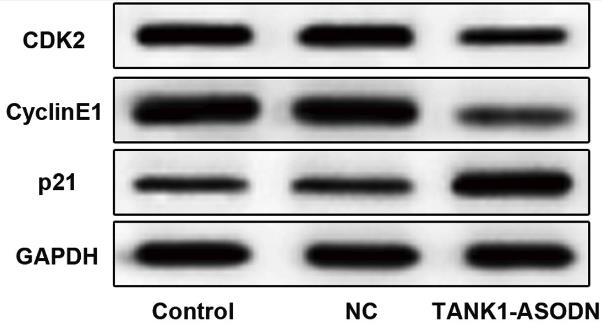
Fig3. The protein expressions of CDK2, cyclin E1 and p21 were determined by western blot.
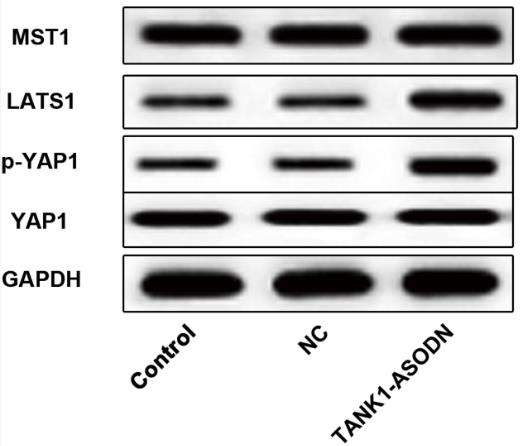
Fig4. The relative protein expression of Hippo/YAP signaling was examined by western blot.
Quality Guarantee
High Purity
.jpg)
Fig1. SDS-PAGE (TNKS-459H)
Involved Pathway
TNKS involved in several pathways and played different roles in them. We selected most pathways TNKS participated on our site, such as Degradation of AXIN,Disease,Diseases of signal transduction, which may be useful for your reference. Also, other proteins which involved in the same pathway with TNKS were listed below. Creative BioMart supplied nearly all the proteins listed, you can search them on our site.
| Pathway Name | Pathway Related Protein |
|---|---|
| Diseases of signal transduction | CCNC,CDK8,MIB1,KREMEN1,CDC37,RBP1,FKBP1A,LRRFIP1,CUX1,FGFR1OP |
| TCF dependent signaling in response to WNT | HECW1B,SOX6,SOX9A,LGR4,SOX13,CCDC88C,CDC73,RNF43,SRY,SOX4B |
| Signal Transduction | PDK3B,NTS,TULP3,WDR35,OXGR1A.3,SOX9B,CNR2,AMOTL2A,FGFBP2,TLE3 |
| Degradation of AXIN | TNKS2,RNF146 |
| Signaling by Wnt | CDC73,WLS,LGR5,KREMEN1,DACT1,GPR177,FMNL3,LGR6,SRY,WIF1 |
| Signaling by WNT in cancer | TNKS2,KREMEN1,RNF43,KREMEN2 |
| Disease | SFTPB,AP1G1,MTRR,SUPT5H,HDAC5,CHMP4C,ARF1,MMAA,WHSC2,OPN1MW |
| Regulation of Telomerase | SP3,DKC1,MXD1,PINX1,CMTM2A,NR2F2 |
Protein Function
TNKS has several biochemical functions, for example, NAD+ ADP-ribosyltransferase activity,protein binding,zinc ion binding. Some of the functions are cooperated with other proteins, some of the functions could acted by TNKS itself. We selected most functions TNKS had, and list some proteins which have the same functions with TNKS. You can find most of the proteins on our site.
| Function | Related Protein |
|---|---|
| NAD+ ADP-ribosyltransferase activity | PARP12,GIG2L,ART1,GIG2F,GIG2E,PARP14,PARP9,SIRT4,CHAT2,PARP8 |
| protein binding | C16orf48,KCNJ10,PYCARD,MAP2,DIS3L2,NOL11,RGS8,CCDC70,PIKFYVE,DUSP5 |
| zinc ion binding | RNF212,RNF169,AGBL1,CPA5,RNF25,MARCH4,CHMP1A,RP9,TTC3,AGBL2 |
Interacting Protein
TNKS has direct interactions with proteins and molecules. Those interactions were detected by several methods such as yeast two hybrid, co-IP, pull-down and so on. We selected proteins and molecules interacted with TNKS here. Most of them are supplied by our site. Hope this information will be useful for your research of TNKS.
TERF1;FNBP1;Axin1;xav939;CENPJ;nad+
Resources
Related Services
Related Products
References
- Shebzukhov, YV; Lavrik, IN; et al. Human tankyrases are aberrantly expressed in colon tumors and contain multiple epitopes that induce humoral and cellular immune responses in cancer patients. CANCER IMMUNOLOGY IMMUNOTHERAPY 57:871-881(2008).
- Kuimov, AN; Kuprash, DV; et al. Cloning and characterization of TNKL, a member of tankyrase gene family. GENES AND IMMUNITY 2:52-55(2001).


