RTKN
-
Official Full Name
rhotekin -
Overview
This gene encodes a scaffold protein that interacts with GTP-bound Rho proteins. Binding of this protein inhibits the GTPase activity of Rho proteins. This protein may interfere with the conversion of active, GTP-bound Rho to the inactive GDP-bound form by RhoGAP. Rho proteins regulate many important cellular processes, including cytokinesis, transcription, smooth muscle contraction, cell growth and transformation. Dysregulation of the Rho signal transduction pathway has been implicated in many forms of cancer. Alternative splicing results in multiple transcript variants encoding different isoforms. -
Synonyms
RTKN;rhotekin;B5
Recombinant Proteins
- Human
- Mouse
- Rhesus macaque
- Rat
- E.coli
- Mammalian Cells
- HEK293
- His
- GST
- Non
- T7
- Avi
- Fc
- DDK
- Myc
Background
What is RTKN Protein?
Rhotekin (RTKN) teams up with Rho GTPases, playing a big role in how cells grow, change shape, and move around. These GTPases are like the cell's internal switches, guiding the cell's reactions to its surroundings. RTKN itself has been found to have differing roles depending on the type of cancer. For instance, in some cancers, its expression levels are heightened, linking it to tumor growth and metastasis. Additionally, RTKN is associated with certain signaling pathways, like the p53 pathway involved in cell cycle regulation and apoptosis. Understanding RTKN's function could potentially aid in developing targeted therapies for cancers where it plays a significant role.
What is the Function of RTKN Protein?
RTKN proteins, including RTKN1 and RTKN2, are important components in cell communication, especially with the Rho GTPase family. They regulate cellular functions by preserving cell structure and managing cell division and movement. When it comes to cancer, RTKN2 is a bit of a double agent—while it seems to help suppress tumors in colon cancer, it can also fuel the fire in breast cancer by revving up the Wnt/β-catenin pathway, a major player in cancer development. In lung cancer, RTKN2 can also promote the disease by keeping the NF-κB signaling pathway active, which is linked to cancer cell growth and spread. Basically, RTKN proteins are like cellular traffic cops, directing the flow of cell behavior, and when they're not doing their job right, it can lead to some serious health issues, especially in the form of cancer.

Fig1. Physiological roles of Rhotekin and its binding partners. (Hidenori Ito, 2018)
RTKN Related Signaling Pathway
RTKN proteins, especially RTKN2, are tied into some crucial signaling pathways that control how cells behave, particularly when it comes to cancer. They mess with the Wnt/β-catenin pathway, which is a big deal in cell growth and survival. When RTKN2 is less active, it can slow down cancer development by putting the brakes on the Wnt/β-catenin pathway, which usually spurs cells to grow and divide. On top of that, RTKN proteins also get involved with the NF-κB pathway, which can promote cancer by keeping cells alive and helping them spread. Basically, RTKN proteins are like switches that can turn these pathways up or down, and when they're not working right, it can lead to problems like cancer. Understanding their role in these pathways is helping researchers figure out new ways to treat diseases.
RTKN Related Diseases
RTKN proteins, especially RTKN2, are involved in a bunch of diseases, mostly in the cancer scene but also in some non-cancer issues. They mess with how cells grow and move, which can lead to problems like cancer spreading and other inflammation-related diseases. Basically, when RTKN2 isn't doing its job right, it can cause a mess in our body, leading to some serious health problems.
Bioapplications of RTKN
Recombinant RTKN proteins are pretty versatile tools in various research and industrial fields. In scientific research, they're employed to study cell signaling pathways, shedding light on processes like cell movement and growth, which can be pivotal for cancer research. In industrial production, these proteins can be used in the development of biomaterials and biosensors due to their ability to interact with cellular structures. Clinically, they're being explored for their potential in regenerative medicine and drug delivery systems, offering exciting avenues for treatment innovations. So, whether it's in a lab or a therapeutic application, RTKN proteins have a lot to offer.
Case Study
Case Study 1: Xiaomei Zhang, 2023
RTKN2, a protein linked to Rho GTPase, is known to help curb tumors in colon cancer. This study checked out what RTKN2 does in breast cancer cells. By using various lab techniques like RT-qPCR and Western blots, it was found that RTKN2 levels were higher in BC tissues and cells. Reducing RTKN2 led to decreased cancer cell growth, migration, invasion, and increased cell death. This was linked to blocking the Wnt/β-catenin pathway, as shown by the lowered expression of pathway markers like Wnt3A, β-catenin, C-Myc, and Cyclin D1. Overall, knocking down RTKN2 hindered BC progression by disrupting this signaling pathway.

Fig1. The expression of RTKN2 in MCF-10A, MDA-MB-231, MDA-MB-468 and BT549 cells.
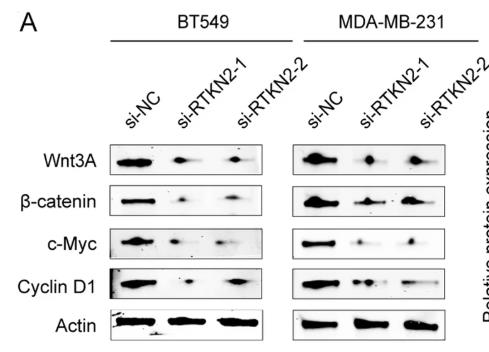
Fig2. RTKN2 regulated Wnt/β-catenin pathway in BC cells.
Case Study 2: Meng-Yao Sun, 2019
Gastric cancer (GC) is a major global health threat, and the protein Rhotekin (RTKN), linked to Rho activities, is often found at higher levels in GC tissues. This study focused on RTKN's roles in GC's behavior. They found that RTKN is highly expressed in GC tissues compared to normal tissues and is linked with larger tumors, advanced stage, lymph node spread, and poor outcomes. Cutting down RTKN levels curbed GC cell growth, pushed more cells into the G1/S phase, and triggered cell death. The study also connected RTKN to the p53 signaling and Class I histone deacetylase (HDAC) pathways. Lowering RTKN increased p53 acetylation and the expression of p53-target genes, while reducing HDAC1, a p53 deacetylase. Interestingly, reducing HDAC1 mirrored the effects of RTKN knockdown, with RTKN overexpression unable to reverse these changes in GC cells.
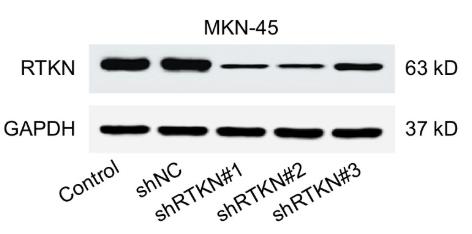
Fig3. RTKN protein levels were evaluated at 48 hours post transduction.

Fig4. GSEA plot showed that the HDAC Class I pathway was strongly associated with RTKN expression on TCGA GC dataset.
Quality Guarantee
High Purity
.jpg)
Fig1. SDS-PAGE (RTKN-8057H)
.
.jpg)
Fig2. SDS-PAGE (RTKN-6216H)
Involved Pathway
RTKN involved in several pathways and played different roles in them. We selected most pathways RTKN participated on our site, such as Alpha6-Beta4 Integrin Signaling Pathway,G13 Signaling Pathway,RHO GTPase Effectors, which may be useful for your reference. Also, other proteins which involved in the same pathway with RTKN were listed below. Creative BioMart supplied nearly all the proteins listed, you can search them on our site.
| Pathway Name | Pathway Related Protein |
|---|---|
| G13 Signaling Pathway | RHPN2,CIT,SH3RF1,ARHGEF1A,DIAPH1,MYBPH,TNK2,GNA13,CFL2,MYL1 |
| Signal Transduction | SPOP,RLBP1B,DEPDC1B,NPSR1,VIP,PRLRB,ARHGAP23,PENKA,NPHP4,GRB10A |
| Alpha6-Beta4 Integrin Signaling Pathway | EIF4EB,COL17A1,SMAD3B,CDKN1A,MST1R,CD151L,EIF4E,CLCA1,EGFR,DST |
| RHO GTPases Activate Rhotekin and Rhophilins | RHPN1,RHPN2,RHOC,TAX1BP3,LIN7B,ROPN1 |
| Signaling by Rho GTPases | KIF14,PRC1,RHOT1,MKL1B,OPHN1,NF2A,ARAP1,TAGAP1,ARHGAP33,WIPF3 |
| RHO GTPase Effectors | SPC24,ZWINT,RCC2,FMNL1,NDEL1B,CLIP1,ABI1B,KDM4C,ERCC6L,CCDC99 |
Protein Function
RTKN has several biochemical functions, for example, GTP binding,GTP-Rho binding,GTPase inhibitor activity. Some of the functions are cooperated with other proteins, some of the functions could acted by RTKN itself. We selected most functions RTKN had, and list some proteins which have the same functions with RTKN. You can find most of the proteins on our site.
| Function | Related Protein |
|---|---|
| GTPase inhibitor activity | CDC42SE1,IPO5,GPS1,PDE6D,TNK2,ARL2,SLIT2,RHOH,UBE4A,GPS2 |
| protein binding | KISS1R,SUPT6H,SMCR7,PCSK5,STUB1,RAB43,TNS4,HSPB8,KRTAP10-8,ATF7 |
| GTP binding | ACSM5,RRAGC,GTPBP1L,DNM2,MTG1,ARL15,TUBA3E,TUBB2B,GNAO1B,ERCC3 |
| GTP-Rho binding | TRIOBP,RTKN2B,TNFAIP1,KCTD13,ROCK1,NET1,PKN1,WHAMM,CDC42EP4A,EXOC1 |
Interacting Protein
RTKN has direct interactions with proteins and molecules. Those interactions were detected by several methods such as yeast two hybrid, co-IP, pull-down and so on. We selected proteins and molecules interacted with RTKN here. Most of them are supplied by our site. Hope this information will be useful for your research of RTKN.
RHOA;Rhoa;SORBS3;SORBS3;sseJ;gtp;Rhoa;RAC1;q8jhe2_xenla;YWHAB
Resources
Related Services
Related Products
References
- Sun, HR; Breslin, JW; et al. Rho and ROCK signaling in VEGF-induced microvascular endothelial hyperpermeability. MICROCIRCULATION 13:237-247(2006).
- Jung, JW; Jung, SH; et al. High-throughput analysis of GST-fusion protein expression and activity-dependent protein interactions on GST-fusion protein arrays with a spectral surface plasmon resonance biosensor. PROTEOMICS 6:1110-1120(2006).


