SEMA6B
-
Official Full Name
sema domain, transmembrane domain (TM), and cytoplasmic domain, (semaphorin) 6B -
Synonyms
SEMA6B;sema domain, transmembrane domain (TM), and cytoplasmic domain, (semaphorin) 6B;SEMAN;semaphorin-6B;SEM SEMA Y;Sema VIb;SEMA VIB;semaphorin VIB;semaphorin Z;semaZ;semaphorin-6Ba;SEMA-VIB;SEM-SEMA-Y
Recombinant Proteins
- Human
- Mouse
- Rat
- Mammalian Cells
- HEK293
- Fc
- His
- Avi
| Cat.# | Product name | Source (Host) | Species | Tag | Protein Length | Price |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| SEMA6B-1925H |
Active Recombinant Human SEMA6B, Fc Chimera
|
Mammalian Cells | Human | Fc |
|
|
| Sema6b-987M |
Active Recombinant Mouse Sema6b Protein, Fc Chimera
|
HEK293 | Mouse | Fc |
|
|
| SEMA6B-14875M | Recombinant Mouse SEMA6B Protein | Mammalian Cells | Mouse | His |
|
|
| SEMA6B-5315R | Recombinant Rat SEMA6B Protein | Mammalian Cells | Rat | His |
|
|
| SEMA6B-138H | Recombinant Human SEMA6B Protein, His (Fc)-Avi-tagged | HEK293 | Human | Avi&Fc&His |
|
|
| SEMA6B-138H-B | Recombinant Human SEMA6B Protein Pre-coupled Magnetic Beads | HEK293 | Human |
|
||
| SEMA6B-4974R | Recombinant Rat SEMA6B Protein, His (Fc)-Avi-tagged | HEK293 | Rat | Avi&Fc&His |
|
|
| SEMA6B-4974R-B | Recombinant Rat SEMA6B Protein Pre-coupled Magnetic Beads | HEK293 | Rat |
|
||
| SEMA6B-8010M | Recombinant Mouse SEMA6B Protein, His (Fc)-Avi-tagged | HEK293 | Mouse | Avi&Fc&His |
|
|
| SEMA6B-8010M-B | Recombinant Mouse SEMA6B Protein Pre-coupled Magnetic Beads | HEK293 | Mouse |
|
Background
What is SEMA6B Protein?
SEMA6B is a protein that's part of the semaphorins family, which mostly helps guide axons during neural development. Interestingly, SEMA6B has caught researchers' eyes because it's thought to be involved in cancer progression. Studies, particularly ones using breast cancer tissues, have shown that its levels are often knocked down in cancerous versus normal tissues. There's also a newly identified version of this protein called SEMA6Ba, which interestingly lacks a specific part that's crucial for certain cell signaling processes. This variant was found to hang out in the endoplasmic reticulum and plasma membrane. All in all, while SEMA6B is mostly known for its role in nerve guidance, it may have significant implications in cancer research as well.
What is the Function of SEMA6B Protein?
SEMA6B is a protein that plays a role in guiding nerves and cellular interactions. Recently, it's been looked at for its part in cancer, especially since it's expressed differently in some cancer tissues compared to normal ones. In the case of breast cancer, SEMA6B levels drop significantly. There's also a new version of it called SEMA6Ba, which differs in how it's spliced, missing some parts that normally interact with other molecules, and it seems to hang out in places like the cell's endoplasmic reticulum and plasma membrane.
SEMA6B Related Signaling Pathway
SEMA6B is a protein that's part of the semaphorin family, mainly known for guiding axons during neural development. But it's not just about nerves; SEMA6B also dabbles in various cellular pathways, impacting how cells move and interact. It's been found to play roles in both promoting and hindering processes depending on the context. For instance, in cancer research, folks have noticed it might influence tumor growth or suppression. Overall, SEMA6B acts like a cellular traffic cop, guiding and controlling different signaling pathways to maintain balance in bodily functions.
SEMA6B Related Diseases
SEMA6B, known as a member of the semaphorin family, is primarily involved in guiding axons during neural development. Recently, studies have linked SEMA6B to various diseases, especially cancer. It seems that changes in SEMA6B expression might influence cancer progression, with evidence pointing towards its downregulation in some breast cancer tissues. This suggests SEMA6B could play a role in tumor growth or suppression. Apart from cancer, there's ongoing research exploring its involvement in other conditions due to its role in cell signaling and tissue development. Overall, while SEMA6B's functions in diseases are still being unraveled, its importance in cancer biology is becoming increasingly evident.
Bioapplications of SEMA6B
SEMA6B is part of the semaphorin family, known for guiding axons during neural development, and has caught researchers' interest, particularly in cancer studies. It's been noted that SEMA6B might play a role in how cancer progresses, making it a topic of investigation for those trying to understand tumor growth and metastasis. In research and industry, synthesizing SEMA6B could be helpful for developing cancer therapies or even diagnostic tools. By understanding how SEMA6B interacts within signaling pathways, scientists hope to pinpoint how it affects cancer cells - information that can lead to novel treatment strategies. Overall, it's a promising area for those looking to tackle cancer from a molecular angle.
Case Study
Case Study 1: Luciana D'Apice, 2013
SEMA6B, a part of the semaphorin family that guides axons, is gaining traction for its potential role in cancer. Recent studies reveal that in breast cancer tissues, SEMA6B expression is markedly reduced compared to normal tissues. A new twist in the tale is the discovery of an isoform, SEMA6Ba, which was identified through real-time PCR analysis. This variant results from distinct splice site usage within exon 17, leading to a transcript lacking some miRNA binding sites, which might affect its expression. Additionally, SEMA6Ba's protein product, identified via immunofluorescence, is found in the endoplasmic reticulum and plasma membrane but lacks the important cytoplasmic tail, impacting its signaling abilities. In short, SEMA6B's downregulation and this novel isoform's characterization in breast cancer offer fresh avenues for understanding its role in cancer biology.

Fig1. Representative Western blotting of cell culture supernatant (lane 1) and crude MCF-7 extract (lane 2) with anti-SEMA6B antibody.

Fig2. Total cell lysate of MCF-7 cells treated with 1): non targeting siRNA, 2) SEMA6B siRNA 100 nM or 3) SEMA6B siRNA 150 nM.
Case Study 2: Hunsang Lee, 2020
Pathogenic clostridia release toxins that cause major tissue harm, with Paeniclostridium sordellii's toxin (TcsL) often leading to deadly toxic shock, especially in gynecological cases. TcsL shares a lot with C. difficile's toxin but impacts different body parts, like blood vessels, hinting it uses different entryways into cells. Through CRISPR/Cas9, SEMA6A and SEMA6B were identified as TcsL gateways. Interestingly, engineered SEMA6A can defend mice from TcsL's effects. Structural analysis reveals TcsL binds to SEMA6A similar to how TcdB latches onto a distinct receptor, Frizzled, and just 15 tweaks can change TcsL's binding to mimic TcdB's method.
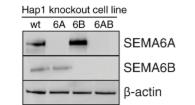
Fig3. Expression of SEMA6A and SEMA6B in single and double knockout cell lines was assessed by western blotting.

Fig4. Hap1 and HeLa cells were treated with increasing concentrations of TcsL and cell viability.
Involved Pathway
SEMA6B involved in several pathways and played different roles in them. We selected most pathways SEMA6B participated on our site, such as Axon guidance, which may be useful for your reference. Also, other proteins which involved in the same pathway with SEMA6B were listed below. Creative BioMart supplied nearly all the proteins listed, you can search them on our site.
| Pathway Name | Pathway Related Protein |
|---|---|
| Axon guidance | RAC2,RGMB,FRS2,EPHB4,HRAS,CDK5,DUSP2,SPTBN1,DUSP7,RAC3 |
Protein Function
SEMA6B has several biochemical functions, for example, chemorepellent activity,semaphorin receptor binding. Some of the functions are cooperated with other proteins, some of the functions could acted by SEMA6B itself. We selected most functions SEMA6B had, and list some proteins which have the same functions with SEMA6B. You can find most of the proteins on our site.
| Function | Related Protein |
|---|---|
| semaphorin receptor binding | SEMA3B,SEMA4A,SEMA3C,SEMA6E,SEMA4BA,SEMA4B,SEMA4E,SEMA3E,SEMA6C,SEMA3H |
| chemorepellent activity | SEMA3B,SEMA3AB,SEMA5B,SEMA3A,SEMA4C,SEMA3GB,SEMA6DL,SEMA3H,SEMA4D,SEMA3D |
Interacting Protein
SEMA6B has direct interactions with proteins and molecules. Those interactions were detected by several methods such as yeast two hybrid, co-IP, pull-down and so on. We selected proteins and molecules interacted with SEMA6B here. Most of them are supplied by our site. Hope this information will be useful for your research of SEMA6B.
Resources
Related Services
Related Products
References


