RNASEH1
-
Official Full Name
ribonuclease H1 -
Overview
Ribonuclease H1 also known as RNase H1 is an enzyme that in humans is encoded by the RNASEH1 gene. The RNase H1 is a non-specific endonuclease and catalyzes the cleavage of RNA via a hydrolytic mechanism. -
Synonyms
RNASEH1;ribonuclease H1;RNase H1;H1RNA;MGC108918;Ribonuclease H type II;RibonucleaseH1;RNH1;OTTHUMP00000115314
Recombinant Proteins
- Human
- Rhesus macaque
- Rat
- Chicken
- Zebrafish
- Mouse
- E.coli
- Insect Cells
- Mammalian Cells
- HEK293
- His
- GST
- Non
- DDK
- Myc
- Avi
- Fc
- Flag
Background
What is RNASEH1 protein?
RNASEH1 gene (ribonuclease H1) is a protein coding gene which situated on the short arm of chromosome 2 at locus 2p25. The RNASEH1 protein is an enzyme found in all life forms and belongs to the endonuclease family. The primary function of RNASEH1 is to play a role in the DNA repair process, especially in the cutting of RNA-DNA hybrids. This enzyme helps maintain genomic stability, prevents the accumulation of unwanted hybrid structures by eliminating hybridization of RNA with DNA, and maintains the normal function of cells. The RNASEH1 protein is consisted of 286 amino acids and RNASEH1 molecular weight is approximately 32.1 kDa.
What is the function of RNASEH1 protein?
The RNASEH1 protein is a key enzyme that plays a role in the nucleus and mitochondria and is primarily involved in processing RNA-DNA hybrid molecules such as R-rings and RNA primers. RNASEH1 helps maintain the stability of the genome by hydrolyzing the RNA components in RNA-DNA hybrid molecules, preventing the accumulation of RNA-DNA hybrid molecules that could interfere with DNA replication and repair processes. The activity of RNASEH1 is essential to prevent the development of certain genetic diseases and cancers, and its abnormal function has been linked to neurodegenerative diseases such as Aicardi-Goutieres syndrome. In addition, RNASEH1 also plays a role in the antiviral response, as it is involved in the degradation of certain viral RNA-DNA intermediates.
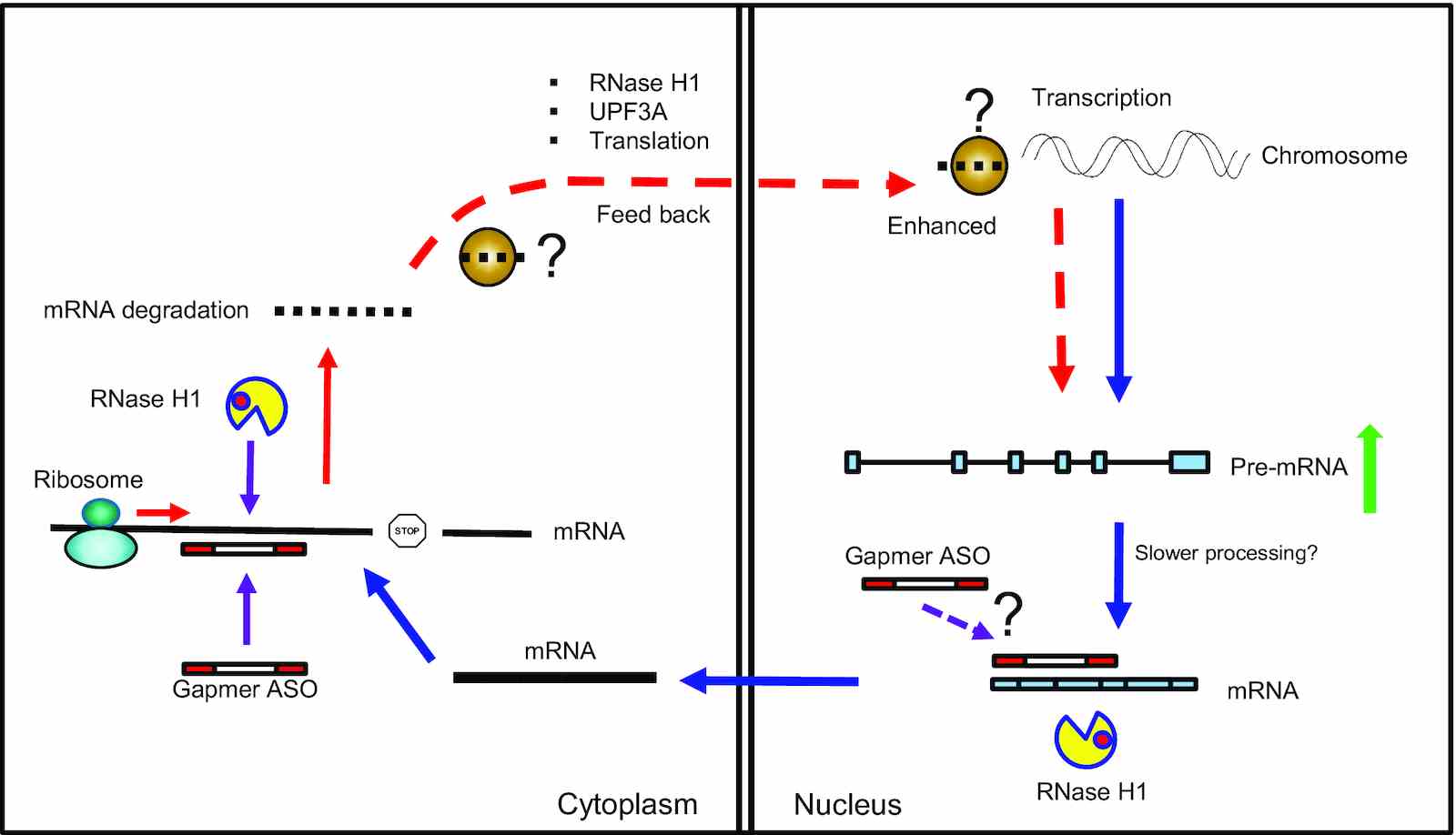
Fig1. Proposed model of gapmer ASO-induced pre-mRNA increase. (Xue-Hai Liang, 2020)
RNASEH1 related signaling pathway
The RNASEH1-related signaling pathway is pivotal in the regulation of gene expression and immune responses. RNASEH1, or Ribonuclease H1, plays a critical role in degrading RNA molecules within RNA:DNA hybrids, thereby preventing illegitimate recombination and maintaining genomic stability. This function is essential for processing microRNA precursors, which are involved in post-transcriptional gene silencing. Additionally, RNASEH1 contributes to the innate immune response by targeting and degrading viral RNA during infection, thus inhibiting viral replication. Dysregulation of this pathway can lead to aberrant gene expression patterns and has been implicated in various diseases, including cancer and autoimmune disorders.
RNASEH1 related diseases
RNASEH1-related diseases encompass a range of conditions primarily associated with aberrant gene expression and impaired immune responses. This includes cancers, where dysregulation of RNASEH1 can lead to uncontrolled cell proliferation and resistance to apoptosis, contributing to tumorigenesis and metastasis. Additionally, mutations or altered activity of RNASEH1 are implicated in neurodegenerative disorders, such as amyotrophic lateral sclerosis (ALS), due to its role in processing RNA and maintaining mitochondrial function. Furthermore, defects in the RNASEH1 pathway can impair antiviral immunity, increasing susceptibility to viral infections and possibly influencing the pathogenesis of autoimmune diseases by disrupting immune tolerance mechanisms.
Bioapplications of RNASEH1
By restoring or enhancing the enzymatic activity of RNASEH1, rhRNASEH1 can be utilized in therapeutic strategies aimed at degrading aberrant RNA species, thereby correcting misregulated gene expression patterns observed in various diseases, including cancer and neurodegenerative disorders. Additionally, its role in targeting viral RNA makes it a promising candidate for antiviral therapies, particularly against infections where RNA viruses are involved. Furthermore, modulating the activity of rhRNASEH1 could potentially improve immune responses by facilitating the removal of pathogenic RNA and reducing autoimmunity triggers.
Case Study
Case Study 1: Lukasz J Kielpinski, 2021
Phosphorothioate (PS) modification is essential for the therapeutic application of antisense oligonucleotides (ASOs). Traditional synthesis adds PS in a random stereochemistry, but controlling this has been extensively studied. This research deeply characterizes how E. coli RNase H interacts with RNA-DNA heteroduplexes containing defined PS chiralities. At least one Rp-PS group is vital for effective RNase H cleavage, and it must align with RNase H's phosphate-binding pocket. The chirality of other nearby PS groups does not impact cleavage. RNase H's chiral preference for PS to direct cleavage to specific bonds and proposed an ASO optimization strategy by identifying preferred RNase H cleavage sites in non-thioated compounds and strategically introducing Rp-PS.
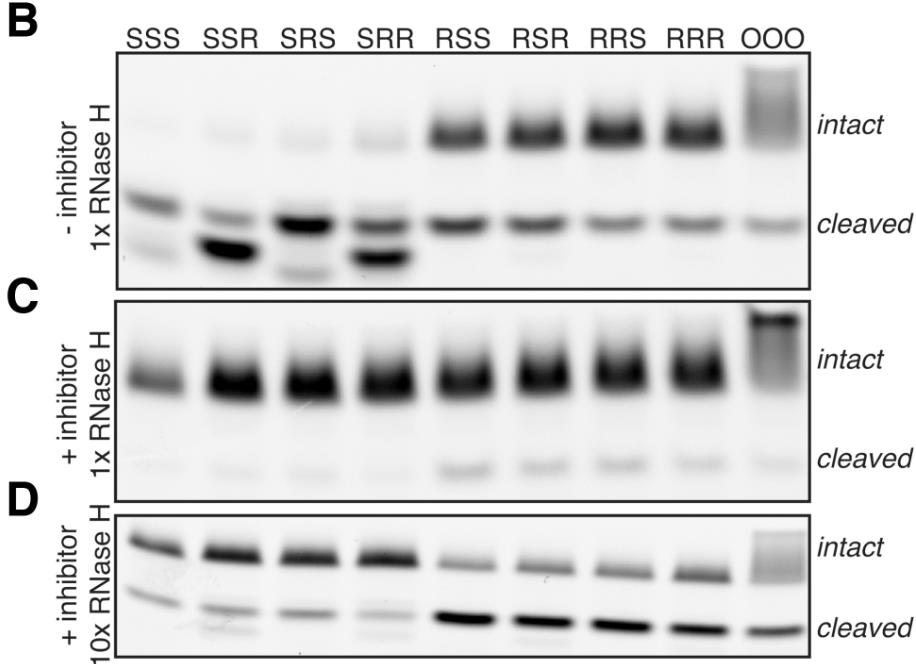
Fig1. Denaturing gel electrophoresis of RNA hydrolysis reactions.
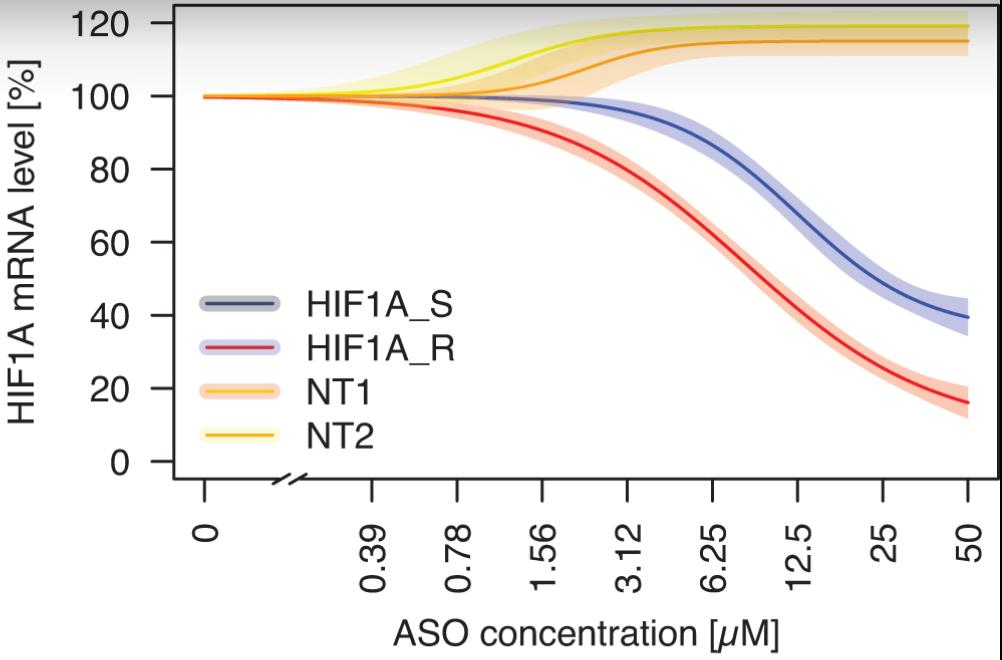
Fig2. Concentration–response curves of HIF1A mRNA level to ASO treatment in A549 cells
Case Study 2: Lukasz J Kielpinski, 2017
RNase H, crucial for mammalian development and HIV replication, cleaves RNA in RNA-DNA duplexes and is found across life domains and viruses. Researchers developed a sequencing method to analyze the cleavage preferences of HIV-1, human, and E. coli RNase H on numerous RNA-DNA duplexes. They discovered that E. coli and human RNase H share similar sequence preferences, influencing the efficacy of antisense oligonucleotides. HIV-1 RNase H's preferences appear evolutionarily optimized for efficient RNA cleavage. These insights can enhance antisense oligonucleotide design and suggest that HIV-1 RNase H preferences have influenced the virus's genome evolution and use of tRNA-Lys3 as a replication primer.
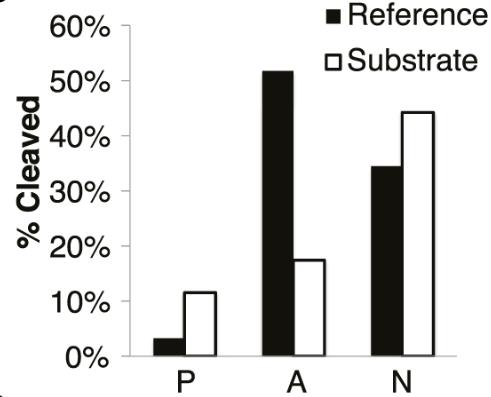
Fig3. Cleavage of sequences predicted to be preferred ('P'), avoided ('A') and neutral ('N') with respect to cleavage with human RNase H1 compared to the cleavage of a reference substrate.
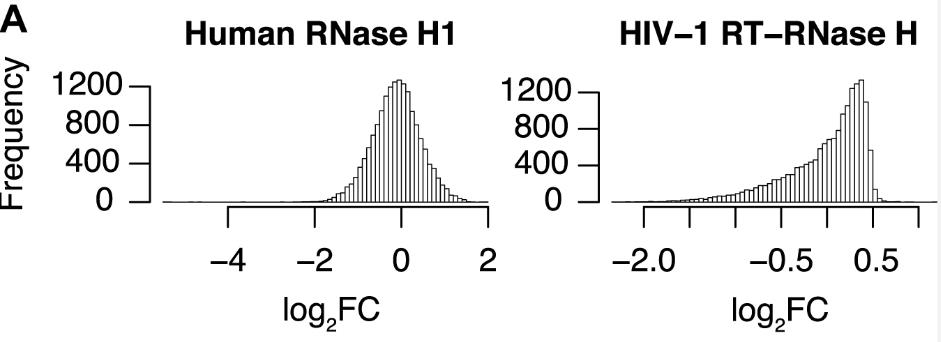
Fig4. Distributions of the observed log2 fold changes of RNA heptamers in R7 for human RNase H1 (right) and HIV-1 RNase H.
Quality Guarantee
High Purity
.jpg)
Fig1. SDS-PAGE (RNASEH1-164H)
.
.jpg)
Fig2. SDS-PAGE (RNASEH1-1574H)
Involved Pathway
RNASEH1 involved in several pathways and played different roles in them. We selected most pathways RNASEH1 participated on our site, such as DNA replication, which may be useful for your reference. Also, other proteins which involved in the same pathway with RNASEH1 were listed below. Creative BioMart supplied nearly all the proteins listed, you can search them on our site.
| Pathway Name | Pathway Related Protein |
|---|---|
| DNA Replication | DBF4,CDT1,POLE,MCM2,POLE3,RFC3,RFC1,MCM4,DNA2,RNASEH2C |
Protein Function
RNASEH1 has several biochemical functions, for example, RNA binding,RNA-DNA hybrid ribonuclease activity,magnesium ion binding. Some of the functions are cooperated with other proteins, some of the functions could acted by RNASEH1 itself. We selected most functions RNASEH1 had, and list some proteins which have the same functions with RNASEH1. You can find most of the proteins on our site.
| Function | Related Protein |
|---|---|
| magnesium ion binding | IDH3B,ENOPH1,WRN,CDC42BPA,TESC,NUAK2,PKM2,ATP9B,GTPBP5,TSSK1 |
| ribonuclease activity | ANG,EAR2,RNASE7,RNASE3,AZGP1,ANG4,RNASET2B,RSFR,EAR4,EAR1 |
| nucleic acid binding | ZFP827,ZXDB,ZNF200,EAR2,RNASE4,USP6,SFRS3B,ZFP35,SRSF9,SALL1A |
| RNA-DNA hybrid ribonuclease activity | FEN1,RNASEH2C,RNASEH2B,EXO1,RNASEH2A,APEX1 |
| RNA binding | RPUSD1,HNRNPR,NOVA2,TRIM71,MRPL12,BICC1,RBMS3,PPIE,MARF1,ZNF385C |
Interacting Protein
RNASEH1 has direct interactions with proteins and molecules. Those interactions were detected by several methods such as yeast two hybrid, co-IP, pull-down and so on. We selected proteins and molecules interacted with RNASEH1 here. Most of them are supplied by our site. Hope this information will be useful for your research of RNASEH1.
TM9SF1;acrA7;pre-let-7a;SLX4IP
Resources
Related Services
Related Products
References



