PLP1
-
Official Full Name
Proteolipid Protein 1 -
Overview
This gene encodes a transmembrane proteolipid protein that is the predominant myelin protein present in the central;nervous system. It may play a role in the compaction, stabilization, and maintenance of myelin sheaths, as well as in;oligodendrocyte development and axonal survival. Mutations in this gene cause X-linked Pelizaeus-Merzbacher disease;and spastic paraplegia type 2. Alternatively spliced transcript variants encoding distinct isoforms or having;different 5 UTRs, have been identified for this gene. -
Synonyms
PLP1;PMD;HLD1;MMPL;SPG2;PLP/DM20;PLP;proteolipid protein 1;myelin proteolipid protein;lipophilin;OTTHUMP00000023761;OTTHUMP00000023762;major myelin proteolipid protein;spastic paraplegia 2, uncomplicated
Recombinant Proteins
- Mouse
- Rhesus macaque
- Rat
- Chicken
- Human
- Taeniopygia guttata (Zebra finch) (Poephila guttata)
- Macaca fascicularis
- Pongo Abelii
- Mus musculus
- Oryctolagus cuniculus
- Sus scrofa (Pig)
- Bovine
- Dog
- Mammalian Cells
- HEK293
- E.coli
- His
- Non
- GST
- Avi
- Fc
Background
What is PLP1 Protein?
The PLP1 protein, short for Proteolipid Protein 1, is pretty essential for our central nervous system. It's a major part of the myelin sheath, you know, that insulating layer wrapping around nerve fibers. This protein helps in speeding up how nerves send messages. If there's a glitch or mutation in the PLP1 gene, it can cause some serious neurological issues, like Pelizaeus-Merzbacher disease, which messes with movement and thinking skills. Scientists focus a lot on PLP1 because studying it can really help in understanding and maybe even finding ways to treat myelin-related disorders.What is the Function of PLP1 Protein?
The PLP1 protein is like a vital component for the insulation of nerve fibers, which we call the myelin sheath. Think of this sheath as the plastic coating around electrical wires. PLP1’s role is to ensure that nerve signals can travel quickly and efficiently without getting lost. Apart from speeding things up, it also helps keep the whole nerve structure in good shape. If PLP1 isn’t doing its job right, nerve messages can get all mixed up, leading to various neurological hiccups. So, basically, PLP1 is crucial for making sure our nerves work properly, keeping everything in our brain and body running smoothly.PLP1 Related Signaling Pathway
PLP1 is involved in some really important signaling pathways that help keep our nerves in good working order. It plays a big role in how the myelin sheath develops and stays healthy. This involves working together with other proteins and signals that guide the myelination process, which is basically how the protective myelin layer forms. PLP1 also connects with pathways that are all about keeping cells alive and helping them grow and mature. If these pathways don’t work right, it can mess up myelin development and lead to nerve-related issues. Researchers are diving deep into these pathways to better understand conditions like multiple sclerosis and Pelizaeus-Merzbacher disease, aiming to find new ways to treat them.PLP1 Related Diseases
PLP1 plays a big role in certain nerve-related diseases. When there are glitches in the PLP1 gene, it can lead to problems like Pelizaeus-Merzbacher disease. This is a rare condition, mostly affecting boys, that impacts how they move and talk because their myelin sheath—the protective nerve coating—doesn't form correctly. Another issue tied to PLP1 is spastic paraplegia type 2, which causes leg stiffness and weakness. Both conditions fall under genetic disorders that mess with normal nerve functions. Figuring out exactly how PLP1 mutations cause these issues is key to coming up with better ways to diagnose and treat folks dealing with these tough conditions.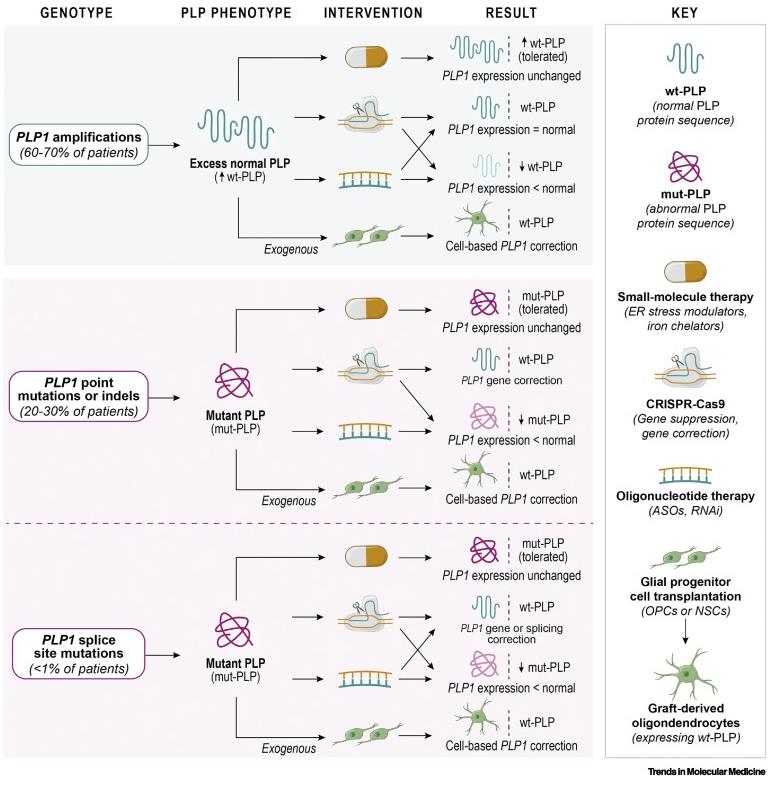
Fig1. Pelizaeus–Merzbacher disease (PMD) therapeutic approaches with preclinical validation. (Matthew S Elitt, 2024)
Bioapplications of PLP1
PLP1 offers some exciting possibilities in neuroscience research. It's a key player in keeping the myelin sheath—which protects our nerves—in good shape. Because of this, studying PLP1 helps scientists understand disorders related to myelin better. This is super important for creating treatments for problems like multiple sclerosis and some leukodystrophies. There's also potential in using PLP1 to help repair and regenerate damaged nerves, which could change how we treat nerve injuries. Plus, by focusing on PLP1, researchers can monitor myelin health and test how well new drugs work to protect or rebuild it. Basically, PLP1 holds a lot of promise for new approaches to dealing with various nerve-related issues.Case Study
Case Study 1: Woods C. et al. Am J Physiol Gastrointest Liver Physiol. 2023
Proteolipid protein 1 (Plp1) is abundant in enteric glia throughout the gut, but its absence in the usual myelin role hints at a unique function in the digestive system. Plp1 seems to influence gut movement and barrier function. In mice without Plp1, older ones showed more stool production, quicker gut transit, and lower intestinal permeability, yet their enteric nervous system appeared normal in structure. The study found lower levels of active Erk1/2 protein in these older mice, suggesting that Plp1 plays a role in controlling gut motility and function likely through the Erk1/2 signaling pathway.-
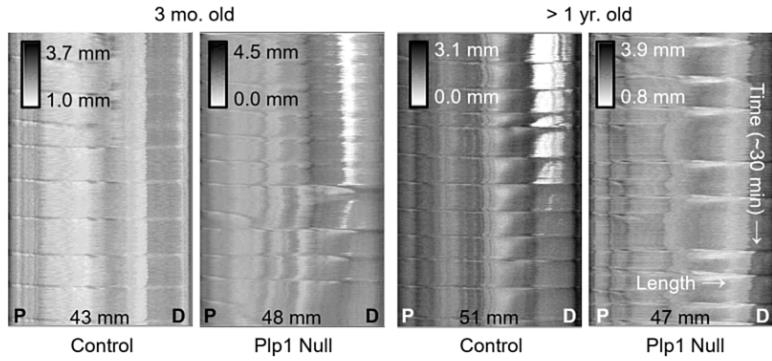 Fig1. Representative spatiotemporal maps of control and Plp1 null colons at 3 mo (C) and greater than 1 yr of age (D).
Fig1. Representative spatiotemporal maps of control and Plp1 null colons at 3 mo (C) and greater than 1 yr of age (D). -
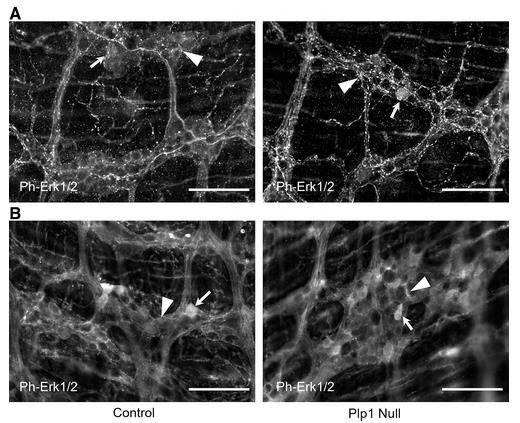 Fig2. Phosphorylated-Erk1/2 expression was localized to the enteric glial cells and few neurons in the myenteric plexus of the distal ileum and proximal colon in young adult Plp1 null mice and age-matched controls.
Fig2. Phosphorylated-Erk1/2 expression was localized to the enteric glial cells and few neurons in the myenteric plexus of the distal ileum and proximal colon in young adult Plp1 null mice and age-matched controls.
Case Study 2: Huynh MH. et al. PLoS Pathog. 2022
Toxoplasma gondii cycles through invading, replicating, exiting, and re-invading host cells. The exit process, involving the perforin-like protein PLP1, depends on breaking the vacuole membrane, which happens in acidic conditions. A key observation is that the vacuole pH drops before the parasite leaves. Using a pH-sensitive GFP, researchers found significant pH changes during parasite exit. Even paralyzed parasites show this pH drop, but only if PLP1 is present, indicating its crucial role. Two transporters, FNT1 and FNT2, are involved in this pH reduction by affecting lactate and pyruvate release. This highlights a pivotal link between pH changes and parasite exit, spotlighting these transporters in the process.-
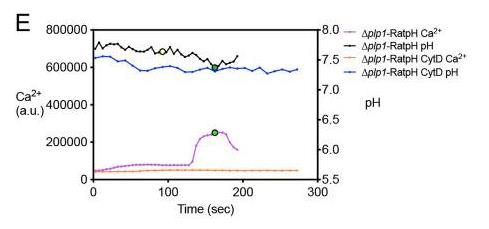 Fig3. Cal-590-AM-loaded HFF cells infected with Δplp1-RatpH following treatment without or with CytD.
Fig3. Cal-590-AM-loaded HFF cells infected with Δplp1-RatpH following treatment without or with CytD. -
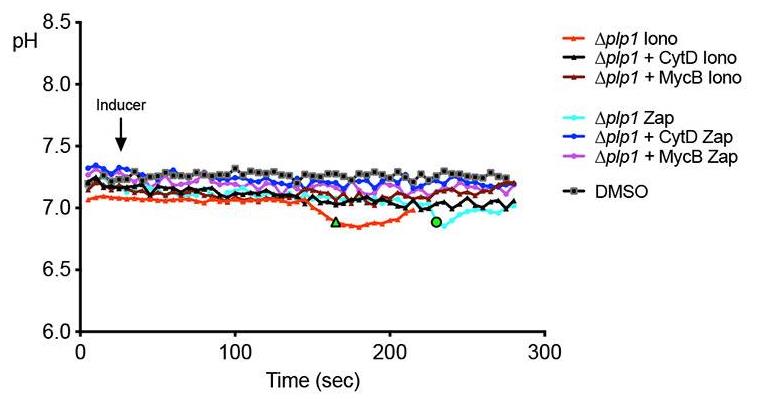 Fig4. Representative traces of Δplp1-RatpH parasites untreated or immobilized with CytD or MycB, followed by ionomycin or zaprinast induction.
Fig4. Representative traces of Δplp1-RatpH parasites untreated or immobilized with CytD or MycB, followed by ionomycin or zaprinast induction.
Quality Guarantee
High Purity
-
.jpg) Fig1. SDS-PAGE (PLP1-10H)
Fig1. SDS-PAGE (PLP1-10H) -
.jpg) Fig2. SDS-PAGE (PLP1-1950H)
Fig2. SDS-PAGE (PLP1-1950H)
Involved Pathway
PLP1 involved in several pathways and played different roles in them. We selected most pathways PLP1 participated on our site, such as Glial Cell Differentiation,SIDS Susceptibility Pathways, which may be useful for your reference. Also, other proteins which involved in the same pathway with PLP1 were listed below. Creative BioMart supplied nearly all the proteins listed, you can search them on our site.
| Pathway Name | Pathway Related Protein |
|---|---|
| SIDS Susceptibility Pathways | CTCF,PHOX2A,IL1RN,KCNH2,RUNX3,TAC1,MBD1,MECP2,CREM,PKNOX1 |
| Glial Cell Differentiation | TPPP,MBP,GAP43,CNP |
-
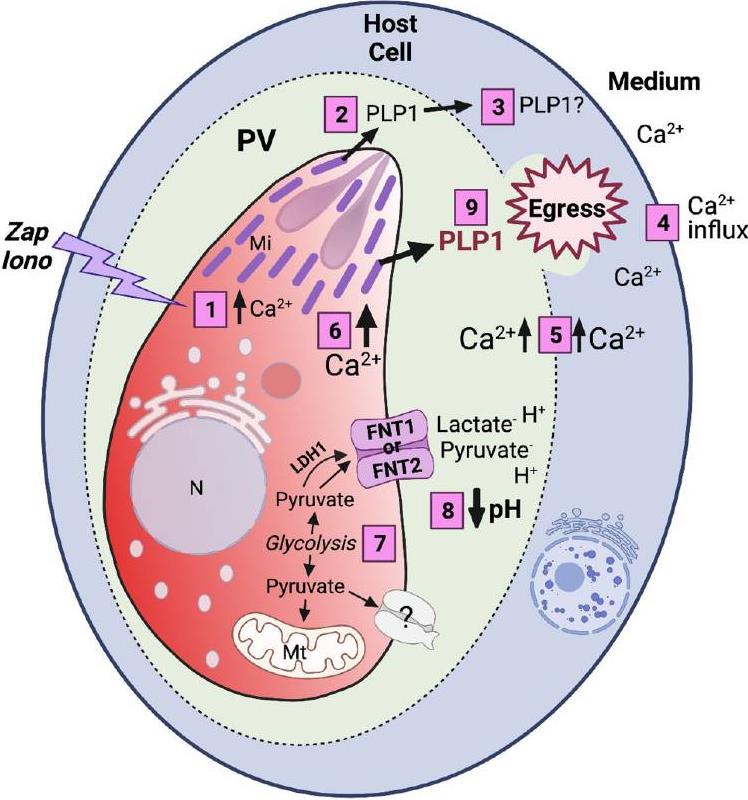 Fig1. Tachyzoites residing inside a parasitophorous vacuole (PV) within a host cell receive signal(s). (My-Hang Huynh, 2022)
Fig1. Tachyzoites residing inside a parasitophorous vacuole (PV) within a host cell receive signal(s). (My-Hang Huynh, 2022) -
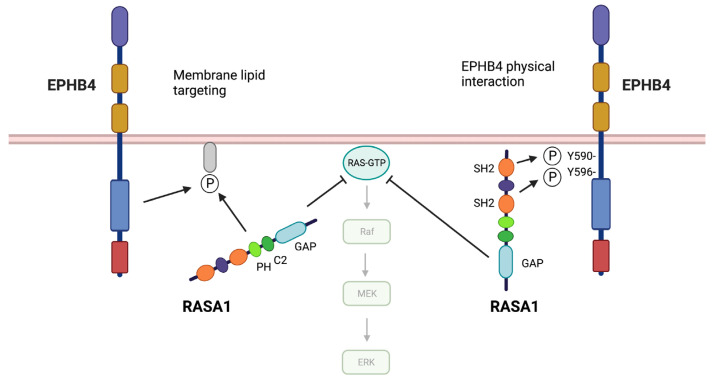 Fig2. Models of EPHB4 and PLP1 cooperation in EC. (Di Chen, 2023)
Fig2. Models of EPHB4 and PLP1 cooperation in EC. (Di Chen, 2023)
Protein Function
PLP1 has several biochemical functions, for example, protein binding,structural constituent of myelin sheath,structural molecule activity. Some of the functions are cooperated with other proteins, some of the functions could acted by PLP1 itself. We selected most functions PLP1 had, and list some proteins which have the same functions with PLP1. You can find most of the proteins on our site.
| Function | Related Protein |
|---|---|
| structural constituent of myelin sheath | MBP,MOBP,NCMAP,MBPB,MAL |
| protein binding | KIAA0319L,TPD52L1,TTBK2,TTC17,PDE6G,EDC3,RNF168,MXD4,DNAJA3,RTN4RL2B |
| structural molecule activity | KRT72-PS,COL18A1,LCE3C,SNTA1,TUBB5,NUMA1,SPRR4,CLDN15LB,NEFLB,KRT82 |
Interacting Protein
PLP1 has direct interactions with proteins and molecules. Those interactions were detected by several methods such as yeast two hybrid, co-IP, pull-down and so on. We selected proteins and molecules interacted with PLP1 here. Most of them are supplied by our site. Hope this information will be useful for your research of PLP1.
PTPRN;AKT1;PTPRN;HTT
Resources
Related Services
Related Products
References
- Vatter, HA; Di, H; et al. Functional Analyses of the Three Simian Hemorrhagic Fever Virus Nonstructural Protein 1 Papain-Like Proteases. JOURNAL OF VIROLOGY 88:9129-9140(2014).
- Takanashi, J; Nitta, N; et al. Neurochemistry in Shiverer Mouse Depicted on MR Spectroscopy. JOURNAL OF MAGNETIC RESONANCE IMAGING 39:1550-1557(2014).


