QSOX1
-
Official Full Name
quiescin Q6 sulfhydryl oxidase 1 -
Overview
Sulfhydryl oxidase 1 is an enzyme that in humans is encoded by the QSOX1 gene. -
Synonyms
QSOX1;quiescin Q6 sulfhydryl oxidase 1;sulfhydryl oxidase 1;FLJ34858;hQSOX;Human quiescin (Q6) mRNA, partial cds;Q6;QSCN6;QSOX1_HUMAN;Quiescin Q6;Skin sulfhydryl oxidase;Sox;Sulfhydryl oxidase 1 precursor;mSOx;QSOX;1300003H02Rik
Recombinant Proteins
- Human
- Mouse
- Rat
- Chicken
- Zebrafish
- Mus musculus
- E.coli
- Mammalian Cells
- Wheat Germ
- HEK293
- GST
- His
- Non
- Myc
- Avi
- Fc
| Cat.# | Product name | Source (Host) | Species | Tag | Protein Length | Price |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| QSOX1-2095H | Recombinant Human QSOX1, GST-tagged | E.coli | Human | GST | N-term-329aa | |
| Qsox1-266M |
Active Recombinant Mouse Qsox1 protein, His-tagged
|
E.coli | Mouse | His | 36-550 a.a. |
|
| QSOX1-285H |
Active Recombinant Human QSOX1 protein, His-tagged
|
E.coli | Human | His | 33-546 a.a. |
|
| QSOX1-13771M | Recombinant Mouse QSOX1 Protein | Mammalian Cells | Mouse | His |
|
|
| QSOX1-31036TH | Recombinant Human QSOX1 | Wheat Germ | Human | Non | 100 amino acids |
|
| QSOX1-4868R | Recombinant Rat QSOX1 Protein | Mammalian Cells | Rat | His |
|
|
| QSOX1-5701C | Recombinant Chicken QSOX1 | Mammalian Cells | Chicken | His |
|
|
| QSOX1-6869Z | Recombinant Zebrafish QSOX1 | Mammalian Cells | Zebrafish | His |
|
|
| QSOX1-2635HCL | Recombinant Human QSOX1 293 Cell Lysate | HEK293 | Human | Non |
|
|
| QSOX1-255H | Recombinant Human QSOX1 protein(101-175aa), His-GST&Myc-tagged | E.coli | Human | GST&His&Myc | 101-175aa |
|
| QSOX1-4527R | Recombinant Rat QSOX1 Protein, His (Fc)-Avi-tagged | HEK293 | Rat | Avi&Fc&His |
|
|
| QSOX1-4527R-B | Recombinant Rat QSOX1 Protein Pre-coupled Magnetic Beads | HEK293 | Rat |
|
||
| QSOX1-6090H | Recombinant Human QSOX1 Protein (Ser37-Ala181), N-His tagged | E.coli | Human | His | Ser37-Ala181 |
|
| QSOX1-7328M | Recombinant Mouse QSOX1 Protein, His (Fc)-Avi-tagged | HEK293 | Mouse | Avi&Fc&His |
|
|
| QSOX1-7328M-B | Recombinant Mouse QSOX1 Protein Pre-coupled Magnetic Beads | HEK293 | Mouse |
|
||
| RFL13911RF | Recombinant Full Length Rat Sulfhydryl Oxidase 1(Qsox1) Protein, His-Tagged | E.coli | Rat | His | Full L. Full Length of Mature Protein (33-750) |
|
| RFL28779HF | Recombinant Full Length Human Sulfhydryl Oxidase 1(Qsox1) Protein, His-Tagged | E.coli | Human | His | Full L. Full Length of Mature Protein (30-747) |
|
| RFL32590GF | Recombinant Full Length Chicken Sulfhydryl Oxidase 1(Qsox1) Protein, His-Tagged | E.coli | Chicken | His | Full L. Full Length of Mature Protein (43-743) |
|
| RFL6355MF | Recombinant Full Length Mouse Sulfhydryl Oxidase 1(Qsox1) Protein, His-Tagged | E.coli | Mus musculus | His | Full L. Full Length of Mature Protein (33-748) |
|
Background
What is QSOX1 protein?
QSOX1 gene (quiescin sulfhydryl oxidase 1) is a protein coding gene which situated on the long arm of chromosome 1 at locus 1q25. QSOX1 is an enzyme that plays a significant role in the oxidation of sulfhydryl groups in peptides and proteins, converting them to disulfides with the reduction of oxygen to hydrogen peroxide. It is involved in the formation of disulfide bonds in various extracellular proteins and is essential for normal cell-cell adhesion and cell migration in fibroblasts. QSOX1 gene expression is induced as cells exit the proliferative cycle and enter a state of quiescence, suggesting its importance in growth regulation. The QSOX1 protein is consisted of 747 amino acids and QSOX1 molecular weight is approximately 82.6 kDa.
What is the function of QSOX1 protein?
QSOX1 is an enzyme that catalyzes the oxidation of sulfhydryl groups in peptides and proteins, converting them to disulfide bonds with the reduction of oxygen to hydrogen peroxide. This process is crucial for protein folding, production of extracellular matrix, redox regulation, protection from apoptosis, angiogenesis, and cell differentiation. In fibroblasts, QSOX1 is required for the normal incorporation of laminin into the extracellular matrix, which is essential for normal cell-cell adhesion and migration. Additionally, the expression of the QSOX1 gene is induced as cells exit the proliferative cycle and enter quiescence, indicating a role in growth regulation.
QSOX1 Related Signaling Pathway
The activity of QSOX1 leads to the reduction of oxygen to hydrogen peroxide, indicating its role in redox balance within the cell. QSOX1 is required for normal incorporation of laminin into the extracellular matrix, which is essential for cell-cell adhesion and migration in fibroblasts. It has been implicated in protection from apoptosis, suggesting a role in cell survival. QSOX1 has been associated with angiogenesis and cell differentiation processes. It has been suggested that QSOX1 may play a role in the innate immune system, possibly through its involvement in redox regulation and protein folding. Recent studies suggest that QSOX1 may regulate autophagy, an essential cellular process for maintaining homeostasis and responding to stress.
QSOX1 Related Diseases
In the context of oncology, QSOX1 has been found to be overexpressed in several cancer types, including breast, pancreatic, and prostate cancer, where it may contribute to tumor growth, invasion, and metastasis. Its involvement in atherosclerosis suggests a role in cardiovascular diseases. QSOX1's association with stroke points to its relevance in cerebrovascular health. Furthermore, QSOX1 has been implicated in inner ear diseases like Meniere's, which affect balance and hearing, and in immune-related disorders such as lymphoproliferative syndromes. Its mention in the pathology of glioma, diabetes, fibrosis, and mood disorders like bipolar disorder highlights the enzyme's wide-ranging impact on health.
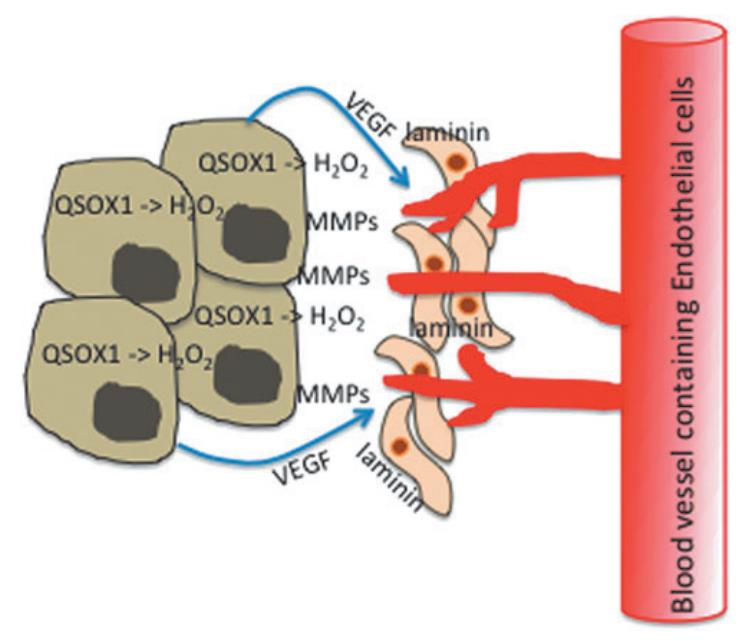
Fig1. Model for QSOX1-mediated tumor cell invasion. (Douglas F Lake, 2014)
Bioapplications of QSOX1
In bioresearch, QSOX1 is utilized in assays to understand the redox environment's impact on cellular processes and to investigate its role in the development and progression of various cancers. Its involvement in the extracellular matrix and cell adhesion makes it a candidate for research into fibrosis and wound healing. QSOX1's potential as a therapeutic target is being explored, particularly in cancer therapy like QSOX1 inhibitors and QSOX1 drugs, where modulating its activity could impact tumor behavior. Additionally, the enzyme's role in the innate immune system and the response to oxidative stress suggests applications in developing treatments for diseases involving immune dysregulation.
Case Study
Case Study 1: Yueqin Wang, 2023
RNA 5-methylcytosine (m5C) modification plays critical roles in the pathogenesis of various tumors. However, the function and molecular mechanism of RNA m5C modification in tumor drug resistance remain unclear. The effects of NSUN2 on EGFR-TKIs resistance were investigated by gain- and loss-of-function assays in vitro and in vivo. Furthermore, the regulatory mechanism of NSUN2 modulating the target gene expression was investigated by functional rescue and puromycin incorporation assays. The results showed that integrated RNA-seq and m5C-BisSeq analyses identified quiescin sulfhydryl oxidase 1 (QSOX1) as a potential target of aberrant m5C modification. NSUN2 methylated QSOX1 coding sequence region, leading to enhanced QSOX1 translation through m5C reader Y-box binding protein 1 (YBX1).
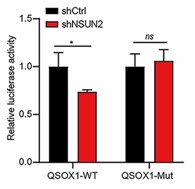
Fig1. Relative luciferase activity of the wild-type and mutant form of QSOX1 CDS reporter vectors.

Fig2. QSOX1 protein level was detected by western blotting.
Case Study 2: Amber L Fifield, 2020
Quiescin sulfhydryl oxidase 1 (QSOX1) is an enzyme overexpressed by many different tumor types. QSOX1 catalyzes the formation of disulfide bonds in proteins. Because short hairpin knockdowns (KD) of QSOX1 have been shown to suppress tumor growth and invasion in vitro and in vivo, researchers hypothesized that chemical compounds inhibiting QSOX1 enzymatic activity would also suppress tumor growth, invasion, and metastasis. High throughput screening using a QSOX1-based enzymatic assay revealed multiple potential QSOX1 inhibitors. One of the inhibitors, known as "SBI-183," suppresses tumor cell growth in a Matrigel-based spheroid assay and inhibits invasion in a modified Boyden chamber, but does not affect viability of nonmalignant cells. Oral administration of SBI-183 inhibits tumor growth in 2 independent human xenograft mouse models of renal cell carcinoma.
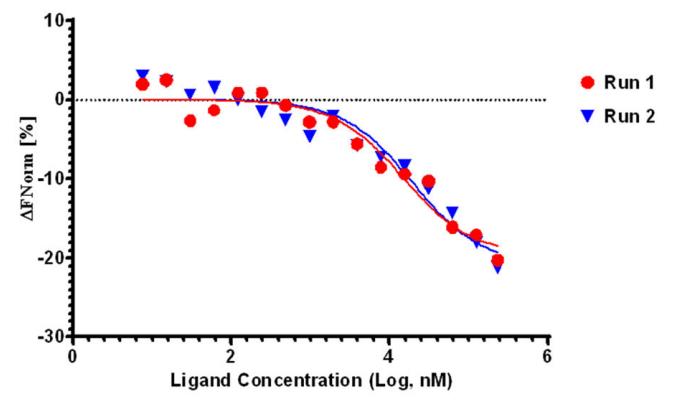
Fig3. MST titrations of rQSOX1 with SBI-183.

Fig4. Partial rescue of invasive phenotype by addition of exogenous rQSOX1.
Quality Guarantee
High Purity
.jpg)
Fig1. SDS-PAGE (QSOX1-6090H)
.
.jpg)
Fig2. SDS-PAGE (QSOX1-255H)
Involved Pathway
QSOX1 involved in several pathways and played different roles in them. We selected most pathways QSOX1 participated on our site, such as , which may be useful for your reference. Also, other proteins which involved in the same pathway with QSOX1 were listed below. Creative BioMart supplied nearly all the proteins listed, you can search them on our site.
| Pathway Name | Pathway Related Protein |
|---|
Protein Function
QSOX1 has several biochemical functions, for example, flavin-linked sulfhydryl oxidase activity,protein disulfide isomerase activity. Some of the functions are cooperated with other proteins, some of the functions could acted by QSOX1 itself. We selected most functions QSOX1 had, and list some proteins which have the same functions with QSOX1. You can find most of the proteins on our site.
| Function | Related Protein |
|---|---|
| protein disulfide isomerase activity | PDIA6,GLRX2,PDIA5,P4HB,PDIP5,ITGB3,ERO1L,PDIA2,QSOX2,ZNF169 |
| flavin-linked sulfhydryl oxidase activity | QSOX2,ZNF169 |
Interacting Protein
QSOX1 has direct interactions with proteins and molecules. Those interactions were detected by several methods such as yeast two hybrid, co-IP, pull-down and so on. We selected proteins and molecules interacted with QSOX1 here. Most of them are supplied by our site. Hope this information will be useful for your research of QSOX1.
BEGAIN
Resources
Related Services
Related Products
References


