PLCZ1
-
Official Full Name
phospholipase C, zeta 1 -
Synonyms
PLCZ1;phospholipase C, zeta 1;1-phosphatidylinositol 4,5-bisphosphate phosphodiesterase zeta-1;NYD SP27;PLCzeta;PLC-zeta-1;phospholipase C-zeta-1;PI-phospholipase C zeta 1;testis-development protein NYD-SP27;testis-development related NYD-SP27;p
Recombinant Proteins
- Human
- Mouse
- Chicken
- Rat
- E.coli
- Mammalian Cells
- HEK293
- His
- SUMO
- Avi
- Fc
- GST
| Cat.# | Product name | Source (Host) | Species | Tag | Protein Length | Price |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| PLCZ1-1769H | Recombinant Human PLCZ1 protein, His-tagged | E.coli | Human | His | 56-220 aa | |
| PLCZ1-12932M | Recombinant Mouse PLCZ1 Protein | Mammalian Cells | Mouse | His |
|
|
| PLCZ1-137H | Recombinant Human PLCZ1 protein, His/sumo-tagged | E.coli | Human | His&SUMO | 1-415aa |
|
| PLCZ1-3337C | Recombinant Chicken PLCZ1 | Mammalian Cells | Chicken | His |
|
|
| PLCZ1-4508R | Recombinant Rat PLCZ1 Protein | Mammalian Cells | Rat | His |
|
|
| PLCZ1-2596H | Recombinant Human PLCZ1 Protein, His-tagged | E.coli | Human | His | Ser469-Thr572 |
|
| PLCZ1-4168R | Recombinant Rat PLCZ1 Protein, His (Fc)-Avi-tagged | HEK293 | Rat | Avi&Fc&His |
|
|
| PLCZ1-4168R-B | Recombinant Rat PLCZ1 Protein Pre-coupled Magnetic Beads | HEK293 | Rat |
|
||
| PLCZ1-5267H | Recombinant Human PLCZ1 Protein (Ser469-Thr572), N-GST tagged | E.coli | Human | GST | Ser469-Thr572 |
|
| PLCZ1-6822M | Recombinant Mouse PLCZ1 Protein, His (Fc)-Avi-tagged | HEK293 | Mouse | Avi&Fc&His |
|
|
| PLCZ1-6822M-B | Recombinant Mouse PLCZ1 Protein Pre-coupled Magnetic Beads | HEK293 | Mouse |
|
Background
What is PLCZ1 Protein?
PLCZ1 gene (phospholipase C zeta 1) is a protein coding gene which situated on the short arm of chromosome 12 at locus 12p12. The protein encoded by this gene is a member of the phosphoinositide-specific phospholipase C family. Members in this family, classified into six isotypes that are tissue- and organ-specific, hydrolyze phosphatidylinositol 4,5-bisphosphate just before the phosphate group to yield diacylglycerol and inositol 1,4,5-trisphosphate. This protein localizes to the acrosome in spermatozoa and elicits Ca(2+) oscillations and egg activation during fertilization that leads to early embryonic development. The PLCZ1 protein is consisted of 608 amino acids and PLCZ1 molecular weight is approximately 70.4 kDa.
What is the Function of PLCZ1 Protein?
The main function of PLCZ1 is to trigger calcium ion (Ca2+) oscillations in the egg after sperm fuses with the egg, a key step in egg activation, which in turn encourages the egg to complete meiosis, release the second polar body, and start the embryonic development process. The PLCZ1 protein consists of several distinct domains, including the four N-terminal EF chiral domains, the X and Y catalytic domains, and the C-terminal C2 domain. The EF hand domain gives PLCZ1 a high sensitivity to calcium ions, while the X and Y catalytic domains are responsible for catalyzing phosphatidylinositol 4, 5-diphosphate (PI(4,5)P2) into the messenger molecule inositol 1,4, 5-triphosphate (IP3) capable of mobilizing calcium ions. The C2 domain may help PLCZ1 anchor to intracellular vesicles through direct interaction with specific phosphatidylinositol.
Fig1. Schematic linear representation of the domain structure of PLCζ. (Michail Nomikos, 2013)
PLCZ1 Related Signaling Pathway
When sperm fuses with the egg, PLCZ1 is released into the cytoplasm of the egg and catalyzes the hydrolysis of phosphatidylinositol 4, 5-diphosphate (PIP2) to produce inositol 1,4, 5-triphosphate (IP3) and diacylglycerol (DAG). IP3 binds to the IP3 receptor on the endoplasmic reticulum, resulting in the release of calcium ions, which triggers calcium ion oscillations. This process is essential for egg activation. DAG remains on the sperm cell membrane and activates protein kinase C (PKC), which may also be involved in the regulation of sperm function.
PLCZ1 Related Diseases
Abnormalities in PLCZ1 are strongly associated with male infertility, particularly in cases of failed fertilization after intracytoplasmic sperm injection (ICSI). Since PLCZ1 plays a key role in sperm in triggering egg activation, anything that affects its function, such as genetic mutations or changes in expression levels, can lead to obstacles during fertilization. Specifically, certain point mutations in PLCZ1 can result in reduced protein levels or activity, leading to fertilization failure after ICSI. In addition, abnormal expression or loss of function of PLCZ1 can also lead to egg activation failure (OAF), a critical step in the fertilization process.
Bioapplications of PLCZ1
In clinical practice, functional analysis and gene sequencing of PLCZ1 are used to diagnose fertilization disorders due to failure of egg activation, particularly in cases of fertilization failure after intracytoplasmic sperm injection (ICSI). In addition, the activity test of PLCZ1 helps to identify those patients who may benefit from assisted oocyte activation (AOA) therapy, thereby improving fertilization rates and fertility success. With further understanding of PLCZ1's function, new therapeutic strategies, such as gene therapy or small molecule drugs, may be developed in the future to correct PLCZ1's defects and restore its function, thus providing new avenues for treating specific types of male infertility. In addition, the PLCZ1 study may also shed light on the development of new contraceptive drugs that prevent fertilization by targeting sperm function.
Case Study
Case Study 1: Alaa Hachem, 2017
The sperm protein PLCζ has been proposed as the physiological agent that triggers the Ca2+ oscillations that normally initiate embryogenesis. However, there has been no evidence that knockout of the gene encoding PLCζ abolishes the ability of sperm to induce Ca2+ oscillations in eggs. Here, researchers show that sperm derived from Plcz1-/- male mice fail to trigger Ca2+ oscillations in eggs, cause polyspermy and thus demonstrate that PLCζ is the physiological trigger of these Ca2+ oscillations. Remarkably, some eggs fertilized by PLCζ-null sperm can develop, albeit at greatly reduced efficiency, and after a significant time-delay. In addition, Plcz1-/- males are subfertile but not sterile, suggesting that in the absence of PLCζ, spontaneous egg activation can eventually occur via an alternative route. This is the first demonstration that in vivo fertilization without the normal physiological trigger of egg activation can result in offspring.
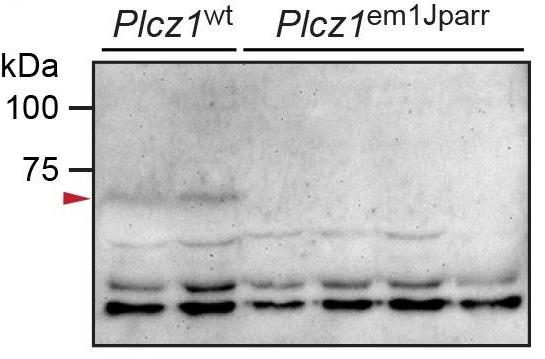
Fig1. Immunoblotting analysis of PLCζ in sperm.
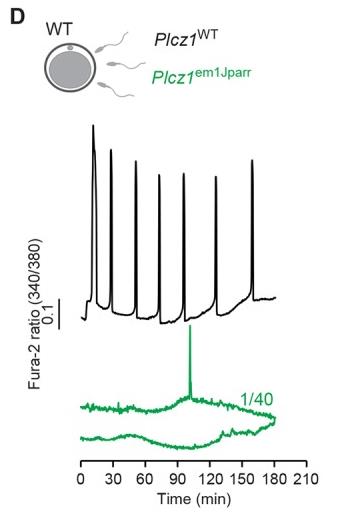
Fig2. Representative traces of Ca2+ responses in wild-type mouse eggs.
Case Study 2: Pablo J Ross, 2008
PLCZ1 has been identified as the factor that the sperm delivers into the egg to induce such a response. This study tested the hypothesis that PLCZ1 cRNA injection can be used to activate bovine oocytes. Mouse and bovine PLCZ1 cRNAs were injected into matured bovine oocytes at different concentrations. Within the concentrations tested, mouse PLCZ1 injection activated bovine oocytes at a maximum rate when the pipette concentration of cRNA ranged from 0.25 to 1 mug/muL, while bovine PLCZ1 was optimal at 0.1 mug/muL. At their most effective concentrations, PLCZ1 induced parthenogenetic development at rates similar to those observed using other activation stimuli such as Ionomycin/CHX and Ionomycin/DMAP. Injection of mouse and bovine PLCZ1 cRNA induced dose-dependent sperm-like calcium oscillations whose frequency increased over time. Injection of bovine and mouse PLCZ1 cRNA also induced IP3R-1 degradation, although bovine PLCZ1 cRNA evoked greater receptor degradation than its mouse counterpart.
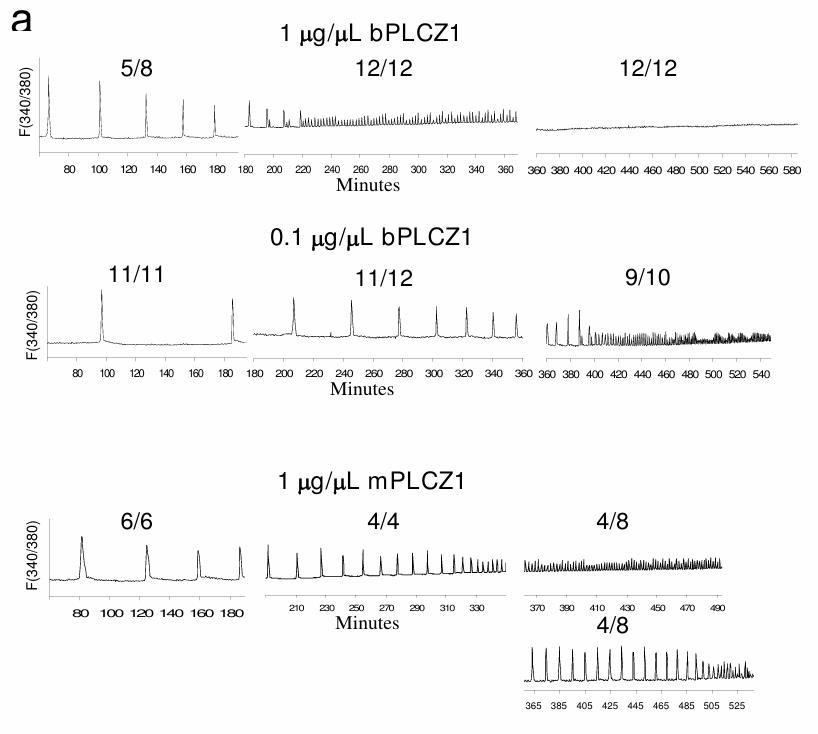
Fig3. Representative [Ca2+]i profiles.
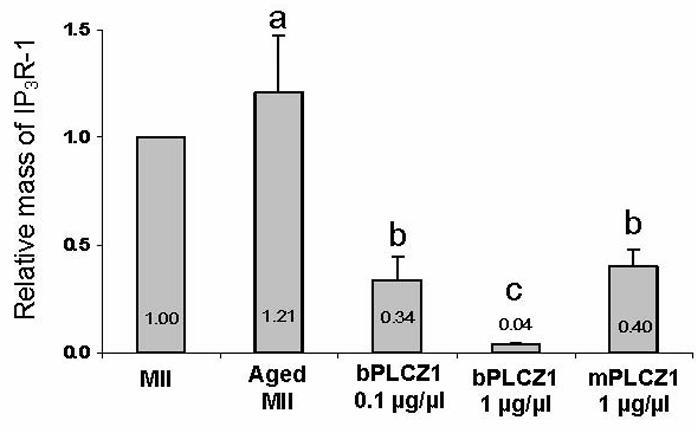
Fig4. Quantification of relative abundance of IP3R-1 versus the levels observed in MII oocytes.
Quality Guarantee
High Purity
.jpg)
Fig1. SDS-PAGE (PLCZ1-2596H)
.
.jpg)
Fig2. SDS-PAGE (PLCZ1-5267H)
Involved Pathway
PLCZ1 involved in several pathways and played different roles in them. We selected most pathways PLCZ1 participated on our site, such as Inositol phosphate metabolism,Metabolic pathways,Calcium signaling pathway, which may be useful for your reference. Also, other proteins which involved in the same pathway with PLCZ1 were listed below. Creative BioMart supplied nearly all the proteins listed, you can search them on our site.
| Pathway Name | Pathway Related Protein |
|---|---|
| Thyroid hormone signaling pathway | PLCG1,MED1,RXRG,EP300,RAF1,KRAS,MAPK1,DIO1,DIO2,PFKFB2 |
| Calcium signaling pathway | PLCB4,GNA15.4,ATP2B2,PHKG1A,PHKG2,PHKB,PPP3R2,GNAL,ADRB2,CYSLTR1 |
| Inositol phosphate metabolism | MTMR3,IMPA1,INPP4B,MTMR1,PTENB,PLCE1,IMPA2,ITPKB,NUDT10,MTMR1A |
| Metabolic pathways | NDUFA6,RDH12,G6PDX,COX5A,TKTL1,MGAT4A,UROS,Nat3,ALG2,NDUFS1 |
| Oocyte meiosis | CCNB1,YWHABB,REC8B,STAG3,CALM3B,CALM,PPP1CAB,CPEB1B,PPP3R1B,PPP3CA |
| Phosphatidylinositol signaling system | CALM,PIK3R2,CALM3A,IPPK,PLCD4,MTMR7B,DGKE,INPP5K,INPP5B,PTENA |
Protein Function
PLCZ1 has several biochemical functions, for example, calcium ion binding,phosphatidylinositol phospholipase C activity,signal transducer activity. Some of the functions are cooperated with other proteins, some of the functions could acted by PLCZ1 itself. We selected most functions PLCZ1 had, and list some proteins which have the same functions with PLCZ1. You can find most of the proteins on our site.
| Function | Related Protein |
|---|---|
| signal transducer activity | RHOL,OPN1MW1,MGAA,PTK2BB,ITGB3BP,OLFR151,OLFCG3,SH2B3,GPR141,GPR25 |
| phosphatidylinositol phospholipase C activity | BDKRB2,PLCB3,CASR,PLCD1B,PLCD3A,CCR1,PLCB1,CHRM5,PLCG1,CCKBR |
| calcium ion binding | CIB2,PLCB1,GRM7,CAPN1B,HPCA,S100P,RASGRP3,PTBP3,NOTCH3,VSNL1 |
Interacting Protein
PLCZ1 has direct interactions with proteins and molecules. Those interactions were detected by several methods such as yeast two hybrid, co-IP, pull-down and so on. We selected proteins and molecules interacted with PLCZ1 here. Most of them are supplied by our site. Hope this information will be useful for your research of PLCZ1.
Resources
Related Services
Related Products
References



