PMAIP1
-
Official Full Name
phorbol-12-myristate-13-acetate-induced protein 1 -
Overview
Promotes activation of caspases and apoptosis. Promotes mitochondrial membrane changes and efflux of apoptogenic proteins from the mitochondria. Contributes to p53/TP53-dependent apoptosis after radiation exposure. Promotes proteasomal degradation of MCL1. Competes with BAK1 for binding to MCL1 and can displace BAK1 from its binding site on MCL1 (By similarity). Competes with BIM/BCL2L11 for binding to MCL1 and can displace BIM/BCL2L11 from its binding site on MCL1. -
Synonyms
PMAIP1;phorbol-12-myristate-13-acetate-induced protein 1;APR;NOXA;protein Noxa;PMA-induced protein 1;immediate-early-response protein APR;adult T cell leukemia-derived PMA-responsive
Recombinant Proteins
- Human
- Mouse
- Rhesus macaque
- Zebrafish
- Rat
- E.coli
- Mammalian Cells
- HEK293
- His
- Non
- Avi
- Fc
- GST
- DDK
- Myc
- Flag
Background
What is PMAIP1 protein?
PMAIP1 (phorbol-12-myristate-13-acetate-induced protein 1) gene is a protein coding gene which situated on the long arm of chromosome 18 at locus 18q21. It is involved in various biological processes and has been associated with several diseases, including cancer. The protein is a pro-apoptotic member of the Bcl-2 family, specifically a BH3-only protein, which means it contains a Bcl-2 homology domain 3 (BH3) that is involved in inducing apoptosis or programmed cell death. PMAIP1 is induced by the tumor suppressor protein p53 in response to DNA damage, playing a role in the regulation of cell death. Additionally, PMAIP1 has been identified as a candidate tumor suppressor gene, with its expression vector-mediated introduction suppressing cell proliferation and its knockdown inducing recovery of cell growth, suggesting an important role in the progression of certain cancers, such as pancreatic cancer. PMAIP1 protein is consisted of 54 amino acids and its molecular mass is approximately 6.0 kDa.
What is the function of PMAIP1 protein?
It belongs to the BH3-only subfamily of the Bcl-2 protein family, members of which interact with other Bcl-2 family members through their BH3 domain to influence mitochondria-mediated apoptosis pathways. The expression of PMAIP1 can be induced by the tumor suppressor protein p53 in response to DNA damage, thus playing a role in regulating cell death. PMAIP1 also plays a role in bone metabolism and the development of osteoporosis. Studies have shown that PMAIP1 can regulate autophagy of osteoblasts through AMPK/mTOR signaling pathway, thus affecting the proliferation and differentiation of osteoblasts. It is important to note that the expression and function of PMAIP1 may be influenced by a variety of factors, including epigenetic regulation, post-translational modification, and protein stability. Therefore, PMAIP1 is an important biomarker and potential therapeutic target in multiple fields such as apoptosis, tumor development, neurodegenerative diseases, and bone health.
PMAIP1 Related Signaling Pathway
PMAIP1 is a BH3-only protein in the Bcl-2 family that promotes mitochondria-mediated apoptosis by interacting with other Bcl-2 family members, such as Mcl-1 and Bcl-2. The expression of PMAIP1 can be induced by tumor suppressor protein p53, especially in response to DNA damage, which can activate the transcription of PMAIP1 and further promote apoptosis. In the study of osteoporosis, PMAIP1 regulates autophagy of osteoblasts through AMPK/mTOR signaling pathway and affects proliferation and differentiation of osteoblasts. PMAIP1 may also be involved in cell cycle regulation, controlling cell proliferation and death by affecting cell cycle-related proteins.
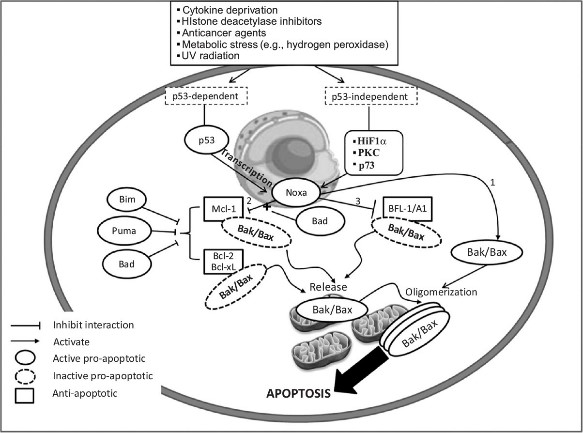
Fig1. Noxa induces apoptosis via p53-dependent and/or p53-independent mechanisms. (Rami Z Morsi, 2018)
PMAIP1 Related Diseases
As a tumor suppressor, the expression level of PMAIP1 may be related to disease progression and treatment response in some cancers. In pancreatic cancer, for example, PMAIP1 may play an important role in disease progression. Studies have shown that PMAIP1 regulates autophagy of osteoblasts through AMPK/mTOR signaling pathway, inhibits proliferation and differentiation of osteoblasts, and thus promotes the development of osteoporosis. PMAIP1 may be involved in the pathological processes of certain neurodegenerative diseases, such as Alzheimer's disease, acting by affecting mitochondrial function and apoptosis. The expression and function of PMAIP1 may be related to metabolic diseases such as type 2 diabetes, and participate in the occurrence and development of diseases by affecting metabolic pathways and apoptosis. Some studies have suggested that PMAIP1 may be associated with certain viral infections, such as subtype J avian leukemia virus, and PMAIP1 promotes viral replication by regulating mitochondrial function.
Bioapplications of PMAIP1
According to the study, PMAIP1 has been found to be a potential risk factor for osteoporosis and significantly inhibits osteoblast autophagy through the AMPK/mTOR signaling pathway, thereby inhibiting osteoblast proliferation and differentiation. In a rat model of osteoporosis induced by ovariectomy (OVX), the application of si-PMAIP1 significantly inhibited the development of osteoporosis, suggesting that PMAIP1 may be a novel therapeutic target. The expression level of PMAIP1 may serve as a biomarker for certain diseases. A series of experiments have shown that the PMAIP1 gene can promote bone formation, migration and proliferation of bone marrow stromal stem cells (BMSC), and PMAIP1 has been identified as a potential biomarker for the diagnosis and treatment of osteoporosis.
Case Study
Case Study 1: Gerlinde Karbon, 2021
Breast cancer (BC) treatment frequently involves microtubule-targeting agents (MTAs), such as paclitaxel, that arrest cells in mitosis. Sensitivity to MTAs is defined by a subset of pro- and anti-apoptotic BCL2 family proteins controlling mitochondrial apoptosis. Here, the researchers aimed to determine their prognostic value in primary tumour samples from 92 BC patients. The analysis identified high NOXA/PMAIP mRNA expression levels as an independent prognostic marker for improved relapse-free survival (RFS) and overall survival (OS) in multivariate analysis in BC patients, independent of their molecular subtype. Analysis of available TCGA datasets of 1060 BC patients confirmed our results and added a clear predictive value of NOXA mRNA levels for patients who received MTA-based therapy. In this TCGA cohort, 122 patients received MTA-treatment and high NOXA mRNA levels correlated with their progression-free interval (PFI) and OS. The follow-up analyses in a panel of BC cell lines of different molecular subtypes identified NOXA protein expression as a key determinant of paclitaxel sensitivity in triple-negative breast cancer (TNBC) cells. Moreover, the researchers noted highest additive effects between paclitaxel and chemical inhibition of BCLX, but not BCL2 or MCL1, documenting dependence of TNBC cells on BCLX for survival and paclitaxel sensitivity defined by NOXA expression levels.
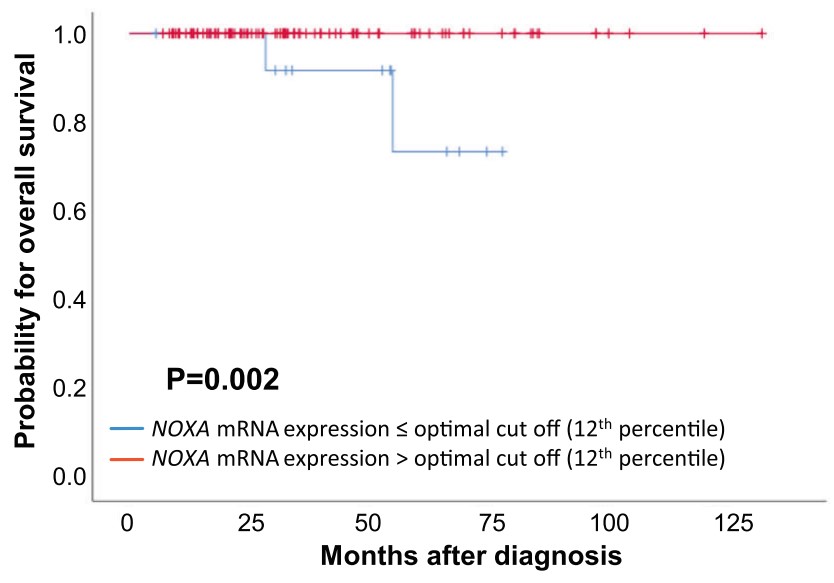
Fig1. OS based on NOXA mRNA-expression in 112 BC patients treated with MTA chemotherapy.
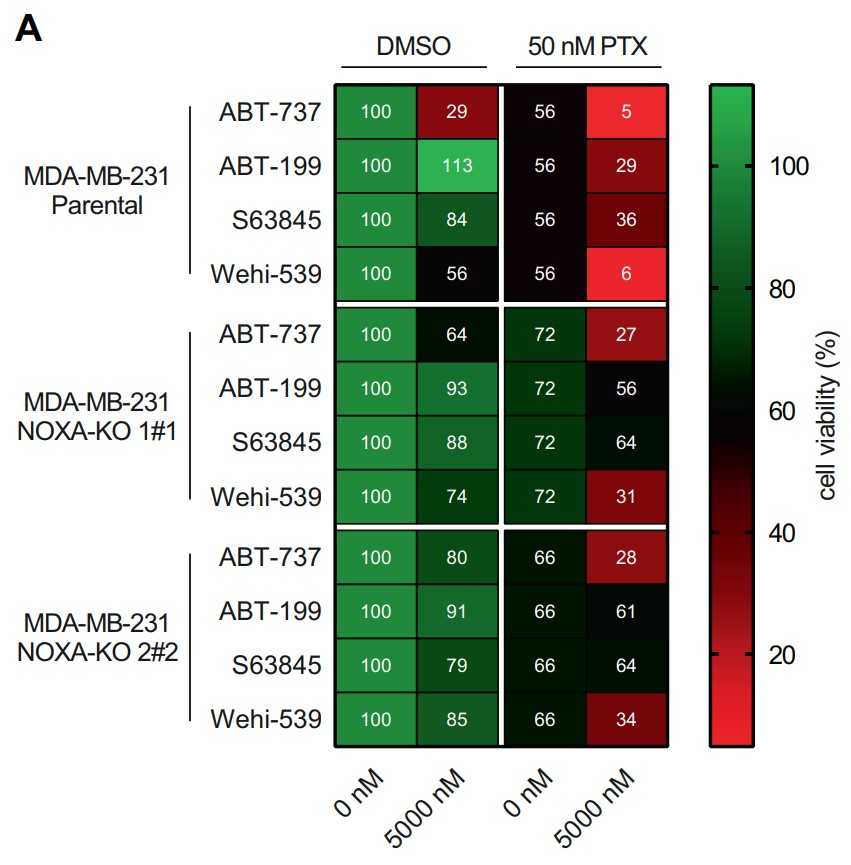
Fig2. NOXA deletion protects TNBC from PTX and BH3-mimetic co-treatment.
Case Study 2: Yuxuan Liu, 2018
Although diffuse large B cell lymphoma (DLBCL) cells widely express the BCL2 protein, they rarely respond to treatment with BCL2-selective inhibitors. Here the researchers show that DLBCL cells harboring PMAIP1/NOXA gene amplification were highly sensitive to BCL2 small-molecule inhibitors. In these cells, BCL2 inhibition induced cell death by activating caspase 9, which was further amplified by caspase-dependent cleavage and depletion of MCL1. In DLBCL cells lacking NOXA amplification, BCL2 inhibition was associated with an increase in MCL1 protein abundance in a BIM-dependent manner, causing a decreased antilymphoma efficacy. In these cells, dual inhibition of MCL1 and BCL2 was required for enhanced killing. Pharmacologic induction of NOXA, using the histone deacetylase inhibitor panobinostat, decreased MCL1 protein abundance and increased lymphoma cell vulnerability to BCL2 inhibitors in vitro and in vivo.
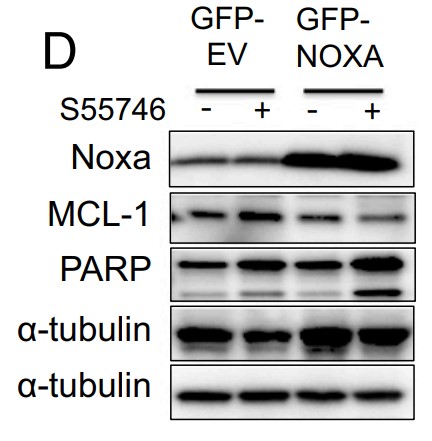
Fig3. NOXA ectopic overexpression enhanced the efficacy of S55746 in HBL-1 DLBCL cells.
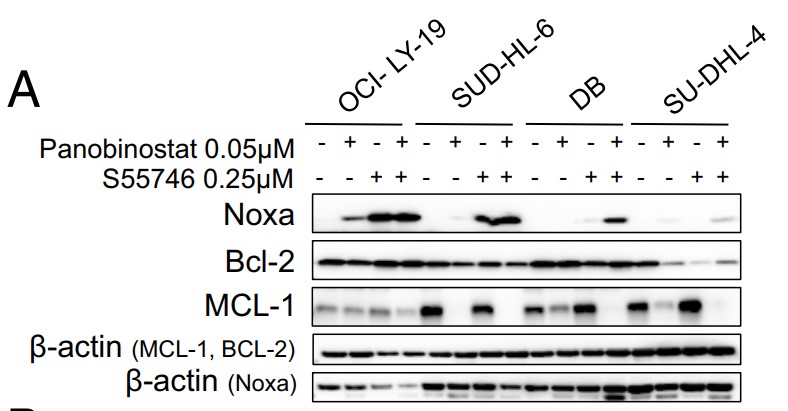
Fig4. Western blot showing increase in NOXA protein levels and decrease in MCL1.
Quality Guarantee
High Purity
.jpg)
Fig1. SDS-PAGE (PMAIP1-3049H)
Involved Pathway
PMAIP1 involved in several pathways and played different roles in them. We selected most pathways PMAIP1 participated on our site, such as p signaling pathway,Viral carcinogenesis, which may be useful for your reference. Also, other proteins which involved in the same pathway with PMAIP1 were listed below. Creative BioMart supplied nearly all the proteins listed, you can search them on our site.
| Pathway Name | Pathway Related Protein |
|---|---|
| p signaling pathway | Casp3,SESN2,APAF1,PERP,MDM4,CYCS,GADD45AB,TP53,IGF1,STEAP3 |
| Viral carcinogenesis | BAK1,SNW1,HRAS,CCND1,TBPL2,ACTN3,HDAC9,CDC42,CREB3L1,HDAC7A |
Protein Function
PMAIP1 has several biochemical functions, for example, protein binding. Some of the functions are cooperated with other proteins, some of the functions could acted by PMAIP1 itself. We selected most functions PMAIP1 had, and list some proteins which have the same functions with PMAIP1. You can find most of the proteins on our site.
| Function | Related Protein |
|---|---|
| protein binding | TRIAP1,ZBTB33,SEPT1,PSMC3,KLHL7,PEX14,PAGE1,AMPD2,ISCA2,NAP1L1 |
Interacting Protein
PMAIP1 has direct interactions with proteins and molecules. Those interactions were detected by several methods such as yeast two hybrid, co-IP, pull-down and so on. We selected proteins and molecules interacted with PMAIP1 here. Most of them are supplied by our site. Hope this information will be useful for your research of PMAIP1.
MCL1;BCL2L1;BCL2L2;BCL2;BCL2;Mcl1;Bcl2a1;BCL2L11;f1_vaccp
Resources
Related Services
Related Products
References


