TNFAIP3
-
Official Full Name
tumor necrosis factor, alpha-induced protein 3 -
Overview
NF-B (nuclear factor B) regulates the expression of a large number of genes that play critical roles in apoptosis, viral replication, tumorigenesis, various autoimmune diseases and inflammation. The zinc finger protein A20 is a tumor necrosis factor and interleukin 1 (IL-1)-inducible protein that negatively regulates NF-B gene expression by interferring with a novel TNF-induced and RIP-or TRAF2-mediated pathway that is different from the NIK-IB kinase pathway. A20, an 70 kDa protein, is expressed at low levels in most organs, the highest expression levels being in lymphoid tissues. -
Synonyms
TNFAIP3;tumor necrosis factor, alpha-induced protein 3;tumor necrosis factor alpha-induced protein 3;A20;OTUD7C;TNFAIP3 (A20);zinc finger protein A20;TNF alpha-induced protein 3;OTU domain-containing protein 7C;putative DNA-binding protein A20;tumor necrosis factor inducible protein A20;TNFA1P2;MGC104522;MGC138687;MGC138688
Recombinant Proteins
- Human
- Cynomolgus
- Rhesus macaque
- Mouse
- E.coli
- Mammalian Cells
- HEK293
- Wheat Germ
- Sf9 Cells
- In Vitro Cell Free System
- GST
- His
- DDK
- Myc
- Flag
- Avi
- Fc
Background
What is TNFAIP3 protein?
TNFAIP3 gene (TNF alpha induced protein 3) is a protein coding gene which situated on the long arm of chromosome 6 at locus 6q23. This gene was identified as a gene whose expression is rapidly induced by the tumor necrosis factor (TNF). The protein encoded by this gene is a zinc finger protein and ubiqitin-editing enzyme, and has been shown to inhibit NF-kappa B activation as well as TNF-mediated apoptosis. The encoded protein also known as A20, which has both ubiquitin ligase and deubiquitinase activities, is involved in the cytokine-mediated immune and inflammatory responses. The TNFAIP3 protein is consisted of 790 amino acids and TNFAIP3 molecular weight is approximately 89.6 kDa.
What is the function of TNFAIP3 protein?
TNFAIP3 is a protein that plays a key role within cells, primarily in regulating inflammation and immune responses. It regulates the NF-κB signaling pathway through deubiquitination and phosphorylation processes, thereby inhibiting inflammatory responses and promoting immune cell homeostasis. Polymorphisms in the TNFAIP3 gene are associated with the risk of multiple autoimmune diseases. Furthermore, biallelic mutations in the TNFAIP3 gene have been linked to the development of certain B-cell lymphomas, suggesting that A20 may act as a tumor suppressor in these cancers. Abnormal expression and function of A20 are closely related to the occurrence and development of a variety of diseases, making it a potential therapeutic target.

Fig1. A20 effect on different cell populations. (Andreas Kommer, 2024)
TNFAIP3 related signaling pathway
TNFAIP3 is a key regulatory protein that regulates immune responses by inhibiting inflammatory responses and apoptosis. In the signaling pathway, TNFAIP3 expression is regulated by many factors, including inflammatory factors, cellular stress and tumor suppressor factors. Activated forms of TNFAIP3, such as IκBα, inhibit the activity of the nuclear factor κB (NF-κB) signaling pathway, thereby reducing the production of inflammatory factors. In addition, TNFAIP3 is involved in regulating other signaling pathways, such as JNK, p38 MAPK, and NF-κB, which further affect cell survival, proliferation, and differentiation. Tnfaip3-related signaling pathways play an important role in a variety of diseases, including inflammatory diseases, autoimmune diseases, and cancer. For example, in cancer, the inactivation or mutation of TNFAIP3 may lead to overactivation of the NF-κB signaling pathway, which promotes tumor cell growth and metastasis.
TNFAIP3 related diseases
Abnormal functioning of TNFAIP3 has been associated with a variety of autoimmune diseases, such as systemic lupus erythematosus, rheumatoid arthritis, and inflammatory bowel disease. In addition, deleterious mutations in the germ line of the TNFAIP3 gene are also associated with these diseases. In the field of cancer, mutations in TNFAIP3 are associated with malignant transformation of lymphomas and have been found in B-cell lymphomas, T-cell large granular lymphocytic leukemia (LGL) and peripheral T-cell lymphomas. In colorectal cancer, TNFAIP3 affects the immune escape of cancer cells and the effect of immunotherapy by modulating the "eat me" signal of immune cells.
Bioapplications of TNFAIP3
The TNFAIP3 protein inhibits inflammation by negatively regulating the NF-κB signaling pathway, a function that makes it potentially therapeutic in the prevention of autoimmune diseases and certain cancers. In non-alcoholic fatty liver disease (NAFLD), TNFAIP3 inhibits the activity of ASK1 as well as downstream P38/JNK, thereby preventing the onset and progression of the disease. In addition, TNFAIP3 also plays a protective role in liver ischemia-reperfusion injury, and decreased expression may lead to more severe liver injury. In cancer treatment, expression levels of TNFAIP3 may influence patient response to tumor necrosis factor (TNF) blocking therapies. Therefore, TNFAIP3 has a wide range of applications in biomedical research and clinical therapy, including as a therapeutic target and its potential value in drug development and clinical applications.
Case Study
Case Study 1: Chi Ma, 2023
This research investigated the role of TNFAIP3 in Parkinson's disease (PD) development, focusing on its links to autophagy and inflammation. The decreased TNFAIP3 levels in the substantia nigra of PD patients, a mouse model, and in MPP+-exposed SK-N-SH cells. TNFAIP3 was shown to suppress inflammation and boost autophagy, which helped ameliorate PD symptoms in mice. The study also noted increased activity of the NFκB and mTOR pathways in the PD mouse model and MPP+-treated cells. TNFAIP3's ability to inhibit these pathways was attributed to its role in preventing NFκB p65 subunit nuclear translocation and in stabilizing DEPTOR, an mTOR antagonist. The protective effects of TNFAIP3 were counteracted by the NFκB activator LPS and the mTOR activator MHY1485 in PD mice and MPP+-treated SK-N-SH cells.
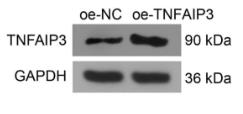
Fig1. TNFAIP3 protein expression in SK-N-SH cells upon treatment of oe-TNFAIP3 or oe-NC and MPP+ induction.
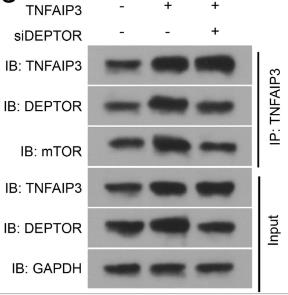
Fig2. Relationship among TNFAIP3, DEPTOR and mTOR using co-IP assay.
Case Study 2: Wanru Feng, 2022
Breast cancer stem cells (BCSCs), a minor self-renewing cell subset, are implicated in tumor initiation, progression, and therapy resistance. The previous research established that TNFAIP3 is crucial for FGFR1 signaling in breast cancer growth. This study further explores TNFAIP3's role in BCSC regulation. Results showed that activation of the FGFR1-MEK-ERK pathway increases ALDH-positive BCSCs, an effect reversed by inhibitors of FGFR1, MEK, or ERK. TNFAIP3 knockout or suppression reduced ALDH-positive BCSCs. In vivo, TNFAIP3 silencing in MDA-MB-231 xenografts resulted in smaller tumors with reduced ALDH levels. Additionally, TNFAIP3 was found to regulate the expression of stemness-related transcription factors.
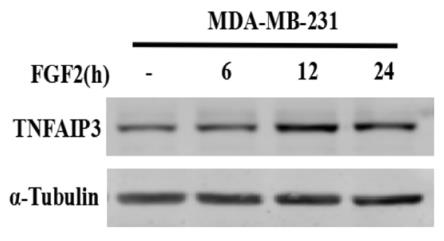
Fig3. TNFAIP3 was detected for periods of FGF2 treatment by western blotting.
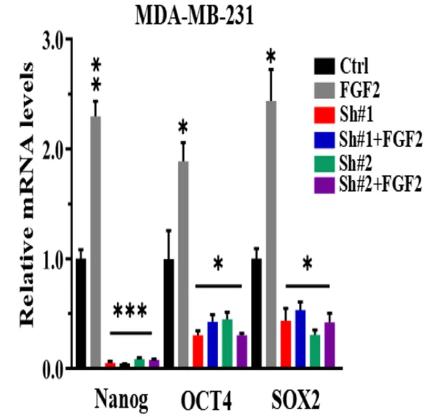
Fig4. Fold change of stemness genes expression in shTNFAIP3 cells.
Quality Guarantee
High Purity
.jpg)
Fig1. SDS-PAGE (TNFAIP3-1013HFL)
.
.jpg)
Fig2. SDS-PAGE (TNFAIP3-566H)
Involved Pathway
TNFAIP3 involved in several pathways and played different roles in them. We selected most pathways TNFAIP3 participated on our site, such as NF-kappa B signaling pathway,NOD-like receptor signaling pathway,TNF signaling pathway, which may be useful for your reference. Also, other proteins which involved in the same pathway with TNFAIP3 were listed below. Creative BioMart supplied nearly all the proteins listed, you can search them on our site.
| Pathway Name | Pathway Related Protein |
|---|---|
| Measles | IL1A,CD28,Fasl,CD3E; CD3D,IL2RG,IL4,OAS1A,CBLB,TP53,IRAK1 |
| NF-kappa B signaling pathway | LTA,CCL4L1,LY96,IKBKG,BTK,SYK,IL-8,MAP3K14,PIAS4,LTB |
| Epstein-Barr virus infection | PSMD1,EIF2AK2,SNW1,POLR2L,ENTPD1,HLA-E,TAB1,SYK,CD58,CCNA1 |
| NOD-like receptor signaling pathway | MAP3K7IP3,CXCL1,MAPK12,SGUT1,ERBB2IP,IL-8,BIRC3,IL18,PYCARD,PYDC1 |
| TNF signaling pathway | NFKB1,NFKBIA,MAPK13,FADD,IL15,CCL2,SOCS3,CREB5,MAPK9,PIK3R5 |
Protein Function
TNFAIP3 has several biochemical functions, for example, DNA binding,K63-linked polyubiquitin binding,kinase binding. Some of the functions are cooperated with other proteins, some of the functions could acted by TNFAIP3 itself. We selected most functions TNFAIP3 had, and list some proteins which have the same functions with TNFAIP3. You can find most of the proteins on our site.
| Function | Related Protein |
|---|---|
| protein self-association | DYRK1A,ABCD3,AGTR1A,CBR2,SVIP,TMEM190,AGTR1B,CNTN2,TRP53,ZFP639 |
| zinc ion binding | KPNB1,UQCRC2B,KAT7B,NR4A2B,ZFP330,LMO1,CPO,SHARPIN,FUS,ALKBH8 |
| DNA binding | PURBB,HER9,PIAS2,FOXE1,NKX2.3,ZNF385A,TAF1A,TSHZ3,RPS3,AGFG1 |
| ubiquitin-protein transferase activity | MIB2,TRIM68,LNX2B,MARCH6,ZNRF1,UBE2D2,NSMCE1,RNF141,WWP1,FBXO40.1 |
| ligase activity | TRAF6,TTLL13,CBLB,RNF216,BIRC2,RNF34,RNF19B,RNF38,UBR5,RNF220 |
| ubiquitin binding | USP13,UCHL3,CRY1,UBXN11,RNF168,FAF2,USP5,UCHL1,SIRT2,UBXN1 |
| kinase binding | SP100,CDC37,C2orf44,CTNNB1,TAX1BP1,PFKFB1,CEBPB,STUB1,HPCA,BARD1 |
| K63-linked polyubiquitin binding | OTUD7B,TAB2,RNF168,ZRANB3,IKBKG,ZRANB1,ATRIP,ZRANB1B,PRPF8,UIMC1 |
| protease binding | ECM1,RFFL,FURIN,ITGAV,FLOT1,CCDC71L,Casp3,SERPINB3,BCL2,XBP1 |
Interacting Protein
TNFAIP3 has direct interactions with proteins and molecules. Those interactions were detected by several methods such as yeast two hybrid, co-IP, pull-down and so on. We selected proteins and molecules interacted with TNFAIP3 here. Most of them are supplied by our site. Hope this information will be useful for your research of TNFAIP3.
IKBKG;TNIP1;TNIP2;RNF11;TRIM23;TRAF2
Resources
Research Area
Regulator of NFkBUbiquitin-related Molecules in the Akt Pathway
Deubiquitinating Enzymes (DUBs)
E3 Ubiquitin Ligases
Glioma/Medulloblastoma Cancer Stem Cell Markers
Related Services
Related Products
References


