SEPP1
-
Official Full Name
selenoprotein P, plasma, 1 -
Synonyms
SEPP1;selenoprotein P, plasma, 1;selenoprotein P;SeP;SELP
Recombinant Proteins
- Mouse
- Chicken
- Rat
- Human
- Bovine
- Mammalian Cells
- Yeast
- E.coli
- HEK293
- His
- Avi
- Fc
- GST
| Cat.# | Product name | Source (Host) | Species | Tag | Protein Length | Price |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| SEPP1-14888M | Recombinant Mouse SEPP1 Protein | Mammalian Cells | Mouse | His |
|
|
| SEPP1-3247C | Recombinant Chicken SEPP1 | Mammalian Cells | Chicken | His |
|
|
| SEPP1-5321R | Recombinant Rat SEPP1 Protein | Mammalian Cells | Rat | His |
|
|
| SEPP1-1513H | Recombinant Human SEPP1 Protein (20-381 aa), His-tagged | Yeast | Human | His | 20-381 aa |
|
| Sepp1-2051R | Recombinant Rat Sepp1 Protein, His-tagged | E.coli | Rat | His | Tyr60-Ser263 |
|
| SEPP1-3478H | Recombinant Human SEPP1 protein, His-tagged | E.coli | Human | His | 20-381aa(U59S,U300S,U318S,U330S,U345S,U352S,U367S,U369S,U376S,U378S) |
|
| SEPP1-4980R | Recombinant Rat SEPP1 Protein, His (Fc)-Avi-tagged | HEK293 | Rat | Avi&Fc&His |
|
|
| SEPP1-4980R-B | Recombinant Rat SEPP1 Protein Pre-coupled Magnetic Beads | HEK293 | Rat |
|
||
| SEPP1-801B | Recombinant Bovine SEPP1 Protein (20-402 aa), GST-tagged | E.coli | Bovine | GST | 20-402 aa |
|
| SEPP1-8021M | Recombinant Mouse SEPP1 Protein, His (Fc)-Avi-tagged | HEK293 | Mouse | Avi&Fc&His |
|
|
| SEPP1-8021M-B | Recombinant Mouse SEPP1 Protein Pre-coupled Magnetic Beads | HEK293 | Mouse |
|
||
| SEPP1-802H | Recombinant Human SEPP1 Protein (20-381 aa), His-tagged | E.coli | Human | His | 20-381 aa |
|
Background
What is SEPP1 protein?
SEPP1 gene (selenoprotein P) is a protein coding gene which situated on the short arm of chromosome 5 at locus 5p12. This gene encodes a selenoprotein that is predominantly expressed in the liver and secreted into the plasma. This selenoprotein is unique in that it contains multiple selenocysteine (Sec) residues per polypeptide (10 in human), and accounts for most of the selenium in plasma. It has been implicated as an extracellular antioxidant, and in the transport of selenium to extra-hepatic tissues via apolipoprotein E receptor-2 (apoER2). The SEPP1 protein is consisted of 381 amino acids and SEPP1 molecular weight is approximately 43.2 kDa.
What is the function of SEPP1 protein?
SEPP1, or selenoprotein P, is a multifunctional protein that plays a critical role in selenium homeostasis and distribution within the body. It is composed of two distinct domains: the N-terminal domain, which has redox properties and is involved in antioxidant defense, and the C-terminal domain, which is rich in selenium and important for the transport of this essential trace element. SEPP1 is secreted by the liver and found in plasma, where it is responsible for carrying selenium to various tissues, including the brain, testes, and kidney. It also plays a protective role in the body's response to infections, such as trypanosomiasis. Furthermore, SEPP1 can be used as a biomarker for selenium nutritional status, as its plasma concentration decreases in cases of selenium deficiency.
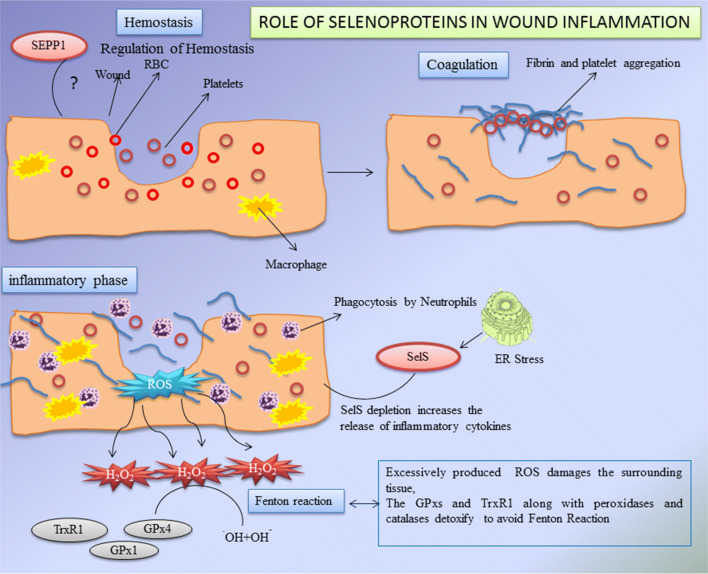
Fig1. Role of selenoproteins during wound healing process. (Sneha Hariharan, 2020)
SEPP1 related signaling pathway
The SEPP1-related signaling pathway is involved in selenium metabolism and plays a crucial role in the biosynthesis of selenoproteins, which are essential for various cellular functions including antioxidant defense, redox homeostasis, and thyroid hormone metabolism. SEPP1 acts as a selenium transport protein, facilitating the delivery of selenium to selenoprotein synthesizing enzymes such as selenocysteine lyase. Dysregulation of this pathway can lead to selenium deficiency or toxicity, affecting overall cellular function and contributing to diseases like Keshan disease and Kashin-Beck disease.
SEPP1 related diseases
SEPP1-related diseases are primarily associated with disorders of selenium metabolism and homeostasis. SEPP1, as a key selenoprotein, plays a crucial role in the transport and distribution of selenium, an essential micronutrient involved in antioxidant defense mechanisms, thyroid hormone metabolism, and immune function. Deficiencies or mutations in SEPP1 can lead to conditions such as Keshan disease and Kashin-Beck disease, which are characterized by cardiomyopathy and osteoarthropathy, respectively. Additionally, imbalances in selenium levels due to altered SEPP1 function may contribute to other health issues, including certain types of cancer and inflammatory diseases, highlighting the importance of this protein in maintaining overall selenium status and preventing related pathologies.
Bioapplications of SEPP1
SEPP1 is the major selenoprotein in plasma and plays a critical role in selenium homeostasis and transport. It is responsible for delivering selenium to various tissues, including the brain and testes, and is involved in maintaining selenium levels in extra-hepatic tissues. SEPP1 also has antioxidant properties and may serve as a biomarker for selenium nutritional status. Research suggests that SEPP1 may have additional functions beyond selenium transport, including roles in the immune response and protection against oxidative stress.
Case Study
Case Study 1: Kristina E. Hill, 2012
Selenoprotein P (Sepp1), which contains 10 selenocysteine residues, is crucial for transporting selenium from the liver to peripheral tissues via apoER2-mediated endocytosis. Mice lacking Sepp1 in hepatocytes exhibited reduced plasma Sepp1, increased urinary selenium excretion, and decreased whole-body selenium levels. Selenium deficiency led to a preference for Sepp1 synthesis over glutathione peroxidase-1 (Gpx1), highlighting Sepp1's role in selenium distribution and homeostasis, particularly during deficiency.
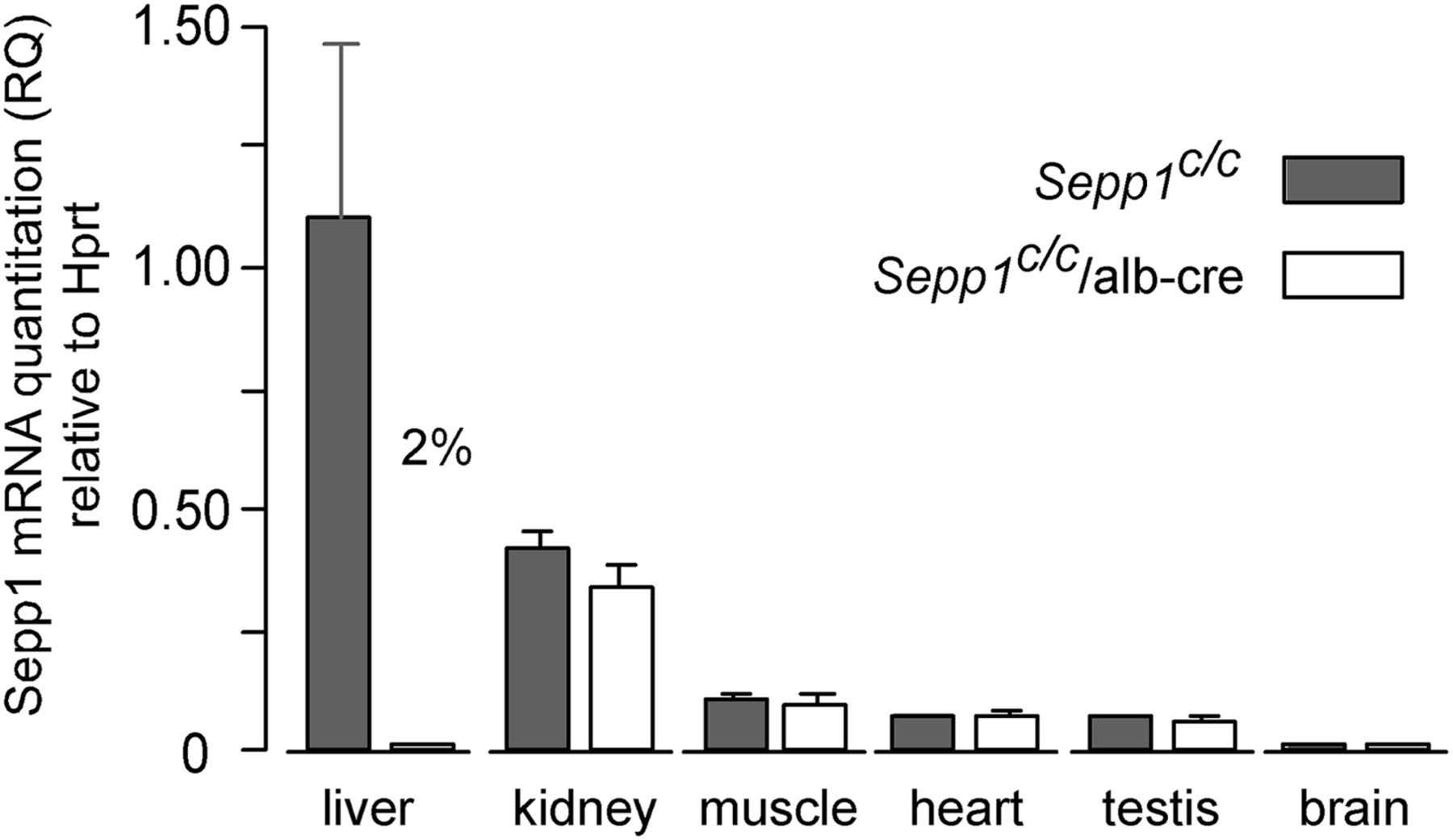
Fig1. Expression of Sepp1 mRNA in tissues from mice with deletion of hepatocyte Sepp1.
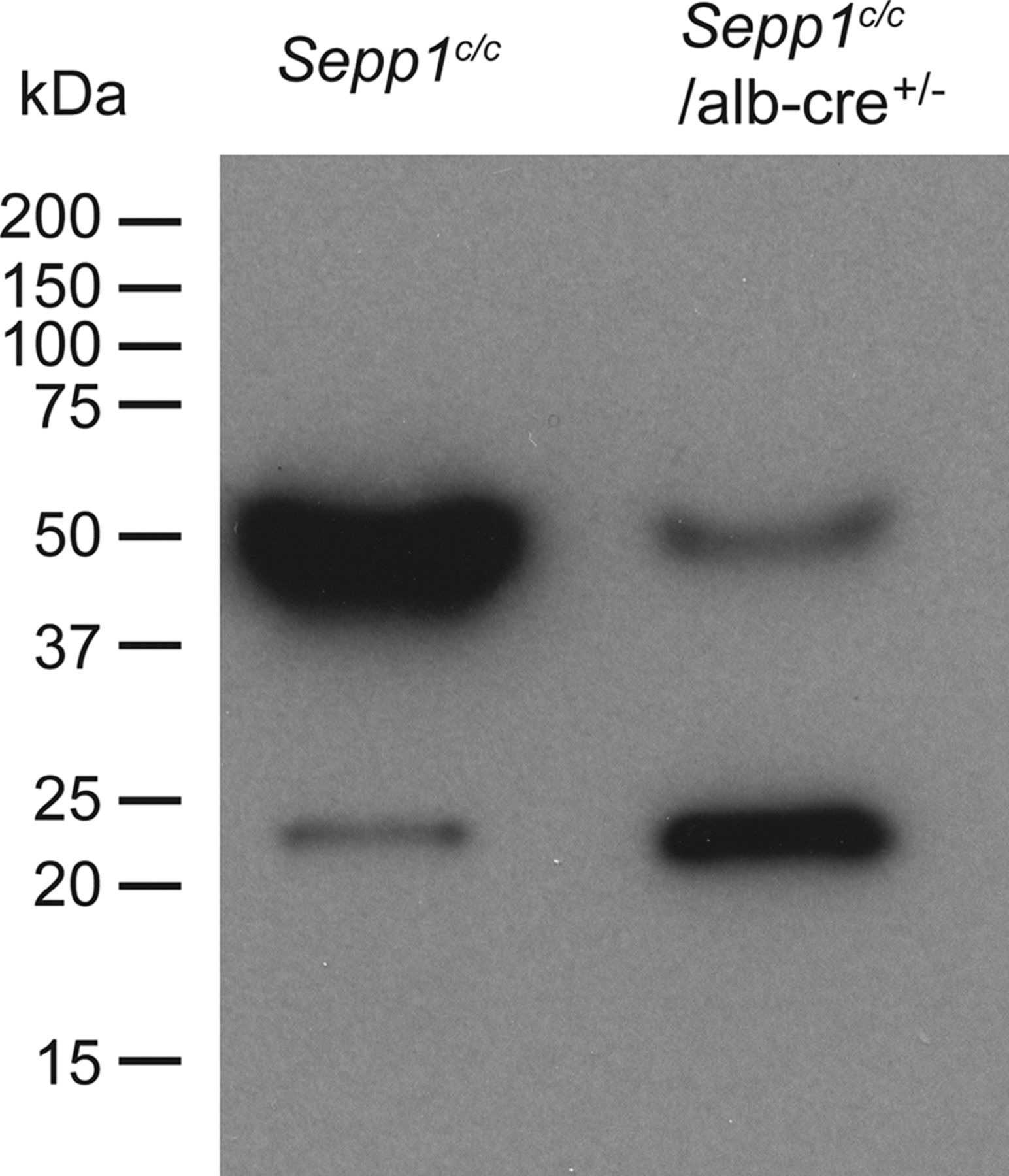
Fig2. Effect of hepatocyte Sepp1 deletion on the presence of plasma selenoproteins.
Case Study 2: Sumangala P. Shetty a, 2014
Selenoproteins contain the 21st amino acid, selenocysteine (Sec), which is incorporated using a recodable UGA stop codon. The study of SEPP1, a selenoprotein with 10 Sec residues, identified factors influencing Sec incorporation efficiency in vitro. Here the process is processive, requiring only SECIS elements, and is affected by selenium concentration. This suggests that unidentified mammalian-specific factors may be involved in efficient Sec incorporation, which is linked to selenium utilization.
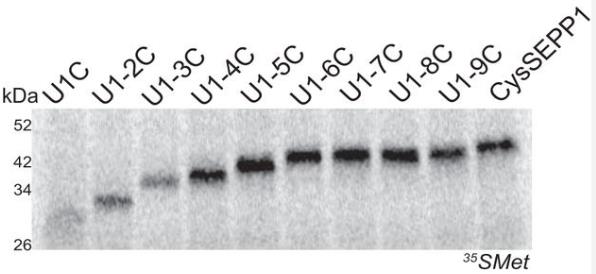
Fig3. All progressively mutated SEPP1 Sec to Cys mRNAs were translated in RRL.
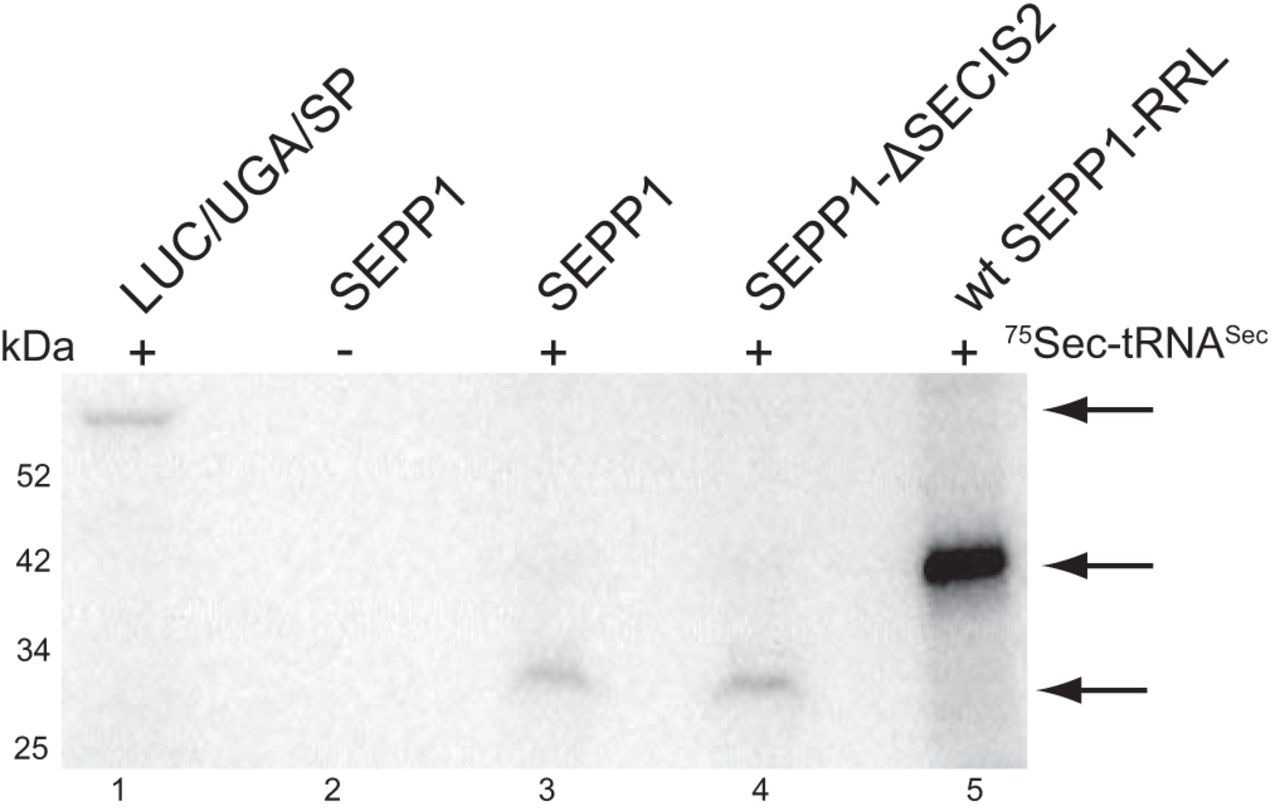
Fig4. Known Sec incorporation factors are not be sufficient for full-length SEPP1 synthesis.
Quality Guarantee
High Purity
.jpg)
Fig1. SDS-PAGE (SEPP1-802H)
.
.jpg)
Fig2. SDS-PAGE (SEPP-2051R)
Involved Pathway
SEPP1 involved in several pathways and played different roles in them. We selected most pathways SEPP1 participated on our site, such as ESC Pluripotency Pathways,Focal Adhesion,Integrin-mediated cell adhesion, which may be useful for your reference. Also, other proteins which involved in the same pathway with SEPP1 were listed below. Creative BioMart supplied nearly all the proteins listed, you can search them on our site.
| Pathway Name | Pathway Related Protein |
|---|---|
| Selenium metabolism/Selenoproteins | SELM,SELENBP2,SEPW1 |
| Focal adhesion | RHOAD,COL6A6,VTN,CAPN2,MYL12.1,SHC1,RAC1B,ACTN4,RAP1B,PIK3CA |
| Integrin-mediated cell adhesion | CAPN11,TNS1,MAPK4,SEPP1A,CAPN9,MAPK6,MYLK2,CAPN3,CAPNS1,CAPN10 |
| Selenium | TXNRD2,FMN1,MSRB1 |
Protein Function
SEPP1 has several biochemical functions, for example, selenium binding. Some of the functions are cooperated with other proteins, some of the functions could acted by SEPP1 itself. We selected most functions SEPP1 had, and list some proteins which have the same functions with SEPP1. You can find most of the proteins on our site.
| Function | Related Protein |
|---|---|
| selenium binding | SELENBP1,DIO2,SEP15,RPH3A,SELENBP2,GPX3,GPX1,SELT,DIO1 |
Interacting Protein
SEPP1 has direct interactions with proteins and molecules. Those interactions were detected by several methods such as yeast two hybrid, co-IP, pull-down and so on. We selected proteins and molecules interacted with SEPP1 here. Most of them are supplied by our site. Hope this information will be useful for your research of SEPP1.
Resources
Related Services
Related Products
References


